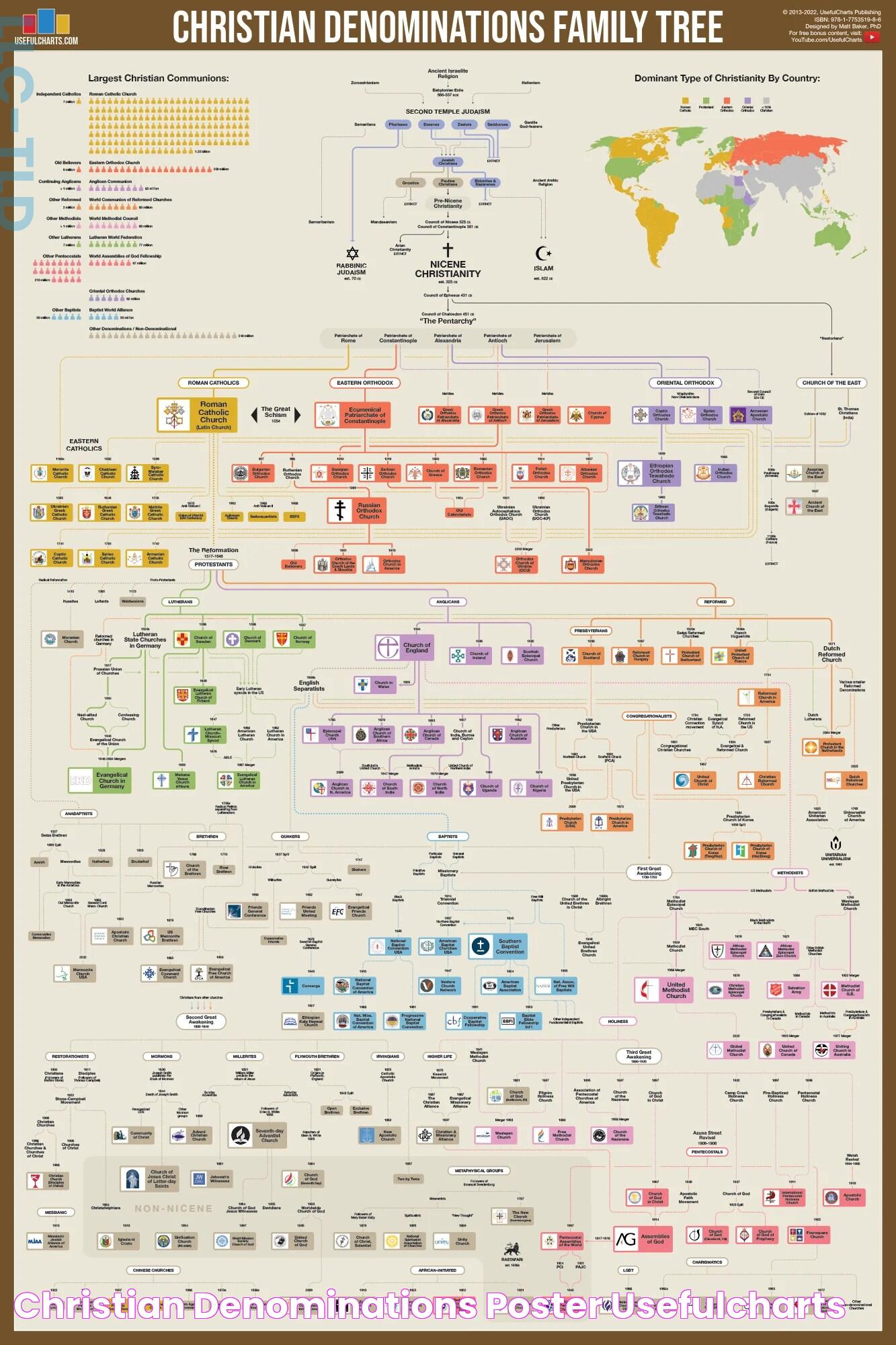
Christian denominations represent a diverse tapestry of beliefs, practices, and traditions within Christianity, highlighting the faith's rich history and global reach. With over two billion followers worldwide, Christianity is the world's largest religion, yet it is far from monolithic. The various denominations within Christianity reflect centuries of theological debates, cultural influences, and historical developments, each contributing a unique voice to the broader Christian narrative. Understanding the distinctions and commonalities among these groups can provide insights into their beliefs, rituals, and roles within society.
At its core, Christianity is centered on the teachings of Jesus Christ, but interpretations of these teachings have led to the formation of numerous denominations. Each denomination often emphasizes different aspects of faith, worship, and governance, resulting in a wide array of practices and doctrines. This diversity can be both a source of strength and a challenge, as denominations strive to maintain their distinct identities while also seeking unity with other Christians. The interactions among these groups can offer lessons in tolerance, cooperation, and respect for differing perspectives.
The exploration of Christian denominations is not only an academic endeavor but also a journey into the heart of what it means to be Christian. It invites believers and non-believers alike to appreciate the complexities and beauty inherent in this faith tradition. By examining the historical roots and contemporary expressions of various denominations, one can gain a deeper appreciation for the ways in which Christians around the world live out their faith. This article aims to illuminate the fascinating world of Christian denominations, offering a comprehensive overview of their origins, beliefs, and practices.
Read also:Ultimate Guide To D A G E Everything You Need To Know
Table of Contents
- The Origins of Christian Denominations
- How Do Christian Denominations Differ?
- The Role of Doctrinal Differences
- What Are the Major Christian Denominations?
- Catholicism: The Largest Christian Denomination
- Orthodox Christianity: Preserving Ancient Traditions
- Protestantism: The Reformation and Its Impact
- Anglicanism: A Middle Way
- Lutheranism: Faith and Grace
- How Has Denominationalism Influenced Global Christianity?
- Baptist Traditions: Emphasizing Individual Belief
- Methodism: A Legacy of Social Justice
- Presbyterianism: Governance and Theology
- What Challenges Do Christian Denominations Face Today?
- Interdenominational Movements and Ecumenism
- FAQs
- Conclusion
The Origins of Christian Denominations
The origins of Christian denominations date back to the earliest days of the Christian church. Initially, Christianity was seen as a sect within Judaism, but it quickly began to establish its identity. The early church was marked by a diversity of beliefs and practices, which eventually led to the formation of distinct groups. Theological disagreements, cultural contexts, and geographical separations all contributed to this process.
One of the first major divisions occurred in 1054 AD, known as the Great Schism, which split Christianity into Western (Roman Catholic) and Eastern (Orthodox) branches. This division was primarily due to disagreements over theological issues, such as the authority of the Pope and the nature of the Holy Spirit. The schism marked a significant turning point in the history of Christianity and set the stage for future denominational splits.
The Protestant Reformation in the 16th century was another pivotal moment in the history of Christian denominations. Sparked by figures like Martin Luther and John Calvin, the Reformation challenged the authority of the Catholic Church and led to the emergence of Protestant denominations. These new groups emphasized the authority of Scripture, the priesthood of all believers, and salvation by faith alone. The Reformation gave rise to a multitude of Protestant churches, each with its own distinct beliefs and practices.
How Do Christian Denominations Differ?
Christian denominations differ in various ways, including theology, liturgy, governance, and cultural expressions. Theology is perhaps the most significant area of difference, as it influences a denomination's beliefs about God, Jesus, salvation, and other core doctrines. For instance, denominations may have differing views on the nature of the Trinity, the role of the sacraments, and the interpretation of Scripture.
Liturgy, or the way worship is conducted, also varies among denominations. Some groups, like Catholics and Orthodox Christians, have highly structured liturgies with set prayers and rituals, while others, such as Baptists and Pentecostals, may have more informal and spontaneous services. These differences in worship style reflect broader theological and cultural distinctions within Christianity.
Governance is another area where Christian denominations differ. Some churches, like the Catholic Church, have a hierarchical structure with a centralized authority, while others, like many Protestant denominations, have a more decentralized or congregational form of governance. These organizational structures can impact everything from decision-making processes to the role of clergy and laity within the church.
Read also:Garage Clothing Near Me Your Ultimate Guide To Trendy And Affordable Fashion
The Role of Doctrinal Differences
Doctrinal differences play a crucial role in shaping Christian denominations. These differences often arise from varying interpretations of Scripture and theological traditions. For example, some denominations may emphasize the doctrine of predestination, while others focus on free will. These theological distinctions can lead to different understandings of salvation, grace, and the Christian life.
Denominations also differ in their views on social and moral issues, such as marriage, gender roles, and social justice. These differences can reflect broader cultural and historical influences and often shape a denomination's identity and mission. Despite these differences, many denominations share common beliefs, such as the divinity of Jesus, the importance of love and compassion, and the call to serve others.
What Are the Major Christian Denominations?
The major Christian denominations include Catholicism, Orthodoxy, and Protestantism, each with its own distinct beliefs and practices. Within these broad categories, there are numerous sub-denominations, each with its own unique identity.
Catholicism: The Largest Christian Denomination
Catholicism is the largest Christian denomination, with over a billion adherents worldwide. The Catholic Church is characterized by its hierarchical structure, with the Pope as its spiritual leader. Catholics place a strong emphasis on the sacraments, particularly the Eucharist, and the authority of tradition alongside Scripture.
The Catholic Church has a rich history and a significant cultural and social impact around the world. It has been influential in areas such as education, healthcare, and social justice. The Church's teachings on issues like marriage, family, and morality continue to shape the lives of millions of people.
Orthodox Christianity: Preserving Ancient Traditions
Orthodox Christianity, also known as Eastern Orthodoxy, is one of the oldest branches of Christianity. It is characterized by its emphasis on preserving ancient traditions and liturgical practices. The Orthodox Church is organized into autocephalous (self-governing) churches, each led by a bishop or patriarch.
Orthodox Christians place a strong emphasis on the sacraments, particularly baptism, chrismation, and the Eucharist. The liturgy is central to Orthodox worship, with its rich symbolism and use of icons. The Orthodox Church has a rich theological tradition, with a focus on the teachings of the Church Fathers and the mystical aspects of faith.
Protestantism: The Reformation and Its Impact
Protestantism emerged in the 16th century as a result of the Reformation, a movement that sought to reform the Catholic Church. Protestant denominations are characterized by their emphasis on the authority of Scripture, the priesthood of all believers, and salvation by faith alone.
There are numerous Protestant denominations, each with its own distinct beliefs and practices. Some of the most prominent include Lutheranism, Anglicanism, and the Reformed tradition. Protestantism has had a significant impact on the development of Western culture and society, influencing areas such as education, politics, and the arts.
Anglicanism: A Middle Way
Anglicanism, also known as the Church of England, is a Protestant denomination that emerged during the English Reformation. It is characterized by its attempt to find a middle way between Catholicism and Protestantism, incorporating elements of both traditions.
Anglicans place a strong emphasis on the Book of Common Prayer and the sacraments, particularly baptism and the Eucharist. The Anglican Church is organized into provinces, each led by an archbishop or bishop. Anglicans value the via media, or middle way, which seeks to balance tradition and reform.
Lutheranism: Faith and Grace
Lutheranism is a Protestant denomination that traces its origins to the teachings of Martin Luther, a key figure in the Reformation. Lutherans emphasize the authority of Scripture, salvation by faith alone, and the importance of grace.
The Lutheran Church is organized into synods or associations, each with its own governance structure. Lutherans place a strong emphasis on preaching and the sacraments, particularly baptism and the Eucharist. The Lutheran tradition has a rich theological heritage, with a focus on the teachings of Luther and other reformers.
How Has Denominationalism Influenced Global Christianity?
Denominationalism has played a significant role in shaping global Christianity, influencing the spread of the faith and its cultural expressions. The diversity of denominations has contributed to the adaptability and resilience of Christianity, allowing it to thrive in a wide range of cultural and social contexts.
Denominations have also played a role in the missionary movement, spreading Christianity to new regions and cultures. The emphasis on evangelism and outreach has led to the growth of Christianity in areas such as Africa, Asia, and Latin America, where new expressions of faith have emerged.
However, denominationalism has also posed challenges, such as divisions and conflicts within the Christian community. The search for unity and cooperation among denominations has led to the rise of interdenominational movements and ecumenism, which seek to promote dialogue and collaboration among Christians.
Baptist Traditions: Emphasizing Individual Belief
Baptist traditions are a group of Protestant denominations characterized by their emphasis on individual belief and the autonomy of the local congregation. Baptists place a strong emphasis on believer's baptism, the authority of Scripture, and the separation of church and state.
The Baptist Church is organized into local congregations, each with its own governance structure. Baptists value religious liberty and the right of individuals to interpret Scripture for themselves. The Baptist tradition has a rich history of social engagement and advocacy for human rights.
Methodism: A Legacy of Social Justice
Methodism is a Protestant denomination that emerged in the 18th century as a revival movement within the Church of England. Methodists emphasize personal holiness, social justice, and the importance of community.
The Methodist Church is organized into conferences or associations, each with its own governance structure. Methodists place a strong emphasis on the teachings of John Wesley, the founder of Methodism, and the importance of living a life of faith and service. The Methodist tradition has a rich history of social activism and engagement with issues such as poverty, education, and healthcare.
Presbyterianism: Governance and Theology
Presbyterianism is a Protestant denomination characterized by its distinctive system of governance and theology. Presbyterians emphasize the authority of Scripture, the sovereignty of God, and the importance of covenant community.
The Presbyterian Church is organized into presbyteries or synods, each with its own governance structure. Presbyterians value the role of elders and the importance of shared leadership within the church. The Presbyterian tradition has a rich theological heritage, with a focus on the teachings of John Calvin and other reformers.
What Challenges Do Christian Denominations Face Today?
Christian denominations face a range of challenges in the contemporary world, including issues related to identity, membership, and social engagement. The diversity of denominations can lead to divisions and conflicts within the Christian community, as groups struggle to balance their distinct identities with a desire for unity.
Denominations also face challenges related to declining membership and participation, particularly in Western countries. Many churches are grappling with questions about how to engage younger generations and adapt to changing cultural and social contexts.
Additionally, denominations are increasingly called to address social and ethical issues, such as climate change, social justice, and human rights. These challenges require churches to navigate complex and often contentious issues while remaining faithful to their beliefs and values.
Interdenominational Movements and Ecumenism
Interdenominational movements and ecumenism have emerged as important responses to the challenges facing Christian denominations. These movements seek to promote dialogue, cooperation, and unity among Christians of different traditions.
Ecumenism emphasizes the importance of understanding and respecting differences while seeking common ground and shared mission. Interdenominational initiatives often focus on areas such as social justice, education, and mission, where Christians can work together for the common good.
These movements represent a hopeful vision for the future of Christianity, where diversity is celebrated and unity is pursued. By fostering dialogue and collaboration, interdenominational movements and ecumenism offer a path forward for Christian denominations in a complex and changing world.
FAQs
What is the difference between a denomination and a sect?
A denomination is a recognized branch within a larger religion, characterized by distinct beliefs, practices, and organizational structures. A sect, on the other hand, often refers to a smaller, more radical group that has broken away from a larger religious tradition, usually with more extreme beliefs or practices.
How many Christian denominations are there?
There are thousands of Christian denominations worldwide, ranging from large, well-known groups like Catholicism and Protestantism to smaller, independent churches. The exact number varies, as new denominations and movements continue to emerge.
Are all Christian denominations recognized as legitimate?
Recognition of legitimacy varies among Christian denominations. While most denominations recognize each other as part of the broader Christian community, some may have specific theological or doctrinal disagreements that affect their recognition of other groups.
Do all Christian denominations use the same Bible?
While all Christian denominations use the Bible as their sacred text, there are variations in the versions and translations used. For example, Catholic and Orthodox Christians include additional books, known as the Deuterocanonical books, in their Bibles, which are not present in most Protestant versions.
Can individuals switch denominations?
Yes, individuals can switch denominations, often after careful consideration and exploration of their beliefs. This process may involve joining a new church, participating in its rituals, and aligning with its teachings and practices.
What role does interfaith dialogue play in Christian denominations?
Interfaith dialogue plays an essential role in fostering understanding and cooperation among different religious traditions, including Christian denominations. It emphasizes respect for diverse beliefs and promotes peaceful coexistence and collaboration on shared values and concerns.
Conclusion
The rich tapestry of Christian denominations reflects the diversity and complexity of the Christian faith. Each denomination contributes its unique perspective and practices, enriching the broader Christian community. While differences exist, there is also a shared commitment to the core teachings of Jesus Christ and a desire to live out the faith in meaningful ways.
As Christian denominations navigate the challenges and opportunities of the modern world, they have the potential to offer valuable insights into issues such as tolerance, unity, and social justice. By embracing their diversity and seeking common ground, denominations can work together to address the pressing issues facing the world today.
Ultimately, the exploration of Christian denominations invites believers and non-believers alike to appreciate the beauty and complexity of this faith tradition. It encourages a deeper understanding of the ways in which Christians around the world live out their beliefs, offering a glimpse into the rich and diverse tapestry of Christianity.