Monetary policy is a critical component of any nation's economic framework. It represents the strategic approach undertaken by a country's central bank to control the money supply, influence interest rates, and achieve economic stability. Through these mechanisms, monetary policy aims to foster economic growth, manage inflation, and reduce unemployment, ultimately contributing to the overall economic health of a nation. As economies continue to evolve, the role of monetary policy becomes even more vital in navigating the complex landscape of global markets.
In the modern era, monetary policy is not just about controlling the money supply; it involves a nuanced understanding of economic indicators and their impact on society. Policymakers must be adept at interpreting data and making informed decisions to ensure financial stability. This involves a delicate balance of various tools, such as open market operations, interest rate adjustments, and reserve requirements, all of which are designed to influence economic variables like inflation and employment. The effectiveness of these tools hinges on the central bank's ability to predict and respond to economic fluctuations with precision.
As we delve into the intricacies of monetary policy, it becomes evident that its impact extends beyond mere numbers and statistics. It affects businesses, consumers, and governments alike, shaping the economic environment in which they operate. Understanding the fundamental principles of monetary policy is essential for economists, policymakers, and citizens who wish to comprehend the forces driving economic trends and developments. By exploring the various aspects of monetary policy, we can gain a deeper appreciation of its role in guiding economic stability and growth.
Read also:The Best Of Summerfield Theater In Santa Rosa
Table of Contents
- What is Monetary Policy and Why is it Important?
- A Historical Perspective on Monetary Policy
- Key Tools and Mechanisms of Monetary Policy
- The Role of Central Banks in Monetary Policy
- How Does Monetary Policy Affect the Economy?
- Monetary Policy and Its Relationship with Inflation
- Can Monetary Policy Influence Employment Rates?
- The Influence of Monetary Policy on the Global Economy
- What are the Challenges in Implementing Monetary Policy?
- The Interplay Between Monetary Policy and Financial Markets
- Monetary Policy vs. Fiscal Policy: What's the Difference?
- The Future of Monetary Policy in an Evolving World
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is Monetary Policy and Why is it Important?
Monetary policy refers to the strategic actions taken by a country's central bank to regulate its money supply, primarily through the manipulation of interest rates and other monetary tools. These actions are aimed at achieving macroeconomic objectives such as controlling inflation, managing employment levels, and fostering economic growth. The importance of monetary policy cannot be overstated, as it plays a crucial role in maintaining economic stability and ensuring the smooth functioning of financial systems.
Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States, the European Central Bank, and the Bank of England, are the primary institutions responsible for formulating and implementing monetary policy. They utilize various tools and mechanisms to influence the economy, including setting interest rates, conducting open market operations, and adjusting reserve requirements for commercial banks. By controlling these aspects, central banks aim to maintain price stability, support economic growth, and keep unemployment low.
Monetary policy is vital for several reasons. Firstly, it helps in controlling inflation, which can erode purchasing power and destabilize the economy if left unchecked. Secondly, it influences interest rates, impacting borrowing and investment decisions by businesses and individuals. Lower interest rates can stimulate economic activity by encouraging spending and investment, while higher rates may help cool down an overheating economy. Lastly, monetary policy can affect exchange rates, which in turn influences international trade and capital flows.
A Historical Perspective on Monetary Policy
The concept of monetary policy has evolved significantly over the centuries. In its earliest forms, monetary policy was primarily concerned with the issuance of currency and the maintenance of metallic standards, such as gold and silver. However, as economies grew more complex and interconnected, the scope and objectives of monetary policy expanded to include a broader range of economic indicators and goals.
One of the most significant developments in the history of monetary policy was the establishment of central banks. The Bank of England, founded in 1694, is often considered the first modern central bank, and it served as a model for other institutions around the world. Central banks were initially created to provide financial stability and act as lenders of last resort, but their roles have since expanded to include the formulation and implementation of monetary policy.
Throughout the 20th century, monetary policy underwent further transformations. The abandonment of the gold standard in the 1930s marked a shift towards a more flexible and responsive approach to monetary management. This allowed central banks to focus on domestic economic conditions rather than maintaining fixed exchange rates. The rise of Keynesian economics in the mid-20th century also influenced monetary policy, emphasizing the importance of managing aggregate demand to achieve full employment and economic growth.
Read also:Theater Mode Unlocking Secrets In Bo6
In recent decades, monetary policy has become increasingly data-driven and reliant on sophisticated economic models. Central banks now closely monitor a wide range of indicators, such as inflation rates, employment levels, and GDP growth, to inform their decisions. This data-driven approach has allowed for more targeted and effective policy interventions, ultimately contributing to greater economic stability and growth.
Key Tools and Mechanisms of Monetary Policy
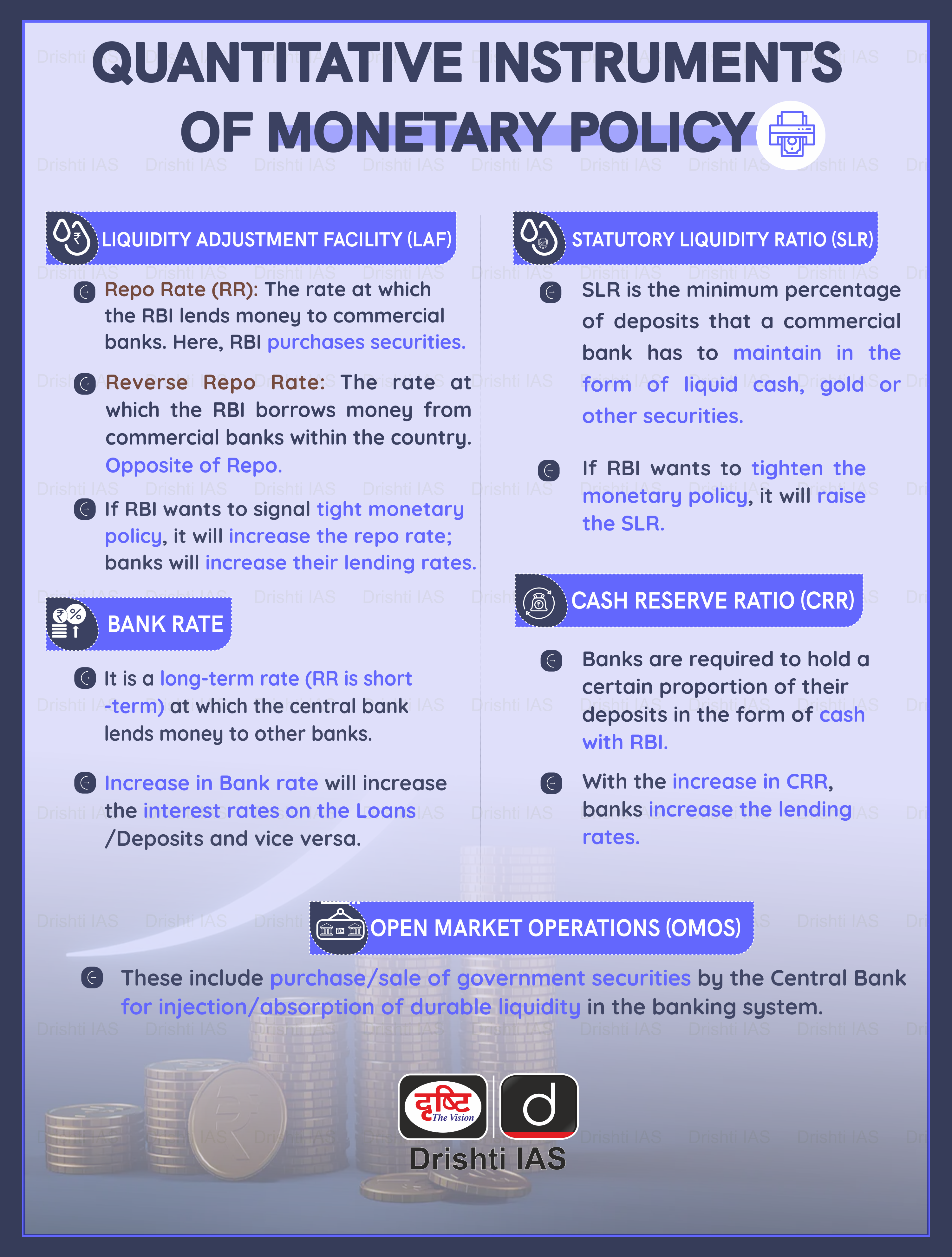
Central banks employ a variety of tools and mechanisms to implement monetary policy and achieve their macroeconomic objectives. These tools can be broadly categorized into three main types: open market operations, interest rate adjustments, and reserve requirements. Each of these tools serves a specific purpose and can be used in different combinations to influence economic variables such as inflation, employment, and economic growth.
Open Market Operations
Open market operations involve the buying and selling of government securities in the open market by the central bank. By purchasing securities, the central bank injects liquidity into the financial system, lowering interest rates and encouraging borrowing and spending. Conversely, selling securities withdraws liquidity, raising interest rates and slowing economic activity. Open market operations are a primary tool for controlling short-term interest rates and managing the money supply.
Interest Rate Adjustments
Central banks have the authority to set benchmark interest rates, such as the federal funds rate in the United States. These rates influence the cost of borrowing and the return on savings, impacting consumer and business behavior. By raising or lowering interest rates, central banks can either stimulate economic activity or cool down an overheating economy. Interest rate adjustments are a powerful tool for managing inflation and promoting economic growth.
Reserve Requirements
Reserve requirements refer to the minimum amount of reserves that commercial banks must hold against their deposits. By adjusting these requirements, central banks can influence the amount of money available for lending and investment. Lower reserve requirements increase the money supply, encouraging borrowing and spending, while higher requirements restrict the money supply, curbing excessive economic activity. Reserve requirements are an essential tool for maintaining financial stability and controlling inflation.
The Role of Central Banks in Monetary Policy
Central banks play a pivotal role in the formulation and implementation of monetary policy. As the primary institutions responsible for maintaining economic stability, they are tasked with managing the money supply, setting interest rates, and ensuring the smooth functioning of financial systems. Central banks operate independently of political influence, allowing them to make objective and data-driven decisions in the best interest of the economy.
One of the key functions of central banks is to serve as the lender of last resort. In times of financial distress, they provide emergency funding to banks and financial institutions, preventing systemic collapses and maintaining stability within the financial system. This role is crucial in times of crisis, as it helps to restore confidence and prevent widespread economic disruptions.
Central banks also play a vital role in regulating and supervising the banking sector. They establish rules and guidelines to ensure the safety and soundness of financial institutions, protecting consumers and maintaining the integrity of the financial system. Through their regulatory oversight, central banks help to prevent excessive risk-taking and promote prudent lending practices.
In addition to these functions, central banks are responsible for conducting research and analysis to inform their monetary policy decisions. They monitor a wide range of economic indicators, such as inflation rates, employment levels, and GDP growth, to assess the current state of the economy and anticipate future trends. This data-driven approach allows central banks to implement targeted and effective policy interventions, ultimately contributing to greater economic stability and growth.
How Does Monetary Policy Affect the Economy?
Monetary policy has a profound impact on the economy, influencing various aspects of economic activity, including inflation, employment, investment, and consumption. By controlling the money supply and interest rates, central banks can shape the economic environment in which businesses and consumers operate, ultimately affecting the overall health and stability of the economy.
One of the primary ways monetary policy affects the economy is through its influence on inflation. By adjusting interest rates and managing the money supply, central banks can either curb inflationary pressures or stimulate price growth, depending on the economic context. Controlling inflation is crucial for maintaining purchasing power and ensuring the long-term stability of the economy.
Monetary policy also impacts employment levels by influencing economic growth and aggregate demand. Lower interest rates can encourage borrowing and investment, leading to increased production and job creation. Conversely, higher interest rates may slow down economic activity, potentially leading to higher unemployment. By carefully managing interest rates and the money supply, central banks can promote full employment and support economic growth.
Investment and consumption are also affected by monetary policy. Lower interest rates reduce the cost of borrowing, making it more attractive for businesses and consumers to invest and spend. This can lead to increased economic activity and higher GDP growth. On the other hand, higher interest rates may discourage borrowing and spending, potentially slowing down the economy.
Exchange rates and international trade are also influenced by monetary policy. Changes in interest rates can affect capital flows and currency values, impacting the competitiveness of exports and imports. By managing exchange rates, central banks can influence trade balances and contribute to economic growth.
Monetary Policy and Its Relationship with Inflation
Inflation is a critical economic indicator that measures the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising, eroding purchasing power. Monetary policy plays a crucial role in managing inflation, as central banks use various tools and mechanisms to influence price levels and maintain stability within the economy.
One of the primary objectives of monetary policy is to achieve price stability by controlling inflation. Central banks closely monitor inflation rates and adjust interest rates and the money supply to keep inflation within a target range. By doing so, they aim to prevent excessive price increases that can destabilize the economy and reduce the purchasing power of consumers.
Interest rates are a key tool used by central banks to manage inflation. By raising interest rates, central banks can reduce borrowing and spending, slowing down economic activity and curbing inflationary pressures. Conversely, lowering interest rates can stimulate economic activity, potentially leading to higher inflation if not managed carefully.
Open market operations are another mechanism used to control inflation. By buying and selling government securities, central banks can influence the money supply and liquidity within the financial system. Increasing the money supply can stimulate economic activity and potentially lead to higher inflation, while reducing the money supply can have the opposite effect.
In addition to these tools, central banks use forward guidance and communication strategies to manage inflation expectations. By clearly communicating their policy intentions and objectives, central banks can influence the behavior of businesses and consumers, helping to anchor inflation expectations and maintain price stability.
Can Monetary Policy Influence Employment Rates?
Monetary policy can have a significant impact on employment rates, as it influences economic growth and aggregate demand. By controlling interest rates and the money supply, central banks can create an environment conducive to job creation and economic expansion.
Lower interest rates can stimulate borrowing and investment, leading to increased production and the creation of new jobs. Businesses are more likely to invest in capital projects and expand their operations when borrowing costs are low, resulting in higher demand for labor and reduced unemployment.
Conversely, higher interest rates can slow economic activity and potentially lead to higher unemployment. By making borrowing more expensive, central banks can curb excessive economic growth and prevent inflationary pressures. However, this may also result in reduced investment and job creation, potentially leading to higher unemployment.
Central banks must carefully balance their policy interventions to achieve both price stability and full employment. By monitoring a wide range of economic indicators, such as inflation rates, employment levels, and GDP growth, central banks can implement targeted and effective policy measures to support job creation and economic growth.
The Influence of Monetary Policy on the Global Economy
Monetary policy has far-reaching implications for the global economy, as central banks' decisions can impact international trade, capital flows, and exchange rates. In an increasingly interconnected world, the actions of major central banks can have significant ripple effects across borders, influencing the economic stability and growth of other nations.
Changes in interest rates and monetary policy in one country can affect exchange rates, impacting the competitiveness of exports and imports. A country's currency may appreciate or depreciate in response to shifts in monetary policy, affecting trade balances and economic growth. This can have significant implications for countries that rely heavily on international trade and exports.
Monetary policy also influences capital flows, as changes in interest rates can impact the attractiveness of investments in different countries. Higher interest rates may attract foreign capital, leading to currency appreciation and increased investment inflows. Conversely, lower interest rates may encourage capital outflows, potentially leading to currency depreciation and reduced investment.
In recent years, the coordination of monetary policy among major central banks has become increasingly important. During times of global economic uncertainty or crisis, central banks may collaborate to implement coordinated policy measures, such as interest rate cuts or liquidity injections, to stabilize financial markets and support global economic growth.
What are the Challenges in Implementing Monetary Policy?
Implementing monetary policy is a complex and challenging task, as central banks must navigate a myriad of economic variables and uncertainties to achieve their objectives. Several challenges can arise in the formulation and execution of monetary policy, requiring careful consideration and expertise from policymakers.
One of the primary challenges is the timing and magnitude of policy interventions. Central banks must accurately assess the current state of the economy and anticipate future trends to implement timely and effective policy measures. Misjudging the timing or magnitude of interventions can lead to unintended consequences, such as excessive inflation or economic stagnation.
Another challenge is the uncertainty and unpredictability of economic conditions. External factors, such as geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, or global economic shifts, can impact the effectiveness of monetary policy and complicate decision-making processes. Central banks must remain adaptable and responsive to changing circumstances to maintain economic stability.
Communication and transparency are also critical challenges in monetary policy implementation. Central banks must effectively communicate their policy intentions and objectives to manage expectations and influence the behavior of businesses and consumers. Clear and transparent communication can help anchor inflation expectations and support the credibility of monetary policy.
In addition to these challenges, central banks must balance competing objectives, such as price stability and full employment. Achieving these goals often requires trade-offs and careful consideration of the potential impacts on various sectors of the economy.
The Interplay Between Monetary Policy and Financial Markets
Monetary policy and financial markets are closely intertwined, as central banks' decisions can significantly impact market behavior, asset prices, and investment flows. Understanding the interplay between monetary policy and financial markets is crucial for policymakers, investors, and market participants.
Interest rate decisions are one of the primary ways monetary policy influences financial markets. Changes in benchmark interest rates can affect the cost of borrowing and the return on investments, impacting the behavior of businesses, consumers, and investors. Lower interest rates can lead to increased borrowing and investment, driving asset prices higher, while higher rates may have the opposite effect.
Monetary policy also affects financial markets through its impact on liquidity and money supply. Central banks' open market operations can influence the availability of credit and liquidity within the financial system, affecting market conditions and asset valuations. Increased liquidity can lead to higher market activity and asset prices, while reduced liquidity may result in tighter market conditions and lower valuations.
Expectations and forward guidance are also critical components of the relationship between monetary policy and financial markets. Central banks' communication strategies can influence market expectations and behavior, impacting asset prices and investment decisions. Clear and transparent communication can help stabilize financial markets and support the effectiveness of monetary policy.
Monetary Policy vs. Fiscal Policy: What's the Difference?
Monetary policy and fiscal policy are two distinct but complementary tools used by governments and central banks to manage the economy. While both aim to achieve macroeconomic objectives such as economic growth, full employment, and price stability, they differ in their mechanisms and implementation.
Monetary policy is primarily concerned with managing the money supply and interest rates to influence economic activity. It is typically implemented by central banks, which use tools such as open market operations, interest rate adjustments, and reserve requirements to control inflation, stimulate growth, and maintain financial stability.
Fiscal policy, on the other hand, involves government decisions on taxation and public spending to influence economic activity. It is implemented by the government through changes in tax rates, government spending, and public investment. Fiscal policy aims to stimulate demand, redistribute income, and promote economic development.
While monetary policy focuses on the financial sector and money supply, fiscal policy directly impacts government budgets and public finances. The two policies can complement each other in achieving macroeconomic objectives, with fiscal policy providing direct support to specific sectors and monetary policy influencing the broader economic environment.
The Future of Monetary Policy in an Evolving World
The future of monetary policy is shaped by a rapidly changing economic landscape, characterized by technological advancements, globalization, and evolving economic challenges. As central banks navigate these changes, they must adapt their strategies and tools to effectively manage the economy and maintain stability.
One of the key trends shaping the future of monetary policy is the increasing use of digital currencies and financial technologies. Central banks are exploring the potential of digital currencies, such as central bank digital currencies (CBDCs), to enhance monetary policy effectiveness and financial inclusion. The integration of technology into monetary policy decision-making is expected to improve data analysis and policy implementation.
Another trend is the growing importance of addressing climate change and sustainability within the context of monetary policy. Central banks are recognizing the impact of climate-related risks on financial stability and are exploring ways to incorporate sustainability considerations into their policy frameworks. This may involve supporting green investments and promoting sustainable economic growth.
Globalization and interconnectedness will continue to influence monetary policy, as central banks must consider the impact of international economic developments on domestic economies. Coordinated policy measures and collaboration among central banks will become increasingly important in addressing global economic challenges and ensuring stability.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary goal of monetary policy?
The primary goal of monetary policy is to achieve macroeconomic objectives such as controlling inflation, maintaining financial stability, supporting economic growth, and promoting full employment.
How do central banks control inflation?
Central banks control inflation by adjusting interest rates, conducting open market operations, and managing the money supply to influence price levels and maintain stability within the economy.
What is the role of interest rates in monetary policy?
Interest rates are a key tool used by central banks to influence borrowing, spending, and investment behavior. By raising or lowering interest rates, central banks can either stimulate economic activity or cool down an overheating economy.
How does monetary policy impact employment?
Monetary policy can impact employment by influencing economic growth and aggregate demand. Lower interest rates can stimulate borrowing and investment, leading to increased job creation, while higher rates may slow down economic activity and potentially lead to higher unemployment.
What are the challenges in implementing monetary policy?
Challenges in implementing monetary policy include timing and magnitude of interventions, economic uncertainty, communication and transparency, and balancing competing objectives such as price stability and full employment.
How do central banks use forward guidance?
Central banks use forward guidance to communicate their policy intentions and objectives to influence market expectations and behavior, helping to stabilize financial markets and support the effectiveness of monetary policy.
Conclusion
Monetary policy serves as a guiding force in modern economics, playing an essential role in maintaining economic stability and supporting growth. Through the use of various tools and mechanisms, central banks influence key economic variables such as inflation, employment, and investment, shaping the environment in which businesses and consumers operate. As the global economy continues to evolve, the importance of effective and adaptive monetary policy becomes increasingly evident. By understanding the principles and challenges of monetary policy, we can appreciate its impact on our everyday lives and the broader economic landscape.