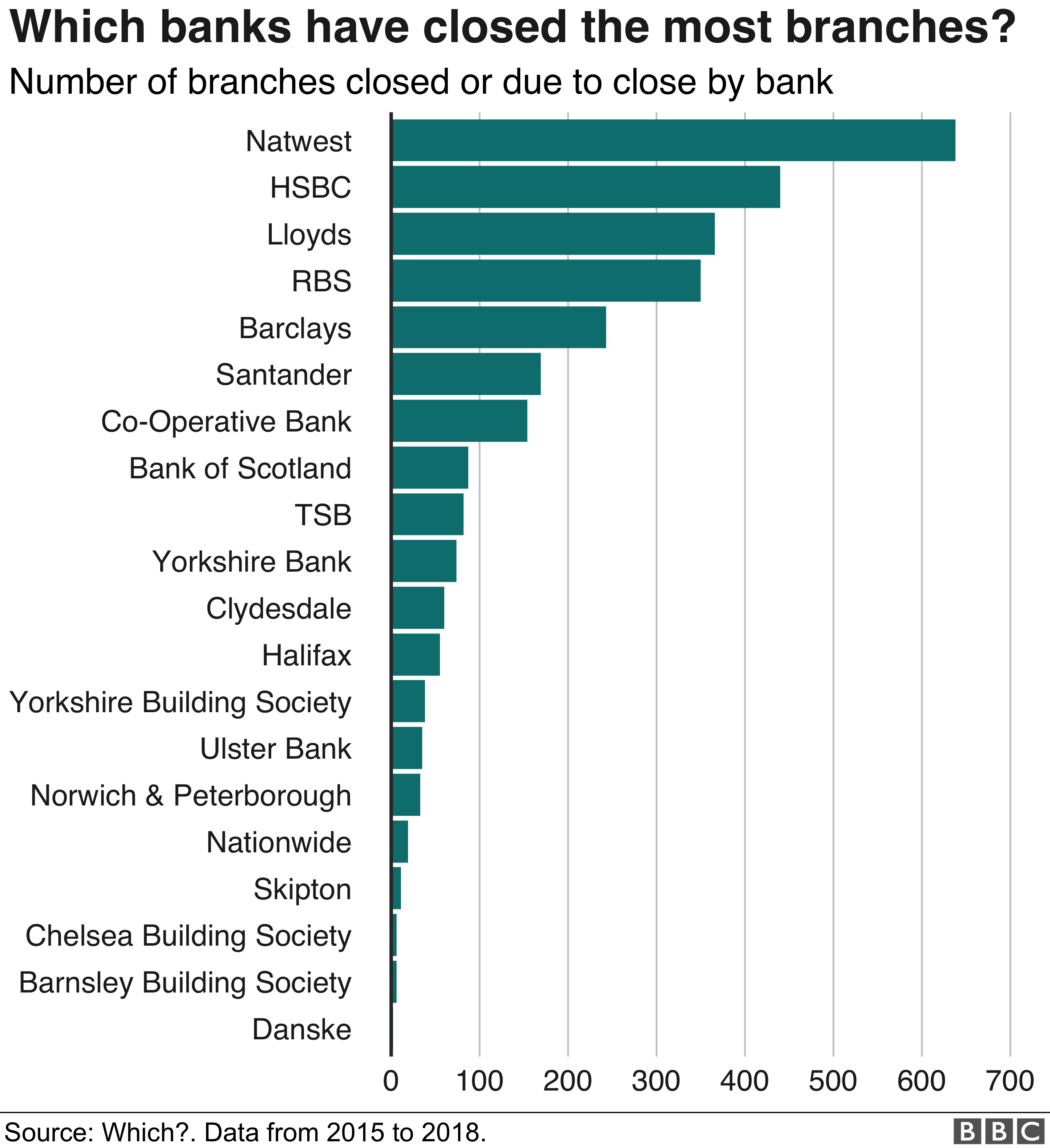
The closure of these branches may be a strategic decision influenced by various factors, including cost-cutting measures, the rise of digital banking, and shifts in customer behavior. It's essential to understand the rationale behind such a move to comprehend its implications on the banking sector and the economy at large. This article will delve into the reasons behind these closures, exploring the broader trends affecting the banking landscape. For customers who rely on physical branches for their banking needs, this development raises questions about accessibility and convenience. As banks continue to reduce their physical presence, many people are left wondering how this will impact their banking experience and what alternatives are available. In this comprehensive analysis, we'll explore the factors driving these closures, the potential impact on consumers, and the future of banking in a rapidly evolving digital world.
Table of Contents
1. History of Bank Branch Closures 2. Why Did Major US Banks Collectively Close 65 Branches? 3. Impact of Technological Advancements on Banking 4. How Does Customer Behavior Affect Bank Decisions? 5. Cost Reduction Strategies in the Banking Sector 6. Economic Impact of Bank Branch Closures 7. The Rise of Digital Banking 8. How Are Customers Affected by These Closures? 9. What Alternatives Are Available for Customers? 10. Future of Physical Bank Branches 11. Regulatory and Compliance Considerations 12. Case Study: A Look at Successful Bank Transformations 13. How Can Banks Improve Customer Experience During Closures? 14. Frequently Asked Questions 15. Conclusion
History of Bank Branch Closures
To understand the recent closure of 65 bank branches by major US banks, it's crucial to examine the historical context of bank branch closures. Over the past few decades, the banking industry has undergone significant transformations, driven by technological advancements, regulatory changes, and evolving consumer preferences.
Read also:Discover The Delights Of Kellys Country Cooking Authentic Flavors For The Modern Kitchen
In the 1980s, the banking landscape was dominated by physical branches, with customers relying heavily on in-person interactions for their banking needs. However, the advent of the internet and digital technology in the late 20th century began to change the way people accessed banking services. As online banking platforms emerged, customers were no longer dependent solely on physical branches to conduct transactions.
The 2008 financial crisis marked another pivotal moment for the banking industry. In response to the economic downturn, banks sought ways to reduce costs and improve efficiency. One of the strategies employed was the closure of underperforming or redundant branches. This trend continued into the 2010s as banks embraced digital transformation to meet the demands of tech-savvy customers.
Fast forward to the present day, the closure of 65 branches in a short span is a continuation of this trend, reflecting the ongoing shift towards digital banking. By examining the history of bank branch closures, we can gain insights into the factors driving these decisions and their implications for the future.
Why Did Major US Banks Collectively Close 65 Branches?
The decision to close a significant number of branches within a short period is not taken lightly by major US banks. Several factors contribute to such a move, each playing a role in shaping the strategic direction of these financial institutions.
Technological Advancements
One of the primary reasons for the closure of bank branches is the rapid advancement of technology. The rise of online and mobile banking platforms has transformed how consumers access financial services. With the convenience of digital banking, customers can perform transactions, manage accounts, and even apply for loans without stepping into a branch.
This technological shift has led to a decline in foot traffic at physical branches, prompting banks to reevaluate their branch networks. As more customers embrace digital banking solutions, banks are increasingly focusing on enhancing their online and mobile offerings to meet the evolving needs of their clientele.
Read also:Ohio Needs Tim Ryan
Customer Behavior
Changes in customer behavior also play a significant role in the decision to close bank branches. In recent years, there has been a noticeable shift in how people prefer to interact with their banks. Millennials and younger generations, in particular, exhibit a strong preference for digital banking channels.
As a result, banks are adapting their strategies to align with these preferences, investing in digital infrastructure and reducing their reliance on physical branches. By doing so, they can allocate resources more efficiently and provide a seamless banking experience across various platforms.
Cost Reduction
Cost reduction is another critical factor driving branch closures. Maintaining a network of physical branches involves substantial expenses, including rent, utilities, staffing, and maintenance. In an increasingly competitive banking environment, financial institutions are under pressure to optimize their operations and improve profitability.
By closing underperforming branches, banks can redirect resources towards areas that offer higher returns, such as digital banking solutions. This strategic approach allows banks to streamline their operations and enhance their financial performance.
Impact of Technological Advancements on Banking
The impact of technological advancements on the banking industry cannot be overstated. Over the past few decades, technology has revolutionized the way financial services are delivered and consumed, leading to significant changes in the banking landscape.
One of the most notable advancements is the proliferation of online and mobile banking platforms. These digital channels have made banking more accessible and convenient for consumers, allowing them to perform transactions, check account balances, and access financial services from the comfort of their homes or on the go.
Furthermore, technology has enabled the development of innovative financial products and services, such as peer-to-peer payment systems, robo-advisors, and digital wallets. These innovations have expanded the range of options available to consumers, providing them with greater flexibility and control over their financial lives.
In addition to enhancing the customer experience, technology has also played a crucial role in improving operational efficiency for banks. Automation, artificial intelligence, and data analytics have streamlined processes, reduced costs, and enhanced risk management capabilities.
As technology continues to evolve, banks must stay ahead of the curve by embracing digital transformation and leveraging technological advancements to meet the changing needs of their customers.
How Does Customer Behavior Affect Bank Decisions?
Customer behavior is a key driver of decision-making in the banking industry. As consumer preferences and expectations evolve, banks must adapt their strategies to remain competitive and relevant in the market.
One of the most significant changes in customer behavior is the increasing demand for digital banking solutions. With the rise of smartphones and mobile technology, consumers now prefer to access banking services through digital channels rather than visiting physical branches.
This shift in behavior has prompted banks to invest heavily in digital infrastructure, developing user-friendly online and mobile platforms that offer a wide range of services. By prioritizing digital solutions, banks can cater to the preferences of tech-savvy customers and enhance their overall experience.
Another important aspect of customer behavior is the growing emphasis on personalization and convenience. Today's consumers expect tailored financial products and services that meet their unique needs and preferences. To address this demand, banks are leveraging data analytics and artificial intelligence to deliver personalized experiences and recommendations to their customers.
As banks continue to evolve in response to changing customer behavior, they must strike a balance between digital innovation and maintaining a human touch in their interactions with customers.
Cost Reduction Strategies in the Banking Sector
Cost reduction is a critical component of strategic decision-making in the banking sector. As financial institutions face mounting pressure to improve profitability and competitiveness, they are increasingly focused on optimizing their operations and reducing expenses.
One of the most common cost reduction strategies employed by banks is the closure of underperforming branches. By consolidating their branch networks, banks can achieve significant savings in terms of rent, utilities, and staffing costs. This approach allows banks to allocate resources more efficiently and invest in areas that offer higher returns, such as digital banking solutions.
In addition to branch closures, banks are also exploring other cost-saving measures, such as process automation and outsourcing. Automation technologies, such as robotic process automation (RPA), can streamline routine tasks, reduce manual errors, and improve operational efficiency. Similarly, outsourcing non-core functions to specialized service providers can help banks achieve cost savings and focus on their core competencies.
Another important aspect of cost reduction is the optimization of technology infrastructure. By leveraging cloud computing and other advanced technologies, banks can reduce IT costs, enhance scalability, and improve agility in responding to changing market conditions.
Ultimately, cost reduction strategies are essential for banks to maintain their competitive edge and deliver value to their shareholders and customers.
Economic Impact of Bank Branch Closures
The closure of bank branches has significant economic implications, affecting various stakeholders, including employees, customers, and local communities. Understanding these impacts is crucial for assessing the broader consequences of branch closures on the economy.
One of the most immediate effects of branch closures is the potential loss of jobs for bank employees. As branches are consolidated or closed, affected employees may face layoffs or redeployment to other roles within the organization. This can create economic challenges for individuals and their families, particularly in communities with limited employment opportunities.
For customers, branch closures can result in reduced accessibility to banking services, particularly for those who rely on in-person interactions for their financial needs. This can be a significant concern for elderly and rural customers who may have limited access to digital banking channels or internet connectivity.
Branch closures can also have ripple effects on local economies, particularly in small towns and rural areas where banks often serve as important community anchors. The departure of a bank branch can lead to reduced foot traffic and economic activity in the surrounding area, impacting local businesses and services.
Despite these challenges, it's important to recognize that branch closures can also present opportunities for banks to reallocate resources and invest in digital transformation. By embracing digital banking solutions, banks can enhance their operational efficiency, expand their reach, and better serve their customers in an increasingly digital world.
The Rise of Digital Banking
The rise of digital banking is one of the most transformative trends in the financial services industry. Over the past decade, digital banking has gained widespread adoption, reshaping how consumers access and interact with financial services.
Digital banking offers a range of benefits that have contributed to its growing popularity among consumers. Convenience is one of the most significant advantages, as digital banking allows customers to perform transactions, check account balances, pay bills, and access financial services from anywhere, at any time.
Another key benefit of digital banking is cost-effectiveness. By leveraging digital channels, banks can reduce their reliance on physical branches and achieve significant cost savings. This, in turn, allows banks to offer competitive pricing and pass on savings to their customers.
Security is also a critical aspect of digital banking. Advanced encryption and authentication technologies ensure that customer data and transactions are protected, providing peace of mind to users.
As digital banking continues to evolve, banks are investing in innovative technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain to enhance their digital offerings. These technologies enable banks to deliver personalized experiences, streamline operations, and improve risk management capabilities.
Overall, the rise of digital banking represents a fundamental shift in the banking industry, offering new opportunities and challenges for financial institutions and their customers.
How Are Customers Affected by These Closures?
The closure of bank branches can have a significant impact on customers, affecting their access to banking services and their overall experience. Understanding these effects is essential for assessing the implications of branch closures on consumers.
For customers who rely on physical branches for their banking needs, closures can result in reduced accessibility to essential services. This can be particularly challenging for elderly and rural customers who may have limited access to digital banking channels or internet connectivity.
Branch closures can also lead to longer travel distances for customers who need to visit a physical branch for transactions or consultations. This can create inconvenience and additional costs, particularly for those in remote or underserved areas.
Despite these challenges, it's important to recognize that branch closures can also present opportunities for customers to embrace digital banking solutions. By adopting online and mobile banking platforms, customers can enjoy greater convenience, flexibility, and control over their financial lives.
For banks, effectively communicating with customers and providing support during the transition to digital banking is crucial for maintaining trust and loyalty. By offering personalized assistance and resources, banks can help customers navigate the changes and ensure a seamless banking experience.
What Alternatives Are Available for Customers?
As banks continue to close branches and shift towards digital channels, customers may wonder what alternatives are available to meet their banking needs. Fortunately, there are several options that can provide convenient and accessible financial services.
One of the most popular alternatives is online banking, which allows customers to perform a wide range of transactions and manage their accounts from the comfort of their homes. Online banking platforms offer features such as bill payment, fund transfers, account management, and access to financial products and services.
Mobile banking is another convenient option, providing customers with access to banking services on their smartphones or tablets. Mobile banking apps offer similar features to online banking, with the added benefit of being accessible on the go.
For customers who prefer in-person interactions, banks may offer alternative channels such as ATMs, customer service centers, and partner networks. These options provide access to essential banking services, such as cash withdrawals, deposits, and account inquiries.
Additionally, some banks offer virtual consultations with financial advisors, allowing customers to receive personalized advice and support without visiting a physical branch.
By exploring these alternatives, customers can find the option that best meets their needs and preferences, ensuring a seamless and convenient banking experience.
Future of Physical Bank Branches
The future of physical bank branches is a topic of considerable debate in the banking industry. As digital banking continues to gain traction, the role of physical branches is evolving, prompting banks to rethink their branch strategies.
While some industry experts predict a decline in the number of physical branches, others believe that branches will continue to play a vital role in the banking ecosystem. The key challenge for banks is to strike a balance between digital innovation and maintaining a physical presence that meets the needs of their customers.
One possible future for physical branches is a shift towards more specialized and value-added services. Rather than focusing solely on routine transactions, branches could evolve into centers for financial advice, education, and personalized consultations. This approach would allow banks to differentiate themselves and strengthen customer relationships.
Another potential direction is the integration of technology within branches to enhance the customer experience. By incorporating digital tools and interactive kiosks, banks can offer a seamless blend of physical and digital services, providing customers with greater flexibility and convenience.
Ultimately, the future of physical bank branches will depend on how banks adapt to changing customer preferences and leverage technology to deliver value and innovation.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Regulatory and compliance considerations play a critical role in the banking industry, influencing decisions related to branch closures and digital transformation. Banks must navigate a complex landscape of regulations and guidelines to ensure compliance and mitigate risks.
One of the primary regulatory considerations is the requirement to provide equitable access to banking services, particularly for underserved and vulnerable populations. As banks close branches and shift towards digital channels, they must ensure that customers have access to alternative banking options and support during the transition.
Data privacy and security are also key compliance considerations, particularly in the digital banking space. Banks must implement robust security measures to protect customer data and transactions, adhering to regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA).
Additionally, banks must comply with anti-money laundering (AML) and know your customer (KYC) regulations to prevent financial crimes and ensure the integrity of the financial system.
By prioritizing regulatory compliance and adopting a proactive approach to risk management, banks can navigate the challenges of branch closures and digital transformation while maintaining trust and credibility with their customers and regulators.
Case Study: A Look at Successful Bank Transformations
To illustrate the potential for successful bank transformations in the face of branch closures and digital disruption, let's examine a case study of a bank that has effectively navigated these challenges.
XYZ Bank, a leading financial institution, faced a decline in foot traffic at its branches and increasing competition from digital-first banks. Recognizing the need for change, XYZ Bank embarked on a strategic transformation to enhance its digital capabilities and improve customer experience.
One of the key initiatives was the development of a comprehensive digital banking platform that offered a wide range of services, including online account management, mobile payments, and virtual consultations with financial advisors. This platform provided customers with a convenient and seamless banking experience, reducing the need for in-person visits to branches.
In addition to digital innovation, XYZ Bank focused on optimizing its branch network by closing underperforming locations and transforming remaining branches into centers for financial advice and education. This approach allowed the bank to differentiate itself and strengthen customer relationships.
By leveraging technology and embracing a customer-centric approach, XYZ Bank successfully navigated the challenges of branch closures and digital disruption, achieving significant growth and customer satisfaction.
How Can Banks Improve Customer Experience During Closures?
Improving customer experience during branch closures is a critical consideration for banks, as it can significantly impact customer satisfaction and loyalty. Here are some strategies that banks can employ to enhance customer experience during this transition:
- Effective Communication: Clearly communicate the reasons for branch closures and the alternatives available to customers. Provide timely updates and information through various channels, such as email, mobile apps, and social media.
- Personalized Support: Offer personalized assistance to customers who may be affected by branch closures. Provide dedicated support teams and resources to help customers navigate the changes and transition to digital banking.
- Seamless Digital Experience: Ensure that digital banking platforms are user-friendly, secure, and reliable. Invest in technology to enhance the digital banking experience and provide customers with a wide range of services and features.
- Alternative Channels: Provide alternative channels for customers who prefer in-person interactions, such as ATMs, customer service centers, and partner networks. Ensure that these channels are easily accessible and offer essential banking services.
- Education and Training: Offer educational resources and training to help customers become familiar with digital banking tools and services. Provide workshops, tutorials, and online resources to empower customers and build confidence in using digital channels.
By implementing these strategies, banks can improve customer experience during branch closures and build lasting relationships with their customers.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why are major US banks closing branches?
Major US banks are closing branches as part of a strategic decision influenced by factors such as technological advancements, changes in customer behavior, and cost reduction efforts. The shift towards digital banking has reduced the need for physical branches, prompting banks to optimize their branch networks.
How will branch closures affect customers?
Branch closures can affect customers by reducing accessibility to in-person banking services, particularly for those who rely on physical branches. However, banks are offering digital banking solutions and alternative channels to ensure customers can still access essential services.
What alternatives are available for customers affected by branch closures?
Customers affected by branch closures can access banking services through online and mobile banking platforms, ATMs, customer service centers, and partner networks. These alternatives provide convenient and accessible options for managing accounts and conducting transactions.
Will branch closures lead to job losses?
Branch closures may lead to job losses for bank employees, as affected branches are consolidated or closed. However, banks may offer redeployment opportunities within the organization or provide support for affected employees in finding new employment.
How are banks ensuring security in digital banking?
Banks are implementing advanced security measures, such as encryption, authentication, and fraud detection technologies, to protect customer data and transactions in digital banking. These measures help ensure the security and integrity of digital banking services.
What is the future of physical bank branches?
The future of physical bank branches is evolving, with a potential shift towards specialized services, such as financial advice and education. While the number of branches may decline, they will continue to play a role in providing value-added services and maintaining customer relationships.
Conclusion
The closure of 65 bank branches by major US banks within three weeks marks a significant development in the ongoing transformation of the banking industry. This decision reflects the broader trends of technological advancement, changes in customer behavior, and cost reduction efforts that are reshaping the banking landscape.
While branch closures present challenges for customers and the economy, they also offer opportunities for banks to embrace digital innovation and improve operational efficiency. By prioritizing digital transformation and enhancing customer experience, banks can navigate these changes and position themselves for success in a rapidly evolving market.
Ultimately, the future of banking will be defined by the ability of financial institutions to adapt to changing customer preferences and leverage technology to deliver value and innovation. As banks continue to evolve, they must strike a balance between digital and physical channels, ensuring that they meet the needs of their diverse customer base while maintaining trust and credibility.