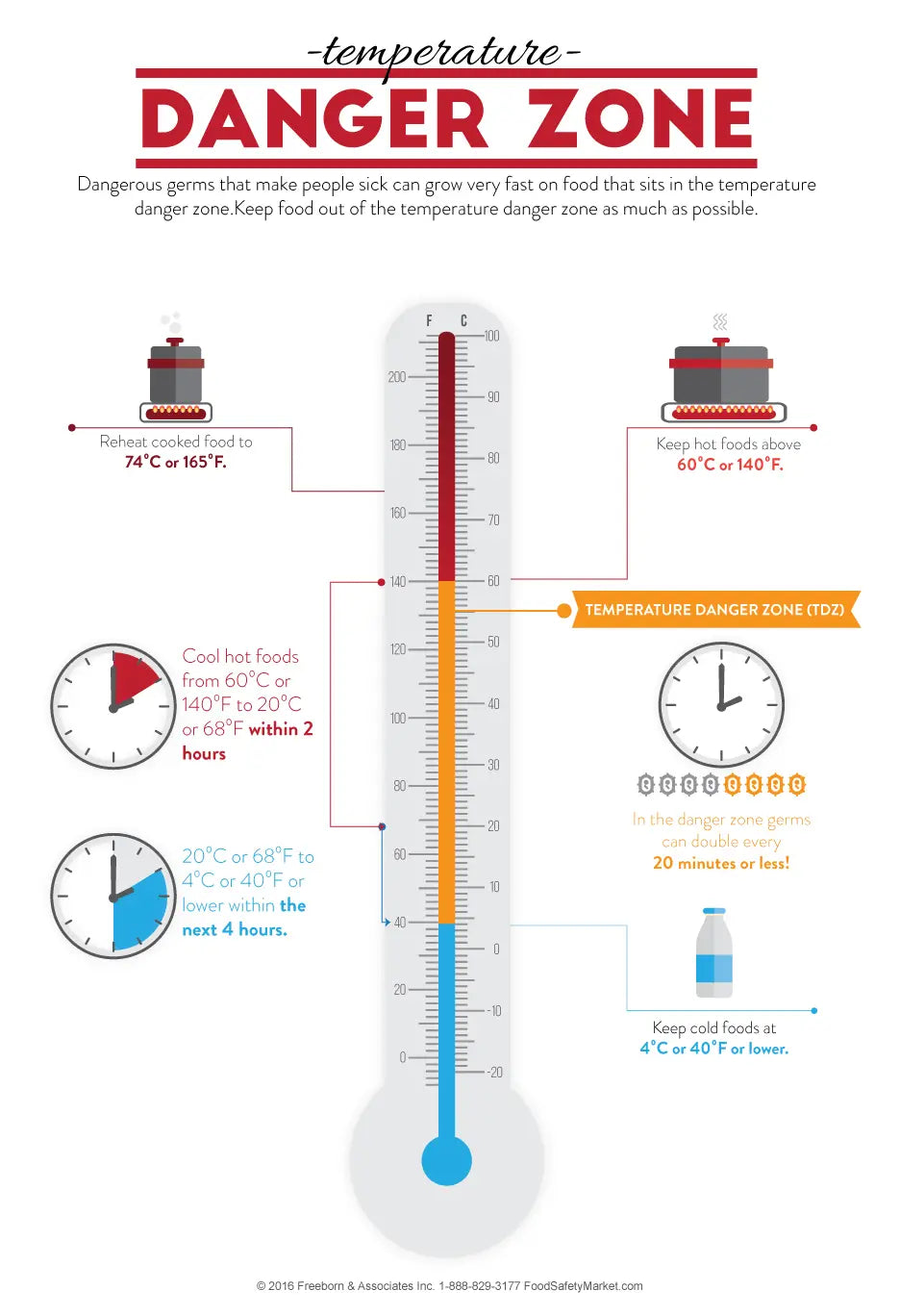
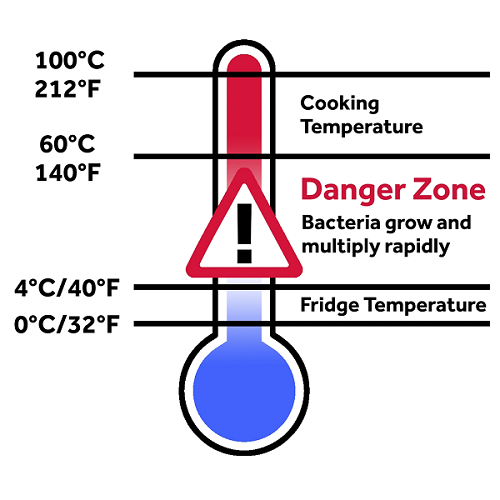
Danger zone temperature refers to the range of temperatures between 40F and 140F (4C and 60C) in which bacteria can grow and multiply rapidly. This temperature range is often found in food storage areas, such as refrigerators and pantries, and can lead to foodborne illnesses if food is not properly stored.
It is important to keep food out of the danger zone to prevent the growth of bacteria. Bacteria can double in number every 20 minutes in the danger zone, so it is important to refrigerate or freeze food as soon as possible after it has been cooked or thawed. Food should also be cooked to the proper internal temperature to kill bacteria.
The danger zone temperature range was first established in the early 20th century by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). The USDA has since developed a number of food safety guidelines to help consumers keep food out of the danger zone and prevent foodborne illnesses.
Read also:Discover Farrukos Pop Body Transformation In Photos
Danger Zone Temperature
The danger zone temperature is the range of temperatures between 40F and 140F (4C and 60C) in which bacteria can grow and multiply rapidly. This temperature range is often found in food storage areas, such as refrigerators and pantries, and can lead to foodborne illnesses if food is not properly stored.
- Bacteria Growth: Bacteria can double in number every 20 minutes in the danger zone.
- Foodborne Illness: Eating food that has been stored in the danger zone can lead to foodborne illness.
- Refrigeration: Refrigerators should be set to 40F or below to keep food out of the danger zone.
- Freezing: Freezing food at 0F or below will stop bacteria from growing.
- Cooking: Food should be cooked to the proper internal temperature to kill bacteria.
- Thawing: Food should be thawed in the refrigerator or in cold water, not at room temperature.
- Food Safety: Following food safety guidelines can help to prevent the growth of bacteria and keep food out of the danger zone.
It is important to keep food out of the danger zone to prevent the growth of bacteria and reduce the risk of foodborne illness. By following these key aspects, you can help to keep your food safe and healthy.
1. Bacteria Growth
The danger zone temperature is the range of temperatures between 40F and 140F (4C and 60C) in which bacteria can grow and multiply rapidly. This means that bacteria can double in number every 20 minutes in the danger zone.
- Exponential Growth: Bacteria grow exponentially, meaning that the number of bacteria doubles with each generation. In the danger zone, bacteria can double in number every 20 minutes, which means that a single bacterium can become over 1 million bacteria in just 10 hours.
- Foodborne Illness: The growth of bacteria in food can lead to foodborne illness. Symptoms of foodborne illness can include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. In some cases, foodborne illness can be fatal.
- Preventing Bacteria Growth: The best way to prevent the growth of bacteria in food is to keep food out of the danger zone. This means refrigerating or freezing food promptly, and cooking food to the proper internal temperature.
The danger zone temperature is a serious food safety concern. By understanding the dangers of the danger zone, you can take steps to protect yourself and your family from foodborne illness.
2. Foodborne Illness
Foodborne illness is a serious public health problem. Each year, millions of people in the United States become sick from eating contaminated food. Foodborne illness can cause a variety of symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. In some cases, foodborne illness can be fatal.
One of the most common causes of foodborne illness is storing food in the danger zone. The danger zone is the range of temperatures between 40F and 140F (4C and 60C) in which bacteria can grow and multiply rapidly. Bacteria can double in number every 20 minutes in the danger zone, so it is important to keep food out of this temperature range to prevent the growth of bacteria.There are a number of ways to keep food out of the danger zone. Refrigerators should be set to 40F or below, and freezers should be set to 0F or below. Food should be cooked to the proper internal temperature to kill bacteria. Leftovers should be refrigerated or frozen within two hours of cooking. And food should not be left out at room temperature for more than two hours.By following these simple steps, you can help to prevent the growth of bacteria and reduce your risk of foodborne illness.
Conclusion:
Read also:Guide To Fixing Meta Sent Verification Code To The Wrong Phone Number
Foodborne illness is a serious public health problem, but it can be prevented by following a few simple steps. Keeping food out of the danger zone is one of the most important things you can do to protect yourself and your family from foodborne illness.
3. Refrigeration
Keeping food out of the danger zone is essential for preventing the growth of bacteria and reducing the risk of foodborne illness. Refrigeration is one of the most effective ways to keep food out of the danger zone. Refrigerators should be set to 40F or below to ensure that food is kept at a safe temperature.
- Inhibition of Bacterial Growth: The growth of bacteria is slowed down at temperatures below 40F. This is because bacteria need a certain amount of energy to grow and reproduce, and at temperatures below 40F, they do not have enough energy to do so.
- Extended Shelf Life: Refrigerating food slows down the spoilage process. This is because the growth of bacteria is slowed down, which means that food will last longer in the refrigerator.
- Food Safety: Refrigerating food helps to keep food safe to eat. This is because it prevents the growth of bacteria that can cause foodborne illness.
Refrigeration is an essential part of food safety. By keeping food out of the danger zone, refrigeration helps to prevent the growth of bacteria and reduce the risk of foodborne illness.
Conclusion:
Keeping food out of the danger zone is essential for preventing the growth of bacteria and reducing the risk of foodborne illness. Refrigeration is one of the most effective ways to keep food out of the danger zone. Refrigerators should be set to 40F or below to ensure that food is kept at a safe temperature.
4. Freezing
Freezing is one of the most effective ways to preserve food and prevent the growth of bacteria. When food is frozen, the water in the food turns to ice, which creates an environment that is too cold for bacteria to grow. This makes freezing an ideal way to store food for long periods of time.
- Inhibition of Bacterial Growth: The growth of bacteria is stopped at temperatures below 0F. This is because bacteria need a certain amount of energy to grow and reproduce, and at temperatures below 0F, they do not have enough energy to do so.
- Extended Shelf Life: Freezing food extends its shelf life significantly. This is because the growth of bacteria is stopped, which means that food will last much longer in the freezer.
- Food Safety: Freezing food helps to keep food safe to eat. This is because it prevents the growth of bacteria that can cause foodborne illness.
Freezing is an essential part of food safety. By keeping food out of the danger zone, freezing helps to prevent the growth of bacteria and reduce the risk of foodborne illness.
5. Cooking
Cooking food to the proper internal temperature is essential for killing bacteria and preventing foodborne illness. The danger zone temperature is the range of temperatures between 40F and 140F (4C and 60C) in which bacteria can grow and multiply rapidly. Cooking food to the proper internal temperature ensures that all bacteria are killed, even if the food has been in the danger zone for a period of time.
- Food Safety: Cooking food to the proper internal temperature is one of the most important things you can do to prevent foodborne illness. Bacteria can cause a variety of symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. In some cases, foodborne illness can be fatal.
- Temperature Guidelines: The USDA has established safe internal cooking temperatures for different types of food. These temperatures are based on the type of food and the size of the food. For example, ground beef should be cooked to an internal temperature of 160F (71C), while chicken should be cooked to an internal temperature of 165F (74C).
- Use a Food Thermometer: The best way to ensure that food is cooked to the proper internal temperature is to use a food thermometer. Food thermometers are inexpensive and easy to use. Simply insert the thermometer into the thickest part of the food and wait for the temperature to stabilize.
- Preventing Recontamination: Once food has been cooked to the proper internal temperature, it is important to prevent recontamination. This means avoiding cross-contamination between cooked and raw food, and washing hands and surfaces thoroughly after handling raw food.
Cooking food to the proper internal temperature is an essential part of food safety. By following these simple steps, you can help to prevent foodborne illness and keep your family safe.
6. Thawing
Thawing food at room temperature can be dangerous because it allows bacteria to grow and multiply. The danger zone temperature is the range of temperatures between 40F and 140F (4C and 60C) in which bacteria can grow rapidly. When food is thawed at room temperature, it can enter the danger zone and bacteria can begin to grow. This can lead to foodborne illness.
The safest way to thaw food is in the refrigerator. This is because the refrigerator's cold temperature keeps the food out of the danger zone. Food can also be thawed in cold water. However, it is important to make sure that the food is in a watertight bag and that the water is changed every 30 minutes.
It is important to never thaw food on the counter at room temperature. This is because the food will quickly enter the danger zone and bacteria will begin to grow. Thawing food at room temperature is a major cause of foodborne illness.
By following these simple tips, you can help to prevent foodborne illness and keep your family safe.
7. Food Safety
Food safety guidelines are essential for preventing the growth of bacteria and keeping food out of the danger zone. The danger zone is the range of temperatures between 40F and 140F (4C and 60C) in which bacteria can grow and multiply rapidly. Following food safety guidelines can help to keep food out of the danger zone and reduce the risk of foodborne illness.
- Proper Storage: Food should be stored at the proper temperature to prevent the growth of bacteria. Refrigerators should be set to 40F or below, and freezers should be set to 0F or below. Food should also be stored in covered containers to prevent contamination.
- Proper Cooking: Food should be cooked to the proper internal temperature to kill bacteria. The USDA has established safe internal cooking temperatures for different types of food. For example, ground beef should be cooked to an internal temperature of 160F (71C), while chicken should be cooked to an internal temperature of 165F (74C).
- Proper Thawing: Food should be thawed in the refrigerator or in cold water, not at room temperature. Thawing food at room temperature can allow bacteria to grow and multiply. Food can be thawed in the refrigerator for several days, or it can be thawed in cold water for several hours.
- Proper Handling: Food should be handled properly to prevent contamination. Hands should be washed thoroughly before handling food, and food should not be touched with bare hands. Food should also be kept separate from raw meat and poultry to prevent cross-contamination.
By following these food safety guidelines, you can help to prevent the growth of bacteria and keep food out of the danger zone. This will help to reduce the risk of foodborne illness and keep you and your family healthy.
FAQs on Danger Zone Temperature
The danger zone temperature is the range of temperatures between 40F and 140F (4C and 60C) in which bacteria can grow and multiply rapidly. This can lead to foodborne illness if food is not properly stored or cooked.
Question 1: What is the danger zone temperature?
Answer: The danger zone temperature is the range of temperatures between 40F and 140F (4C and 60C). Bacteria can grow and multiply rapidly in this temperature range.
Question 2: Why is the danger zone temperature important?
Answer: The danger zone temperature is important because it can lead to foodborne illness if food is not properly stored or cooked. Bacteria can grow and multiply rapidly in this temperature range, which can cause food to become contaminated.
Question 3: How can I keep food out of the danger zone?
Answer: You can keep food out of the danger zone by refrigerating or freezing it promptly. Refrigerators should be set to 40F or below, and freezers should be set to 0F or below. You should also cook food to the proper internal temperature to kill bacteria.
Question 4: What are the symptoms of foodborne illness?
Answer: The symptoms of foodborne illness can include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. In some cases, foodborne illness can be fatal.
Question 5: How can I prevent foodborne illness?
Answer: You can prevent foodborne illness by following food safety guidelines. This includes keeping food out of the danger zone, cooking food to the proper internal temperature, and washing your hands and surfaces thoroughly after handling food.
Question 6: Where can I learn more about food safety?
Answer: You can learn more about food safety from the USDA website or by taking a food safety class.
By following these tips, you can help to prevent foodborne illness and keep your family safe.
Remember, the danger zone temperature is a serious food safety concern. By understanding the dangers of the danger zone, you can take steps to protect yourself and your family from foodborne illness.
Tips on Avoiding the Danger Zone Temperature
The danger zone temperature is the range of temperatures between 40F and 140F (4C and 60C) in which bacteria can grow and multiply rapidly. This can lead to foodborne illness if food is not properly stored or cooked.
Tip 1: Refrigerate or freeze food promptly.
Refrigerators should be set to 40F or below, and freezers should be set to 0F or below. Food should be refrigerated or frozen within two hours of cooking or thawing.
Tip 2: Cook food to the proper internal temperature.
The USDA has established safe internal cooking temperatures for different types of food. For example, ground beef should be cooked to an internal temperature of 160F (71C), while chicken should be cooked to an internal temperature of 165F (74C).
Tip 3: Thaw food in the refrigerator or in cold water.
Never thaw food at room temperature. This is because the food will quickly enter the danger zone and bacteria will begin to grow. Food can be thawed in the refrigerator for several days, or it can be thawed in cold water for several hours.
Tip 4: Keep food out of the danger zone when transporting it.
If you are transporting food, keep it in a cooler with ice packs. This will help to keep the food out of the danger zone.
Tip 5: Wash your hands and surfaces thoroughly.
Bacteria can be spread through contact with contaminated hands or surfaces. Always wash your hands and surfaces thoroughly before handling food.
Tip 6: Avoid cross-contamination.
Cross-contamination occurs when bacteria from one food item is transferred to another food item. To avoid cross-contamination, keep raw meat and poultry separate from other food items.
Summary of key takeaways or benefits:
By following these tips, you can help to prevent the growth of bacteria and keep food out of the danger zone. This will help to reduce the risk of foodborne illness and keep you and your family healthy.
Transition to the article's conclusion:
The danger zone temperature is a serious food safety concern. By understanding the dangers of the danger zone, you can take steps to protect yourself and your family from foodborne illness.
Conclusion
The danger zone temperature is the range of temperatures between 40F and 140F (4C and 60C) in which bacteria can grow and multiply rapidly. This can lead to foodborne illness if food is not properly stored or cooked.
By understanding the dangers of the danger zone, you can take steps to protect yourself and your family from foodborne illness. This includes refrigerating or freezing food promptly, cooking food to the proper internal temperature, and thawing food in the refrigerator or in cold water. You should also keep food out of the danger zone when transporting it, wash your hands and surfaces thoroughly, and avoid cross-contamination.
Foodborne illness is a serious public health concern, but it can be prevented by following food safety guidelines. By taking steps to keep food out of the danger zone, you can help to reduce the risk of foodborne illness and keep you and your family healthy.