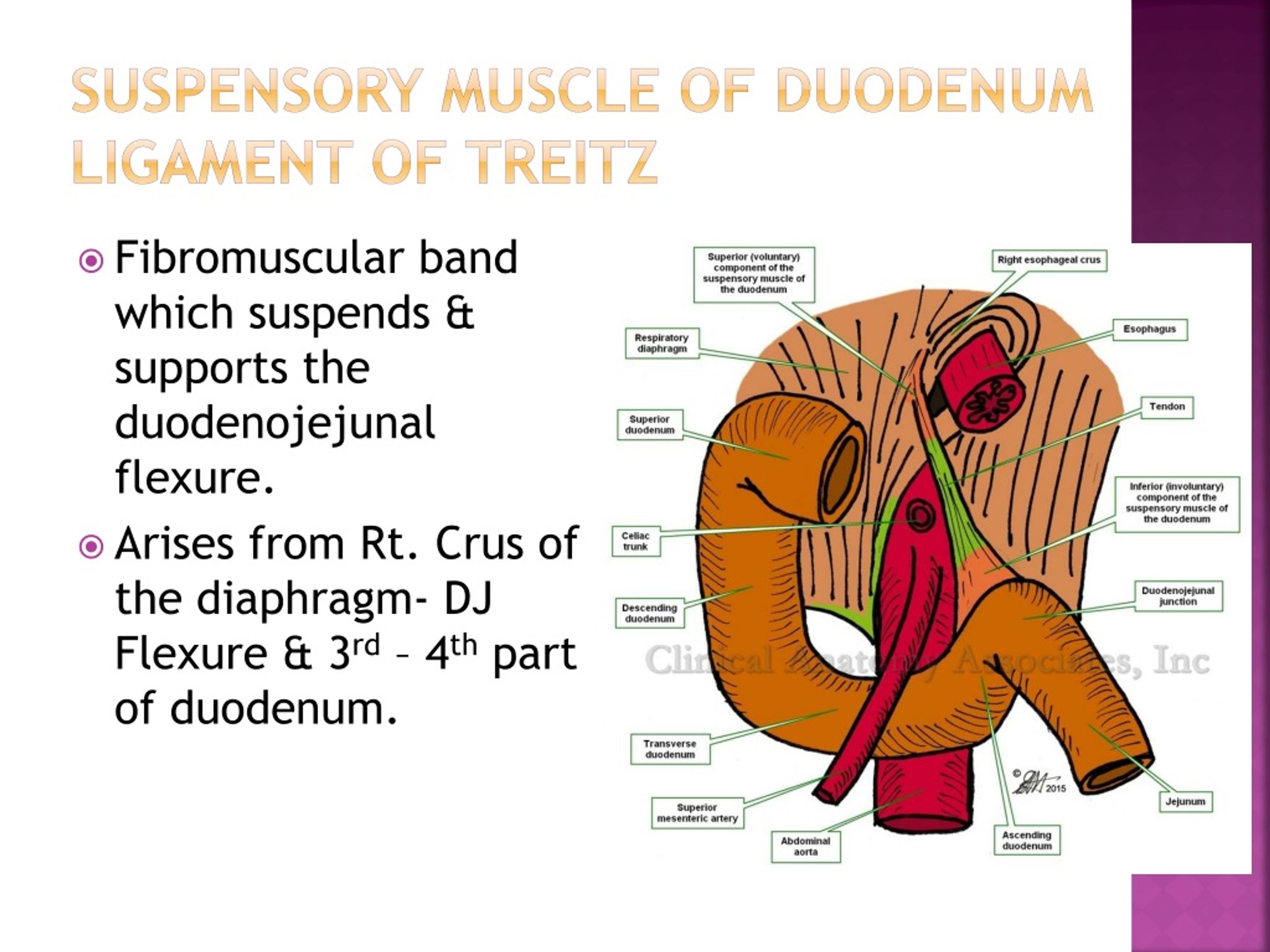
The ligament of Treitz, also known as the suspensory muscle of the duodenum, plays a crucial role in the digestive system. This anatomical structure marks the transition between the duodenum and the jejunum, serving as an important landmark in abdominal surgeries and diagnostic imaging. Its unique location and function have made it a subject of interest in both medical education and clinical practice.
In the realm of gastrointestinal anatomy, the ligament of Treitz stands out due to its strategic positioning and the role it plays in distinguishing the upper and lower gastrointestinal tracts. Its presence is vital for understanding various gastrointestinal disorders and for the surgical management of conditions like malrotation and volvulus. The ligament's importance extends beyond its anatomical definition, offering insights into the intricate workings of the human body.
Understanding the ligament of Treitz involves exploring its anatomical structure, clinical significance, and its role in various medical procedures. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the ligament, delving into its anatomy, function, associated medical conditions, and relevance in clinical settings. By the end of this piece, you will have gained valuable insights into why the ligament of Treitz is considered a cornerstone in the study of human anatomy.
Read also:Read The Latest From Bluefield Daily Telegraph
Table of Contents
- Anatomy of the Ligament of Treitz
- Function and Physiology
- Clinical Significance
- How is the Ligament of Treitz Identified?
- Surgical Relevance of the Ligament of Treitz
- Common Conditions Associated with the Ligament of Treitz
- The Ligament of Treitz in Diagnostic Imaging
- What Happens if the Ligament of Treitz is Damaged?
- The Role of the Ligament of Treitz in Gastrointestinal Health
- Ligament of Treitz and Medical Education
- Is the Ligament of Treitz Visible in All Imaging Techniques?
- FAQs about the Ligament of Treitz
- Conclusion
Anatomy of the Ligament of Treitz
The ligament of Treitz is a fibromuscular band that extends from the right crus of the diaphragm to the duodenojejunal flexure. Its anatomical positioning serves as a critical junction in the digestive tract, marking the transition between the duodenum and jejunum. The structure is composed of a blend of smooth muscle fibers and connective tissue, which helps in anchoring the duodenum to the posterior abdominal wall.
The ligament's anatomical configuration varies among individuals, with some possessing a more prominent or elongated structure. It is this variability that can sometimes complicate its identification during surgical procedures or imaging studies. Despite these differences, the ligament of Treitz remains a consistent landmark for differentiating the upper from the lower gastrointestinal tract.
Understanding the anatomy of the ligament of Treitz is essential for medical practitioners, especially those specializing in gastroenterology and surgery. The ligament's unique positioning and structure play a pivotal role in the diagnosis and treatment of various gastrointestinal disorders, making it an indispensable part of the human anatomy.
Function and Physiology
The primary function of the ligament of Treitz is to support the duodenojejunal flexure, maintaining its position and aiding in the passage of food through the digestive tract. This support is crucial, as it prevents the duodenum from sagging or twisting, which could lead to intestinal obstruction or other gastrointestinal complications.
The ligament's role extends beyond mere support. It acts as a fulcrum around which the gut can rotate, facilitating the movement of food and digestive enzymes. This rotational function is vital for the efficient digestion and absorption of nutrients, highlighting the ligament's importance in maintaining gastrointestinal health.
In terms of physiology, the ligament of Treitz is innervated by the autonomic nervous system, which regulates its contraction and relaxation. This innervation ensures that the ligament can respond to changes in the digestive tract, adjusting its tension as needed to accommodate the flow of food and digestive juices.
Read also:Seattle A Top 10 World City For Economy
Clinical Significance
The ligament of Treitz holds significant clinical importance due to its role in various medical conditions and procedures. It serves as a landmark in imaging studies, helping clinicians identify the location of gastrointestinal bleeding or obstructions. In conditions like malrotation, the ligament's position can indicate abnormal rotation of the midgut, guiding surgical intervention.
Moreover, the ligament of Treitz is involved in the diagnosis and treatment of disorders such as superior mesenteric artery syndrome, where compression of the duodenum leads to obstruction. Recognizing the ligament's involvement in these conditions is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Surgeons often use the ligament of Treitz as a reference point during abdominal surgeries, particularly those involving the small intestine. Its identification can help prevent complications and ensure the successful completion of surgical procedures. As such, a thorough understanding of the ligament's clinical significance is crucial for healthcare professionals.
How is the Ligament of Treitz Identified?
Identifying the ligament of Treitz involves a combination of imaging techniques and physical examination. In radiology, the ligament is often visible in barium studies as the point where the duodenum transitions into the jejunum. Its identification can be confirmed through techniques such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which provide detailed images of the abdominal structures.
During surgical procedures, the ligament of Treitz is identified visually by locating the duodenojejunal flexure. Surgeons often rely on anatomical landmarks and palpation to ensure accurate identification, which is crucial for successful surgical outcomes.
Understanding how to identify the ligament of Treitz is vital for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Accurate identification can aid in diagnosing gastrointestinal disorders and guide surgical interventions, underscoring the ligament's importance in clinical practice.
Surgical Relevance of the Ligament of Treitz
The ligament of Treitz plays a crucial role in various surgical procedures, particularly those involving the small intestine and surrounding structures. Its identification serves as a reference point, helping surgeons navigate the complex anatomy of the abdominal cavity.
In surgeries addressing conditions like malrotation or bowel obstruction, the ligament of Treitz's position can guide corrective procedures, ensuring that the intestines are properly aligned and functioning. Its role as a landmark helps prevent surgical complications, contributing to successful patient outcomes.
Furthermore, the ligament of Treitz is involved in procedures like gastric bypass surgery, where its position can influence the surgical approach and technique. Understanding its surgical relevance is essential for healthcare professionals involved in abdominal surgeries, as it aids in planning and executing effective surgical interventions.
Common Conditions Associated with the Ligament of Treitz
Several medical conditions are associated with the ligament of Treitz, impacting its function and leading to gastrointestinal complications. One such condition is malrotation, where the intestines fail to rotate properly during fetal development, resulting in abnormal positioning of the ligament.
Superior mesenteric artery syndrome is another condition linked to the ligament of Treitz, where the duodenum is compressed between the superior mesenteric artery and the aorta. This compression leads to symptoms like abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting, necessitating medical intervention.
Understanding these conditions and their association with the ligament of Treitz is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Healthcare professionals must be aware of these potential issues to provide optimal care for patients experiencing gastrointestinal symptoms.
The Ligament of Treitz in Diagnostic Imaging
Diagnostic imaging plays a vital role in identifying the ligament of Treitz and assessing its position and function. Techniques like barium studies, CT scans, and MRIs are commonly used to visualize the ligament and the surrounding structures.
In barium studies, the ligament of Treitz is often visible as the point where the duodenum transitions into the jejunum. CT and MRI provide more detailed images, allowing clinicians to assess the ligament's anatomy and identify any abnormalities or associated conditions.
Understanding the role of diagnostic imaging in evaluating the ligament of Treitz is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. These imaging techniques provide valuable insights into the ligament's function and its impact on gastrointestinal health, aiding in the management of various medical conditions.
What Happens if the Ligament of Treitz is Damaged?
Damage to the ligament of Treitz can have significant implications for gastrointestinal health. If the ligament is compromised, it can lead to sagging or twisting of the duodenum, resulting in bowel obstruction or other complications.
Symptoms of damage to the ligament of Treitz may include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and changes in bowel habits. These symptoms can vary depending on the extent of the damage and the underlying cause.
Treatment for damage to the ligament of Treitz typically involves addressing the underlying cause and may include surgical intervention to repair or reposition the ligament. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for preventing complications and ensuring optimal patient outcomes.
The Role of the Ligament of Treitz in Gastrointestinal Health
The ligament of Treitz plays a vital role in maintaining gastrointestinal health by supporting the duodenojejunal flexure and facilitating the movement of food through the digestive tract. Its function is essential for preventing complications like bowel obstruction and ensuring efficient digestion and nutrient absorption.
In addition to its structural support, the ligament of Treitz acts as a landmark for identifying the transition between the upper and lower gastrointestinal tracts, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment of various gastrointestinal disorders.
Understanding the role of the ligament of Treitz in gastrointestinal health is crucial for healthcare professionals, as it provides valuable insights into the complex workings of the digestive system and the importance of maintaining its integrity.
Ligament of Treitz and Medical Education
The ligament of Treitz holds significant educational value for medical students and professionals, serving as a key anatomical landmark in the study of gastrointestinal anatomy. Its unique structure and function provide insights into the complexities of the human body, contributing to a deeper understanding of gastrointestinal health.
Medical education programs often emphasize the importance of the ligament of Treitz in both clinical practice and surgical procedures, highlighting its role in diagnosing and treating various medical conditions.
Understanding the ligament of Treitz is essential for medical professionals, as it provides a foundation for comprehending the intricacies of the digestive system and the importance of maintaining gastrointestinal health.
Is the Ligament of Treitz Visible in All Imaging Techniques?
The visibility of the ligament of Treitz in imaging studies depends on the technique used and the patient's anatomy. While it is often visible in barium studies as the transition point between the duodenum and jejunum, its visibility may vary in other imaging modalities.
CT and MRI provide more detailed images, allowing for a clearer visualization of the ligament and surrounding structures. However, factors such as patient positioning and the presence of other anatomical structures can impact the visibility of the ligament in these studies.
Understanding the limitations and capabilities of different imaging techniques is essential for accurately identifying the ligament of Treitz and assessing its role in gastrointestinal health. Clinicians must be aware of these factors to ensure accurate diagnosis and effective treatment planning.
FAQs about the Ligament of Treitz
- What is the primary function of the ligament of Treitz?
The primary function of the ligament of Treitz is to support the duodenojejunal flexure, maintaining its position and facilitating the passage of food through the digestive tract.
- How is the ligament of Treitz identified during surgery?
During surgery, the ligament of Treitz is identified visually by locating the duodenojejunal flexure, often using anatomical landmarks and palpation to ensure accurate identification.
- What conditions are associated with the ligament of Treitz?
Conditions associated with the ligament of Treitz include malrotation and superior mesenteric artery syndrome, which can lead to gastrointestinal symptoms and require medical intervention.
- Is damage to the ligament of Treitz common?
Damage to the ligament of Treitz is not common but can occur due to trauma or surgical complications, leading to symptoms like abdominal pain and bowel obstruction.
- Can the ligament of Treitz be seen in all imaging techniques?
The visibility of the ligament of Treitz in imaging studies depends on the technique used and the patient's anatomy, with CT and MRI providing more detailed images.
- Why is the ligament of Treitz important in medical education?
The ligament of Treitz is important in medical education due to its role as a key anatomical landmark in the study of gastrointestinal anatomy, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment of various conditions.
Conclusion
The ligament of Treitz is a vital anatomical structure with significant implications for gastrointestinal health and medical practice. Its role in supporting the duodenojejunal flexure, serving as a landmark in imaging studies and surgeries, and its association with various medical conditions underscores its importance in the human body. Understanding the ligament of Treitz is crucial for healthcare professionals, as it provides valuable insights into the complex workings of the digestive system and the importance of maintaining its integrity. Through continued research and education, the ligament of Treitz will remain a cornerstone in the study of human anatomy and its clinical applications.