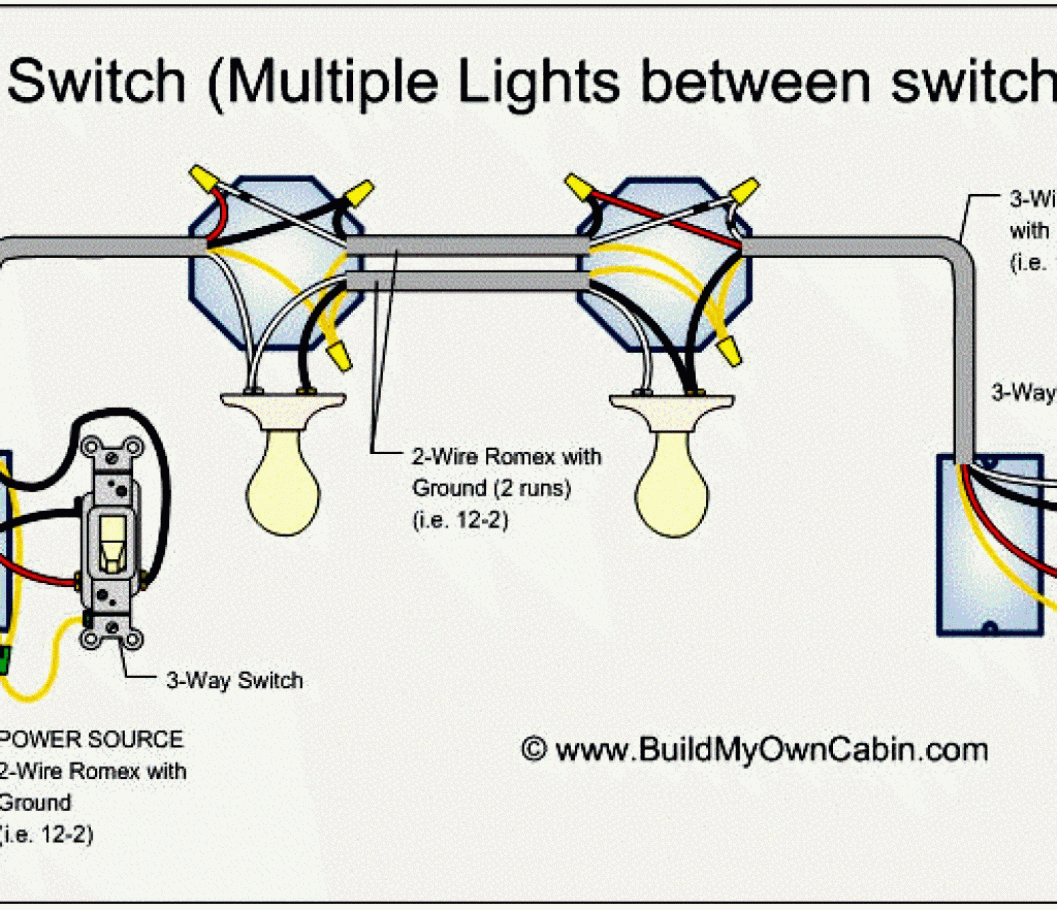
Electrical wiring is a fundamental aspect of electrical systems, providing a pathway for electricity to flow between components. In the context of lighting circuits, a three-way switch allows for the control of a single light fixture from multiple locations. Understanding the appropriate wire connections is crucial for the proper functioning of a three-way switch.
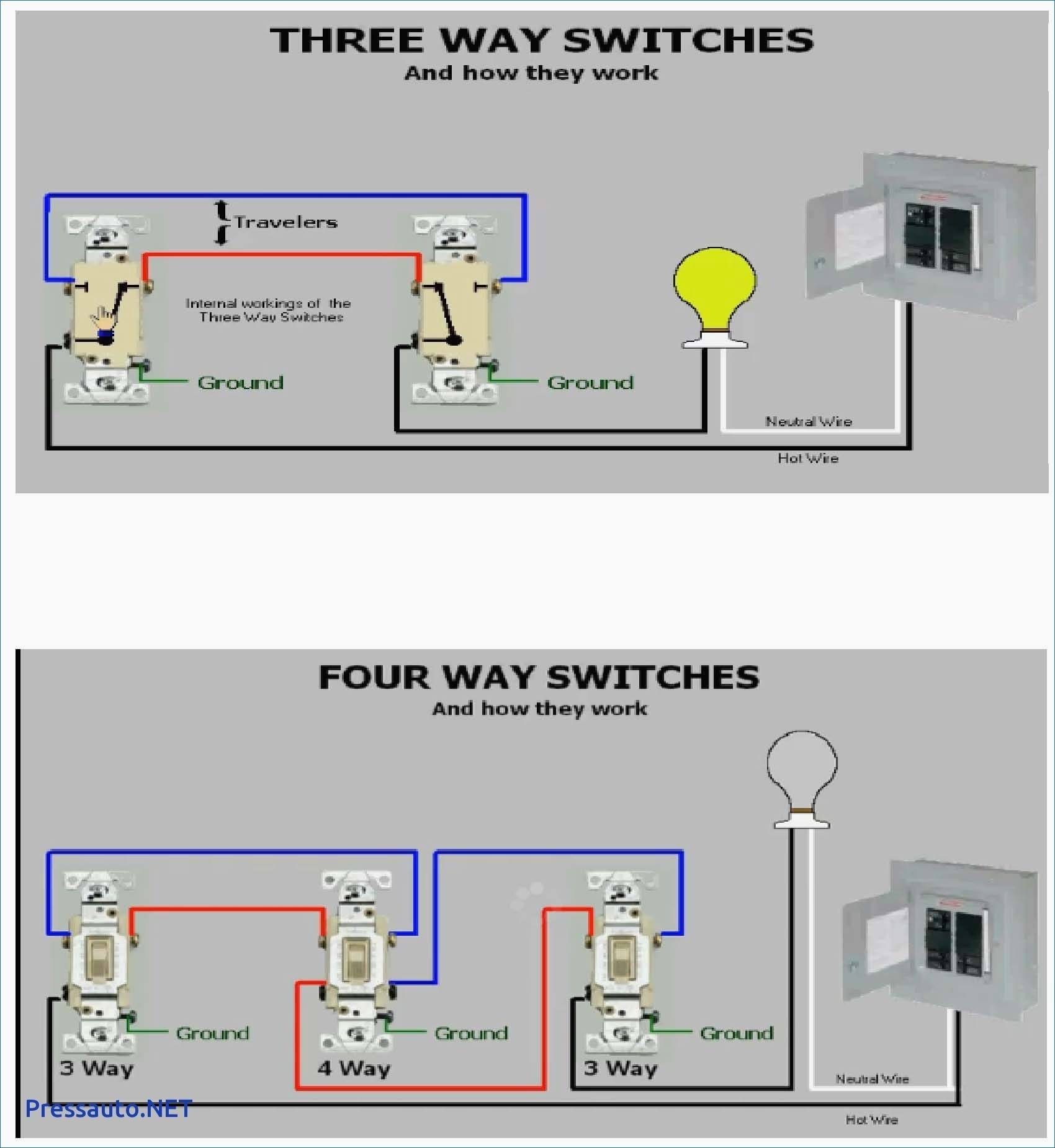
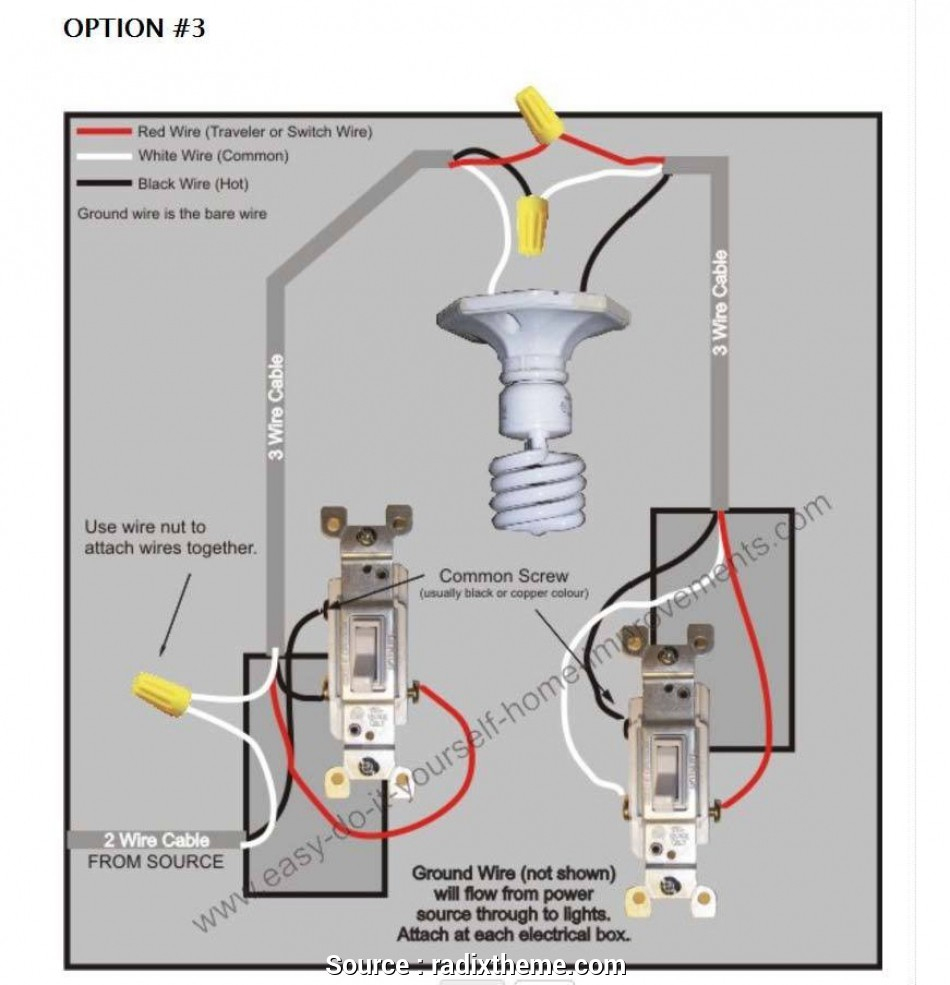
In a three-way switch configuration, two switches are connected to the light fixture. Each switch has three terminals: one common terminal and two traveler terminals. The common terminal is connected to the power source, while the traveler terminals are connected to each other and to the light fixture. The traveler terminals allow the switches to communicate with each other, determining the on/off state of the light fixture.
The type of wire used for a three-way switch is typically 14-gauge stranded copper wire. This wire is flexible and easy to work with, making it suitable for the complex connections required in a three-way switch configuration. It is important to ensure that the wire is rated for the voltage and current requirements of the circuit.
Read also:The Ultimate Messy Bun Guide Master The Effortless Look
Proper wiring of a three-way switch requires careful attention to detail and adherence to electrical codes. Incorrect wiring can lead to safety hazards, including electrical shocks or fires. It is recommended to consult with a qualified electrician for the installation and maintenance of electrical systems, including three-way switches.
What Wire for 3 Way Switch
Electrical wiring is a crucial aspect of electrical systems, providing a pathway for electricity to flow between components. In the context of lighting circuits, a three-way switch allows for the control of a single light fixture from multiple locations. Understanding the appropriate wire connections is crucial for the proper functioning of a three-way switch.
- 14-gauge
- Stranded
- Copper
- Voltage rating
- Current rating
- Electrical codes
The type of wire used for a three-way switch is typically 14-gauge stranded copper wire. This wire is flexible and easy to work with, making it suitable for the complex connections required in a three-way switch configuration. It is important to ensure that the wire is rated for the voltage and current requirements of the circuit. Proper wiring of a three-way switch requires careful attention to detail and adherence to electrical codes. Incorrect wiring can lead to safety hazards, including electrical shocks or fires. It is recommended to consult with a qualified electrician for the installation and maintenance of electrical systems, including three-way switches.
1. 14-gauge
In the context of three-way switch wiring, the term "14-gauge" refers to the thickness and composition of the electrical wire used to connect the switch components. Understanding the significance of 14-gauge wire is crucial for ensuring the proper functioning and safety of the electrical system.
- Conductor Size
The gauge of a wire indicates the thickness of its conductive material, which is typically copper in electrical wiring. A 14-gauge wire has a larger cross-sectional area compared to higher gauge wires, allowing it to carry more electrical current without overheating. - Current Capacity
The larger conductor size of 14-gauge wire enables it to handle higher electrical currents. In the case of three-way switches, the wire must be capable of carrying the current required by the connected light fixture. Using a wire with insufficient current capacity can lead to overheating and potential fire hazards. - Flexibility
14-gauge stranded copper wire is flexible and easy to work with, making it suitable for the complex wiring configurations required in three-way switch installations. The stranded construction consists of multiple thin copper strands twisted together, providing greater flexibility compared to solid core wires. - Voltage Rating
The 14-gauge wire used for three-way switches must be rated for the voltage of the electrical system. Common residential electrical systems operate at 120 volts, and the wire must be rated to withstand this voltage safely.
Overall, the use of 14-gauge wire in three-way switch wiring is essential for ensuring the safe and reliable operation of the electrical system. Its appropriate conductor size, current capacity, flexibility, and voltage rating make it the preferred choice for this application.
2. Stranded
In the context of electrical wiring for three-way switches, the term "stranded" refers to the construction of the wire's conductive material. Stranded wire consists of numerous thin copper strands twisted together to form a single conductor, as opposed to solid core wire, which consists of a single solid copper conductor.
Read also:Hines Va Hospital Your Guide To Care And Services
The use of stranded wire for three-way switches offers several advantages:
- Flexibility: Stranded wire is highly flexible, making it easier to work with in tight spaces and complex wiring configurations. This flexibility is particularly important for three-way switch installations, which often require intricate wiring paths.
- Resistance to breakage: Stranded wire is less prone to breakage compared to solid core wire, especially when subjected to repeated bending or flexing. This durability is crucial for three-way switch wiring, as the wires may be subjected to movement during installation or maintenance.
- Lower resistance: Stranded wire has a lower electrical resistance compared to solid core wire of the same gauge. This lower resistance contributes to efficient current flow and reduces power loss in the circuit.
Overall, the use of stranded wire for three-way switches is essential for ensuring a reliable and long-lasting electrical connection. Its flexibility, durability, and lower resistance make it the preferred choice for this application.
3. Copper
In the context of "what wire for 3 way switch," copper plays a crucial role as the primary conductor material used in electrical wiring. Copper's unique properties make it ideally suited for this application, offering several key advantages:
- Excellent Conductivity: Copper is a highly conductive metal, allowing electrical current to flow efficiently with minimal resistance. This ensures reliable and efficient power transmission in three-way switch circuits.
- Durability: Copper is a robust and durable material, resistant to corrosion and oxidation. This durability contributes to the longevity and reliability of three-way switch wiring, even in demanding environments.
- Flexibility: Copper wire can be easily bent and shaped without compromising its integrity. This flexibility is essential for three-way switch installations, where wires often need to be routed through tight spaces or around obstacles.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Copper is a relatively affordable material, making it a cost-effective choice for electrical wiring. This cost-effectiveness is particularly relevant for three-way switch installations, which can require significant amounts of wire.
Overall, the use of copper wire for three-way switches is essential for ensuring the safe, efficient, and reliable operation of the electrical system. Its excellent conductivity, durability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness make copper the preferred choice for this application.
4. Voltage rating
In the context of "what wire for 3 way switch," voltage rating plays a critical role in ensuring the safety and functionality of the electrical system. Voltage rating refers to the maximum voltage that a wire can safely handle without breaking down or posing a fire hazard.
For three-way switch applications, it is crucial to select a wire with an appropriate voltage rating that matches the voltage of the electrical system. Using a wire with an insufficient voltage rating can lead to insulation breakdown, overheating, and potential electrical fires.
For example, in a typical residential electrical system operating at 120 volts, a wire with a voltage rating of at least 120 volts must be used for three-way switch wiring. Using a wire rated for a lower voltage, such as 100 volts, could lead to dangerous consequences.
Selecting the correct voltage rating for your three-way switch wiring is essential for ensuring the safe and reliable operation of your electrical system. Always refer to the manufacturer's specifications for the voltage rating requirements of your specific switch and electrical system.
5. Current rating
Current rating holds significant importance in determining the appropriate wire for a 3-way switch, as it directly relates to the amount of electrical current the wire can safely carry. Understanding current rating is crucial for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of your electrical system.
The current rating of a wire is measured in amps and indicates the maximum amount of electrical current that can flow through the wire without causing excessive heating or damage to the wire's insulation. Using a wire with an insufficient current rating for your 3-way switch can lead to overheating, insulation breakdown, and potential electrical fires.
For instance, if the 3-way switch controls a lighting circuit with a total load of 6 amps, the wire used for the switch must have a current rating of at least 6 amps or higher. Using a wire with a current rating of only 5 amps, for example, could lead to the wire overheating and becoming a fire hazard.
Selecting the correct current rating for your 3-way switch wiring is essential for ensuring the safety and reliability of your electrical system. Always refer to the manufacturer's specifications for the current rating requirements of your specific switch and electrical system.
6. Electrical codes
Electrical codes establish a comprehensive set of regulations and guidelines governing the design, installation, and maintenance of electrical systems, including the wiring for 3-way switches. These codes are developed and enforced by regulatory bodies to ensure the safety and proper functioning of electrical systems, minimizing the risk of electrical fires, shocks, and other hazards.
Electrical codes provide specific requirements for the type, size, and installation of wires used in 3-way switch circuits. These requirements are based on factors such as the voltage and current rating of the circuit, the type of insulation used on the wire, and the environmental conditions where the wire will be installed.
For example, in the United States, the National Electrical Code (NEC) specifies that 14-gauge wire with a minimum voltage rating of 120 volts and a current rating of 15 amps must be used for 3-way switch circuits. This ensures that the wire can safely handle the electrical load of the circuit and prevents overheating or other hazards.
Understanding and adhering to electrical codes when selecting and installing wire for 3-way switches is crucial for ensuring the safety and reliability of your electrical system. Ignoring or violating electrical codes can lead to serious consequences, including electrical fires, property damage, and even injury or death.
Therefore, it is essential to consult with qualified electricians and refer to the relevant electrical codes when working with 3-way switch wiring or any other electrical system.
FAQs on "what wire for 3 way switch"
This section addresses frequently asked questions (FAQs) related to the topic of "what wire for 3 way switch." These FAQs aim to provide clear and concise answers to common concerns or misconceptions, offering valuable insights for individuals seeking to understand this electrical concept.
Question 1: What type of wire should be used for a 3-way switch?For 3-way switch wiring, stranded 14-gauge copper wire is generally recommended. Stranded wire offers flexibility and is less prone to breakage, making it suitable for the intricate connections required in 3-way switch configurations. Copper is an excellent conductor and is commonly used in electrical wiring due to its durability and cost-effectiveness.
Question 2: What is the importance of voltage rating in wire selection for 3-way switches?The voltage rating of a wire indicates the maximum voltage it can safely handle. For 3-way switch circuits, the wire's voltage rating must match or exceed the voltage of the electrical system. Using a wire with an insufficient voltage rating can lead to insulation breakdown, overheating, and potential fire hazards.
Question 3: How does current rating affect wire selection for 3-way switches?The current rating of a wire determines the amount of electrical current it can safely carry. The wire used for a 3-way switch must have a current rating equal to or greater than the total current draw of the connected lighting fixtures. Using a wire with an insufficient current rating can cause overheating, insulation damage, and potential electrical fires.
Question 4: What safety considerations should be taken into account when choosing wire for 3-way switches?Electrical codes provide specific requirements for the selection and installation of wires in 3-way switch circuits. Adhering to these codes is crucial to ensure the safety and proper functioning of the electrical system. It is advisable to consult with qualified electricians and refer to relevant electrical codes for guidance on safe wiring practices.
Question 5: Can I use solid core wire instead of stranded wire for 3-way switches?While solid core wire can be used for 3-way switches, stranded wire is generally preferred due to its increased flexibility and resistance to breakage. Stranded wire is better suited for the complex wiring configurations and tight spaces often encountered in 3-way switch installations.
Question 6: What are the consequences of using an incorrect wire gauge for a 3-way switch?Using an incorrect wire gauge for a 3-way switch can have several negative consequences. A wire gauge that is too small may not be able to safely carry the required current, leading to overheating and potential fire hazards. Conversely, a wire gauge that is too large may be more difficult to work with and may not fit properly into the switch terminals.
In summary, understanding the appropriate wire selection for 3-way switches is crucial for ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical systems. By considering factors such as wire type, voltage rating, current rating, and safety codes, individuals can make informed decisions when choosing wires for their 3-way switch installations.
If you have any further questions or require additional guidance on this topic, it is advisable to consult with a qualified electrician for professional advice.
Tips for Choosing and Using Wire for 3-Way Switches
When working with electrical systems, it is crucial to select and use the appropriate wire for 3-way switches to ensure safety and proper functioning. Here are some tips to guide you:
Tip 1: Use the Correct Wire Type
For 3-way switch wiring, stranded 14-gauge copper wire is generally recommended. Stranded wire offers flexibility and is less prone to breakage, making it suitable for the intricate connections required in 3-way switch configurations.
Tip 2: Consider Voltage Rating
The voltage rating of a wire indicates the maximum voltage it can safely handle. For 3-way switch circuits, the wire's voltage rating must match or exceed the voltage of the electrical system. Using a wire with an insufficient voltage rating can lead to insulation breakdown, overheating, and potential fire hazards.
Tip 3: Determine Current Rating
The current rating of a wire determines the amount of electrical current it can safely carry. The wire used for a 3-way switch must have a current rating equal to or greater than the total current draw of the connected lighting fixtures. Using a wire with an insufficient current rating can cause overheating, insulation damage, and potential electrical fires.
Tip 4: Adhere to Electrical Codes
Electrical codes provide specific requirements for the selection and installation of wires in 3-way switch circuits. Adhering to these codes is crucial to ensure the safety and proper functioning of the electrical system. It is advisable to consult with qualified electricians and refer to relevant electrical codes for guidance on safe wiring practices.
Tip 5: Avoid Solid Core Wire
While solid core wire can be used for 3-way switches, stranded wire is generally preferred due to its increased flexibility and resistance to breakage. Stranded wire is better suited for the complex wiring configurations and tight spaces often encountered in 3-way switch installations.
Key Takeaways:
- Choose stranded 14-gauge copper wire for 3-way switches.
- Ensure the wire's voltage rating matches or exceeds the electrical system voltage.
- Select a wire with a current rating equal to or greater than the connected load.
- Follow electrical codes and consult with qualified electricians for safe wiring practices.
- Avoid using solid core wire due to its reduced flexibility.
By following these tips, you can ensure the proper selection and use of wire for 3-way switches, contributing to a safe and reliable electrical system.
Conclusion
The selection of appropriate wire for 3-way switches is a crucial aspect of electrical installations, ensuring the safety and reliability of the electrical system. This article has explored the key considerations when choosing wire for 3-way switches, including wire type, voltage rating, current rating, and adherence to electrical codes.
Understanding these factors is essential for making informed decisions when selecting and using wire for 3-way switch installations. By following the recommendations outlined in this article, individuals can contribute to the safe and effective operation of their electrical systems. Proper wire selection not only ensures the functionality of 3-way switches but also minimizes the risk of electrical hazards, such as overheating, insulation breakdown, and potential fires.
It is important to remember that electrical work should always be carried out by qualified electricians who are familiar with the relevant electrical codes and safety regulations. By seeking professional assistance and adhering to the guidelines provided in this article, individuals can ensure the proper selection and use of wire for 3-way switches, contributing to a safe and reliable electrical environment.