When it comes to the South Pacific, few places capture the imagination quite like Samoa and American Samoa. These two enchanting island groups, located in the heart of Polynesia, offer a unique blend of culture, history, and natural beauty. Despite their geographical proximity, Samoa and American Samoa are distinct in many ways, from their governance and languages to their customs and traditions. Understanding the differences and similarities between Samoa vs American Samoa is essential for anyone interested in exploring this captivating region.
As you delve into the nuances of Samoa vs American Samoa, you'll discover a rich tapestry of shared heritage alongside contrasting colonial histories. Samoa, officially known as the Independent State of Samoa, gained independence from New Zealand in 1962 and has since developed its own national identity. On the other hand, American Samoa remains an unincorporated territory of the United States, influenced by American culture while preserving its indigenous roots. This article aims to provide an insightful comparison of these two fascinating destinations.
Beyond the political and cultural distinctions, Samoa and American Samoa each offer unique landscapes and ecosystems. From lush rainforests and volcanic mountains to pristine beaches and coral reefs, these islands boast extraordinary biodiversity. Whether you're planning a visit or simply curious about the region, understanding the key differences in Samoa vs American Samoa will enrich your appreciation of their individual charm and significance.
Read also:Ultimate Guide To Lexus Of Wilmington Excellence In Luxury And Service
Table of Contents
- History and Colonial Background
- Geographical Features
- Political Structure and Governance
- Language and Communication
- Cultural Heritage and Traditions
- Economic Activities and Industries
- Tourism and Attractions
- Samoa vs American Samoa: Which to Visit?
- Environmental Conservation Efforts
- Education and Healthcare Systems
- Transportation and Infrastructure
- Festivals and Celebrations
- Samoa vs American Samoa in Popular Culture
- FAQs About Samoa vs American Samoa
- Conclusion
History and Colonial Background
The history of Samoa and American Samoa is deeply intertwined, yet each has followed a unique path. Both island groups were originally settled by Polynesians, with evidence pointing to human habitation dating back over 3,000 years. The islands were first encountered by European explorers in the 18th century, marking the beginning of significant external influence.
In the late 19th century, the Samoan Islands became the focal point of colonial ambitions, with Germany, the United States, and Great Britain vying for control. This resulted in the partitioning of the islands in 1899. Western Samoa, now known simply as Samoa, was placed under German control while American Samoa came under the jurisdiction of the United States.
Following World War I, Germany's hold on Samoa was relinquished, and the islands were administered by New Zealand until they gained independence in 1962. In contrast, American Samoa has remained a U.S. territory, benefiting from American governance and support.
Geographical Features
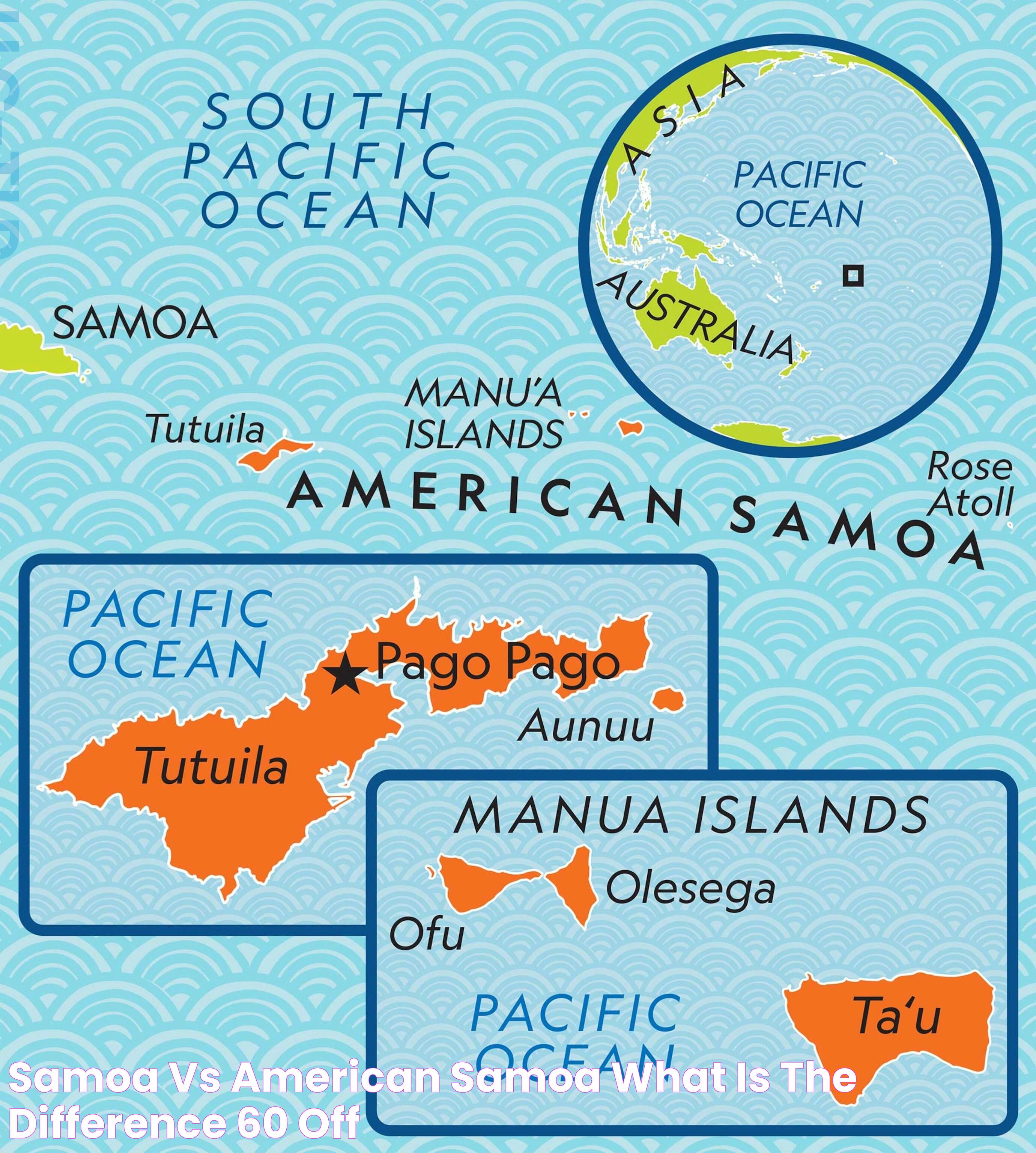
Samoa and American Samoa are located in the central South Pacific Ocean, approximately halfway between Hawaii and New Zealand. The islands are part of the larger Polynesian cultural region and share similar tropical climates.
Samoa comprises two main islands, Upolu and Savai'i, along with several smaller islands. The landscape is characterized by volcanic mountains, lush rainforests, and picturesque coastlines. The highest peak, Mount Silisili, rises to over 1,800 meters on Savai'i.
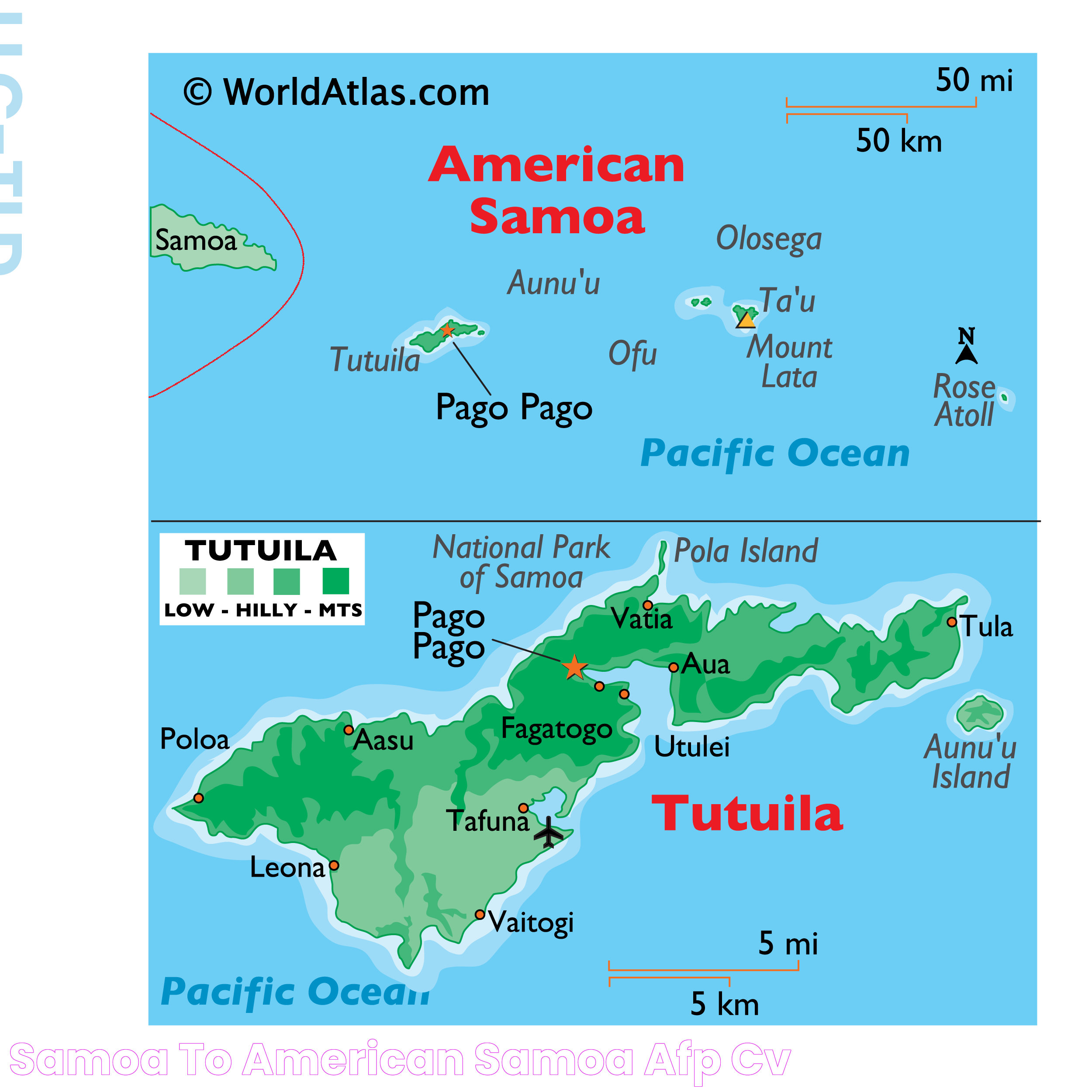
American Samoa consists of five main islands: Tutuila, Aunu'u, Ofu, Olosega, and Ta'u, as well as two coral atolls. The islands are known for their dramatic cliffs, secluded beaches, and vibrant coral reefs. The National Park of American Samoa, located on Tutuila, offers breathtaking natural beauty and diverse wildlife.
Read also:Essential Guide To La County Property Tax Everything You Need To Know
Political Structure and Governance
Samoa operates as an independent parliamentary democracy, with a head of state and a prime minister leading the government. The Samoan political system is deeply rooted in traditional customs, with the matai (chiefs) playing a significant role in governance.
American Samoa, as a U.S. territory, has a different political structure. It is governed by an elected governor and a territorial legislature, but U.S. federal law applies to the islands. While American Samoans are U.S. nationals, they do not have the same voting rights as U.S. citizens.
Language and Communication
The official languages of Samoa are Samoan and English. Samoan is widely spoken and is an integral part of the country's cultural identity. English is used in government, education, and business settings.
In American Samoa, Samoan and English are also the official languages. The prevalence of English reflects the territory's close ties to the United States, although Samoan remains a vital part of daily life.
Cultural Heritage and Traditions
Samoa and American Samoa share a rich cultural heritage, deeply rooted in Polynesian traditions. The Fa'a Samoa, or "the Samoan way," emphasizes community, respect, and family. Traditional ceremonies, dances, and music are important aspects of both societies.
While the cultural foundations are similar, American Samoa has been influenced by American culture, resulting in a unique blend of Polynesian and Western elements. This is evident in various aspects of life, including food, sports, and entertainment.
Economic Activities and Industries
The economies of Samoa and American Samoa are shaped by their geographical isolation and limited natural resources. Agriculture, fishing, and tourism are key sectors in both regions.
In Samoa, agriculture is the backbone of the economy, with copra, taro, and bananas as primary exports. The country has also developed a growing tourism industry, attracting visitors with its natural beauty and cultural experiences.
American Samoa's economy is heavily reliant on the tuna fishing and processing industry, which is a major employer on the islands. The territory also benefits from U.S. federal subsidies and aid, contributing to its economic stability.
Tourism and Attractions
Tourism is a vital industry for both Samoa and American Samoa, offering visitors a chance to experience the islands' stunning landscapes and vibrant cultures.
- Samoa Attractions:
- Upolu Island: Known for its beautiful beaches, waterfalls, and cultural villages.
- Savai'i Island: Offers volcanic landscapes, traditional villages, and pristine rainforests.
- To Sua Ocean Trench: A natural swimming hole surrounded by lush gardens.
- American Samoa Attractions:
- National Park of American Samoa: Features diverse ecosystems, hiking trails, and cultural sites.
- Pago Pago: The capital city with a scenic harbor and vibrant markets.
- Ofu Beach: Renowned for its crystal-clear waters and coral reefs.
Samoa vs American Samoa: Which to Visit?
When deciding between Samoa and American Samoa as a travel destination, several factors come into play. Both offer unique experiences, and the choice largely depends on personal preferences and interests.
Samoa: Ideal for those seeking a blend of cultural immersion and natural beauty. Visitors can explore traditional villages, participate in cultural ceremonies, and enjoy the island's stunning beaches and waterfalls.
American Samoa: Perfect for travelers interested in hiking, wildlife, and exploring American Polynesian culture. The National Park of American Samoa offers unparalleled opportunities to experience the islands' natural wonders.
Ultimately, both destinations provide a unique glimpse into Polynesian culture and natural beauty, making them worthwhile choices for any traveler.
Environmental Conservation Efforts
Both Samoa and American Samoa have taken steps to protect their natural environments and promote sustainable development. Conservation efforts are vital to preserving the islands' unique ecosystems and biodiversity.
In Samoa, initiatives focus on reforestation, marine conservation, and sustainable tourism. Community involvement plays a significant role in these efforts, with local organizations working to educate the public and promote eco-friendly practices.
American Samoa's conservation efforts are supported by the U.S. National Park Service, which manages the National Park of American Samoa. The park is dedicated to preserving the islands' natural habitats and cultural heritage, offering educational programs and research opportunities.
Education and Healthcare Systems
Education and healthcare systems in Samoa and American Samoa reflect their unique political and cultural contexts.
Samoa: Education is a priority, with free primary education provided by the government. The country has made significant strides in improving literacy rates and access to education, although challenges remain in rural areas.
Healthcare in Samoa is primarily government-funded, with a focus on primary care and preventive services. The country faces challenges related to non-communicable diseases and access to specialized medical care.
American Samoa: The education system follows the U.S. model, with public and private schools offering K-12 education. American Samoa Community College provides higher education opportunities for residents.
Healthcare services in American Samoa are supported by U.S. federal funding, with the Lyndon B. Johnson Tropical Medical Center serving as the main hospital. The territory also faces healthcare challenges, including limited access to specialized services.
Transportation and Infrastructure
Transportation and infrastructure in Samoa and American Samoa are influenced by their geographical isolation and limited resources.
Samoa: The country has a network of roads connecting major towns and villages, with public buses and taxis providing transportation options. The main international airport is Faleolo International Airport, located near the capital, Apia.
Infrastructure development is ongoing, with a focus on improving road conditions, expanding telecommunications, and increasing access to clean water and electricity.
American Samoa: Transportation options include buses, taxis, and private vehicles, with a network of roads connecting key areas. The territory is served by Pago Pago International Airport, offering flights to neighboring islands and the U.S. mainland.
Infrastructure improvements in American Samoa focus on enhancing transportation networks, upgrading utilities, and expanding internet access.
Festivals and Celebrations
Festivals and celebrations in Samoa and American Samoa showcase the islands' rich cultural heritage and community spirit. These events offer visitors a chance to experience traditional music, dance, and cuisine.
- Samoa Festivals:
- Teuila Festival: A week-long celebration held in September, featuring cultural performances, sports competitions, and traditional crafts.
- Independence Day: Celebrated on June 1st, marking Samoa's independence with parades, speeches, and cultural events.
- American Samoa Festivals:
- Flag Day: Celebrated on April 17th, commemorating the day American Samoa became a U.S. territory with cultural displays, sports events, and community gatherings.
- Fautasi Races: Traditional longboat races held during major festivals, showcasing teamwork and skill.
Samoa vs American Samoa in Popular Culture
Samoa and American Samoa have made their mark on popular culture, with influences seen in music, film, and sports. The islands' vibrant traditions and unique landscapes have inspired artists and creators worldwide.
Samoan culture is celebrated through traditional music and dance, with groups such as the Te Vaka music ensemble gaining international recognition. The islands' landscapes have been featured in films, including "The Other Side of Heaven," which highlights the beauty of Polynesia.
American Samoa has produced notable athletes, particularly in American football, with several NFL players hailing from the territory. The islands' unique blend of Polynesian and American influences has also been depicted in film and television, showcasing the diverse cultural tapestry of the region.
FAQs About Samoa vs American Samoa
- What are the main differences between Samoa and American Samoa? Samoa is an independent nation with its own government, while American Samoa is a U.S. territory. They have distinct political structures, but both share a common Polynesian heritage.
- Which language is spoken in Samoa and American Samoa? Both Samoa and American Samoa have Samoan and English as their official languages.
- Is it easy to travel between Samoa and American Samoa? Yes, there are regular flights and ferry services connecting the two regions, making travel relatively easy.
- What cultural similarities do Samoa and American Samoa share? Both regions share Polynesian traditions, including the Fa'a Samoa cultural practices, traditional music, and dance.
- Are there any unique attractions in American Samoa? Yes, the National Park of American Samoa offers unique hiking trails, diverse ecosystems, and cultural experiences.
- Can I use U.S. dollars in Samoa? No, Samoa uses its own currency, the Samoan tala, while American Samoa uses the U.S. dollar.
Conclusion
Samoa and American Samoa, though geographically close, offer distinct experiences shaped by their unique histories and cultural influences. Both regions boast breathtaking landscapes, rich traditions, and welcoming communities, making them exceptional destinations for travelers and cultural enthusiasts alike. Whether you're drawn to Samoa's independent spirit and cultural immersion or American Samoa's blend of Polynesian and American influences, each offers a captivating journey into the heart of Polynesia.
For more information on visiting these beautiful islands, consider exploring travel guides, local websites, and official tourism resources to plan your adventure. With careful planning and an open heart, you're sure to create unforgettable memories in the enchanting realms of Samoa and American Samoa.
For further reading and exploration, you can visit Lonely Planet's Guide to Samoa for in-depth travel insights and recommendations.