The question of "when did Islam start" is not just a matter of historical curiosity, but a journey into the heart of a cultural and religious revolution that transformed the world. Islam, one of the world's major religions, began in the 7th century, specifically around 610 CE, in the Arabian Peninsula. Its emergence marked the beginning of a new era, characterized by profound spiritual, social, and political changes that continue to influence millions of lives today.
At its core, Islam was founded on the revelations received by the Prophet Muhammad, a respected merchant and spiritual figure from the powerful Quraysh tribe in Mecca. These revelations, believed to be from Allah (God) through the Angel Gabriel, were compiled into the Quran, Islam's holy book. The message of Islam, which emphasizes monotheism and submission to the will of Allah, quickly spread across the Arabian Peninsula and beyond, leading to the establishment of a vast Islamic empire.
Understanding the origins of Islam is essential for appreciating its rich history and the profound impact it has had on global civilization. From the initial revelation to the growth of the Islamic community, and the spread of Islamic teachings, the story of Islam is one of transformation and enduring influence. In this article, we will delve into the key events, figures, and teachings that shaped the early Islamic world and explore its lasting legacy on culture, politics, and society.
Read also:Best Korean Restaurant Bellevue A Food Lovers Guide To Authentic Korean Cuisine
Table of Contents
- Biography of Prophet Muhammad
- The Pre-Islamic Arabian Peninsula
- When Did Islam Start?
- The Revelations and The Quran
- The Spread of Islam
- The Rise of the Caliphate
- The Golden Age of Islam
- Islamic Law and Its Impact
- Cultural Contributions of Islam
- How Did Islam Influence Other Cultures?
- Modern Day Islam
- Islam and Global Politics
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Biography of Prophet Muhammad
The Prophet Muhammad was born in 570 CE in the city of Mecca, in present-day Saudi Arabia. He was a member of the Quraysh tribe, which was a prominent and influential group in the region. Orphaned at a young age, Muhammad was raised by his grandfather and later by his uncle. Despite the challenges of his early life, Muhammad grew into a respected merchant known for his integrity and honesty, earning him the nickname "Al-Amin," meaning "the trustworthy."
At the age of 25, Muhammad married Khadijah, a wealthy widow who was impressed by his character and business acumen. This marriage provided him with financial stability and social standing, allowing him to focus on his spiritual pursuits. Muhammad frequently withdrew to a cave on Mount Hira to meditate and reflect, seeking answers to the moral and spiritual questions that troubled him about his society.
| Personal Details | Information |
|---|---|
| Full Name | Muhammad ibn Abdullah |
| Birth Year | 570 CE |
| Birthplace | Mecca, Arabian Peninsula |
| Spouse | Khadijah bint Khuwaylid |
| Known For | Proclaiming the message of Islam |
In 610 CE, during one of these retreats, Muhammad received his first revelation from the Angel Gabriel. This marked the beginning of his mission to spread the message of Islam, which emphasized monotheism, social justice, and the importance of following God's guidance. Over the next 23 years, Muhammad continued to receive revelations, which were later compiled into the Quran.
The Pre-Islamic Arabian Peninsula
Before the advent of Islam, the Arabian Peninsula was a region characterized by a diverse mix of cultures, languages, and religions. The inhabitants were primarily tribal, with a strong emphasis on family and clan loyalty. The social structure was patriarchal, with tribal leaders holding significant power and influence over their communities.
Religiously, the region was predominantly polytheistic, with many tribes worshiping multiple deities. The Kaaba in Mecca was a central religious site, housing numerous idols and attracting pilgrims from across the Arabian Peninsula. However, there were also small communities of Christians, Jews, and other monotheistic groups living in the region, contributing to the religious diversity of pre-Islamic Arabia.
- Trade and commerce were vital to the economy, with Mecca serving as a key trading hub due to its strategic location along the caravan routes.
- Poetry and oral tradition played a significant role in preserving the history and culture of the Arabian tribes.
- Social issues, such as tribal warfare, poverty, and the marginalization of women and the poor, were prevalent.
In this context, the message of Islam provided a unifying force, offering a vision of social justice, equality, and spiritual guidance that appealed to many across the Arabian Peninsula.
Read also:Top Reasons To Visit Burbank California A Vibrant City To Explore
When Did Islam Start?
The origins of Islam trace back to the early 7th century in the Arabian Peninsula, specifically around 610 CE. This pivotal moment in history occurred when the Prophet Muhammad, while meditating in the cave of Hira near Mecca, received his first revelation. This event marked the beginning of Islam as a religious movement, with Muhammad being called upon by Allah to spread the divine message to the people of Arabia and beyond.
The initial years of Muhammad's prophetic mission were challenging. The message of monotheism and social reform faced resistance from the Quraysh tribe and other powerful Meccan families who were deeply entrenched in polytheistic beliefs and the established social order. Despite this opposition, Muhammad's teachings began to attract a small but dedicated group of followers, known as Muslims, who embraced the new faith and its principles.
In 622 CE, facing increasing persecution, Muhammad and his followers migrated from Mecca to Yathrib, later known as Medina. This migration, known as the Hijra, is a significant event in Islamic history, marking the beginning of the Islamic calendar. In Medina, Muhammad established a community united by faith, creating a social and political system based on Islamic principles.
The Revelations and The Quran
The Quran, the holy book of Islam, is considered the literal word of God as revealed to the Prophet Muhammad. The revelations occurred over 23 years, beginning in 610 CE and continuing until Muhammad's death in 632 CE. These revelations were delivered by the Angel Gabriel and were initially memorized and later transcribed by Muhammad's followers.
The Quran is composed of 114 chapters, known as surahs, which vary in length and cover a wide range of topics, including theology, morality, guidance for personal conduct, and legal principles. The Quran emphasizes the oneness of God, the importance of prayer and charity, and the need for social justice and compassion.
- Central Themes:
- Monotheism: The belief in one God, Allah, who is all-powerful and merciful.
- Prophethood: Muhammad is the final prophet in a long line of prophets sent by God to guide humanity.
- Afterlife: The Quran describes a day of judgment where individuals are held accountable for their deeds.
- Significance:
- The Quran serves as the primary source of guidance for Muslims worldwide, shaping their beliefs and practices.
- It is recited in Arabic during daily prayers and other religious rituals.
The Quran's teachings, combined with the Hadiths (sayings and actions of Muhammad), form the foundation of Islamic law and ethics, guiding the lives of Muslims across the globe.
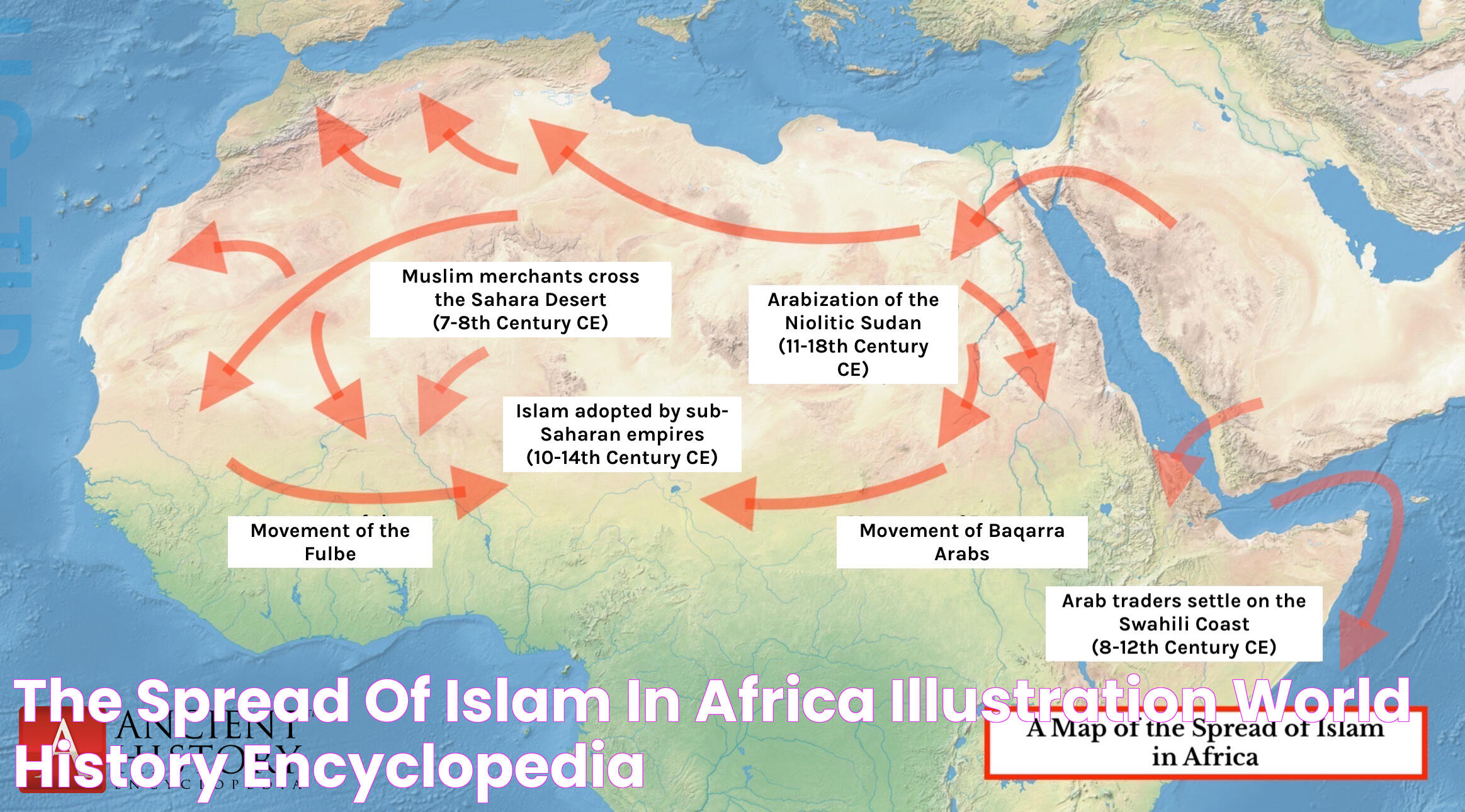
The Spread of Islam
Following the establishment of the Islamic community in Medina, Islam began to spread rapidly across the Arabian Peninsula. Through a combination of preaching, diplomacy, and military campaigns, Muhammad and his followers were able to unify the tribes of Arabia under the banner of Islam. This unification was a remarkable achievement, given the tribal divisions and conflicts that had previously characterized the region.
After Muhammad's death in 632 CE, the Islamic community faced the challenge of continuing his mission. The first four caliphs, known as the "Rightly Guided Caliphs," played a crucial role in the expansion of Islam beyond the Arabian Peninsula. Under their leadership, Islamic armies conquered vast territories, including parts of the Byzantine and Sassanian Empires, spreading the Islamic faith and establishing a new political order.
- Key Factors in the Spread of Islam:
- Trade: Islamic merchants traveled extensively, bringing Islamic teachings to new regions.
- Missionary Work: Muslim scholars and missionaries spread the message of Islam through preaching and education.
- Military Conquests: The early Islamic caliphates expanded their territories through successful military campaigns.
- Regions Influenced by Early Islamic Expansion:
- The Middle East and North Africa
- Parts of Europe, including Spain and Sicily
- Central Asia and the Indian subcontinent
The early spread of Islam laid the foundation for a diverse and dynamic Islamic civilization, characterized by cultural exchange, scientific advancements, and the flourishing of arts and literature.
The Rise of the Caliphate
The establishment of the caliphate marked a new phase in the history of Islam, as political and religious leadership became intertwined. The caliphate served as the governing authority for the Islamic community, with the caliph acting as both a political leader and a religious figurehead.
The first caliphate, known as the Rashidun Caliphate, lasted from 632 to 661 CE and was led by the four Rightly Guided Caliphs: Abu Bakr, Umar, Uthman, and Ali. This period was characterized by significant territorial expansion, administrative reforms, and the consolidation of Islamic law.
- Key Features of the Rashidun Caliphate:
- Expansion: The Islamic empire expanded into Persia, Egypt, and parts of North Africa and the Levant.
- Administration: The caliphs implemented a system of governance based on Islamic principles, ensuring justice and equality.
- Unity: The caliphs worked to maintain unity within the Muslim community, despite internal challenges and conflicts.
- Subsequent Caliphates:
- Umayyad Caliphate (661-750 CE): Known for its extensive empire, reaching from Spain to India.
- Abbasid Caliphate (750-1258 CE): Marked by cultural and intellectual achievements during the Islamic Golden Age.
The caliphate played a crucial role in shaping the political and cultural landscape of the Islamic world, leaving a lasting legacy that continues to influence modern-day Islamic societies.
The Golden Age of Islam
The Islamic Golden Age, spanning from the 8th to the 14th century, was a period of remarkable cultural, scientific, and intellectual achievements. This era was marked by a flourishing of arts, literature, and scholarship, as Islamic civilization became a center of knowledge and innovation.
During this time, Islamic scholars made significant contributions to various fields, including mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and philosophy. The translation of classical Greek and Roman texts into Arabic facilitated the exchange of ideas and laid the groundwork for the European Renaissance.
- Notable Achievements:
- Mathematics: The development of algebra and advancements in geometry and trigonometry.
- Astronomy: The creation of detailed star maps and the development of astronomical instruments.
- Medicine: The establishment of hospitals and the compilation of comprehensive medical texts.
- Philosophy: The integration of Greek philosophy with Islamic thought, leading to new philosophical schools.
- Key Centers of Learning:
- Baghdad: The House of Wisdom, a major center for translation and scholarship.
- Cordoba: A hub of intellectual and cultural exchange in Al-Andalus (Islamic Spain).
The Islamic Golden Age left a profound legacy, shaping the course of scientific and intellectual development in both the Islamic world and beyond.
Islamic Law and Its Impact
Islamic law, known as Sharia, is derived from the Quran and the Hadiths and serves as a comprehensive legal and ethical framework for Muslims. Sharia covers various aspects of life, including personal conduct, family relations, business transactions, and criminal justice.
The development of Islamic jurisprudence was a significant intellectual endeavor, with scholars interpreting religious texts to address new legal and social issues. This led to the establishment of different schools of thought, each offering unique perspectives on Islamic law.
- Main Schools of Islamic Jurisprudence:
- Hanafi: Known for its flexibility and adaptability to different cultural contexts.
- Maliki: Emphasizes the practices of the people of Medina as a source of law.
- Shafi'i: Focuses on the importance of consensus and analogy in legal reasoning.
- Hanbali: Stresses strict adherence to the Quran and Hadith.
- Impact of Islamic Law:
- Sharia has shaped the legal systems of many Muslim-majority countries, influencing their governance and social policies.
- It has also played a role in promoting social justice, equality, and ethical conduct within the Muslim community.
Islamic law continues to be a vital aspect of Muslim identity and cultural heritage, guiding the lives of millions of people around the world.
Cultural Contributions of Islam
Islamic civilization has made significant contributions to global culture, enriching the world with its artistic, architectural, and literary achievements. From the grandeur of Islamic architecture to the beauty of Islamic calligraphy, the cultural legacy of Islam is both diverse and profound.
Islamic art and architecture are characterized by intricate geometric patterns, arabesque designs, and the extensive use of calligraphy. These elements are prominently displayed in mosques, palaces, and public buildings, reflecting the spiritual and aesthetic values of Islamic culture.
- Notable Examples of Islamic Architecture:
- The Great Mosque of Cordoba: A masterpiece of Islamic art in Spain, known for its stunning arches and intricate mosaics.
- The Alhambra: A palatial complex in Granada, Spain, renowned for its exquisite gardens and detailed stucco work.
- The Dome of the Rock: An iconic Islamic shrine in Jerusalem, featuring a striking gold dome and intricate tilework.
- Literary Contributions:
- The development of classical Arabic poetry and literature, including works by famous poets like Rumi and Al-Mutanabbi.
- The compilation of Hadith collections, which serve as essential sources of Islamic teachings and history.
The cultural contributions of Islam have enriched the world's artistic and intellectual heritage, fostering a spirit of creativity and innovation that continues to inspire new generations.
How Did Islam Influence Other Cultures?
Islam has played a significant role in shaping the cultural, social, and political landscapes of regions across the globe. Through trade, conquest, and cultural exchange, Islamic civilization has left an indelible mark on diverse societies, influencing their art, architecture, language, and governance.
The spread of Islam facilitated the exchange of ideas and technologies, contributing to the development of global civilization. Islamic scholars and travelers, such as Ibn Battuta and Al-Kindi, played a crucial role in this exchange, bringing knowledge from the Islamic world to other regions.
- Impact on Art and Architecture:
- Islamic architectural styles influenced the design of churches, synagogues, and palaces in Europe and Asia.
- The use of geometric patterns and calligraphy in Islamic art inspired similar motifs in other cultures.
- Influence on Language and Literature:
- The Arabic language, as the language of the Quran, became a lingua franca in the Islamic world, facilitating communication and scholarship.
- Islamic literature, including poetry and philosophical texts, influenced the literary traditions of other cultures.
- Contributions to Science and Technology:
- Islamic scholars made significant advancements in fields such as mathematics, astronomy, and medicine, which were later adopted by European scholars.
- The introduction of new technologies, such as papermaking and the astrolabe, had a lasting impact on other cultures.
The influence of Islam on other cultures has been profound and enduring, shaping the course of history and contributing to the rich tapestry of human civilization.
Modern Day Islam
Today, Islam is a vibrant and dynamic religion with over 1.8 billion followers worldwide. It is the second-largest religion in the world, with a diverse and multicultural community that spans continents and cultures. Modern-day Islam continues to be a source of spiritual guidance and cultural identity for millions of people.
Contemporary Islamic societies face a range of challenges and opportunities as they navigate the complexities of the modern world. Issues such as globalization, technological advancements, and political conflicts have prompted Muslims to engage with their faith in new and innovative ways.
- Key Aspects of Modern-Day Islam:
- Religious Diversity: Islam is practiced in various forms, with different sects and schools of thought contributing to its richness and diversity.
- Social and Political Engagement: Muslims actively participate in social and political movements, advocating for justice, equality, and human rights.
- Interfaith Dialogue: Efforts to promote understanding and cooperation between different religious communities are ongoing, fostering peace and harmony.
- Challenges Facing Modern-Day Islam:
- Addressing Misconceptions: Muslims work to counter stereotypes and misinformation about their faith, promoting a more accurate understanding of Islam.
- Balancing Tradition and Modernity: Islamic societies strive to preserve their cultural heritage while embracing modern values and technologies.
Modern-day Islam is a testament to the resilience and adaptability of the Islamic faith, as it continues to thrive and evolve in an ever-changing world.
Islam and Global Politics
Islam plays a significant role in global politics, influencing both domestic and international affairs. As a major world religion, Islam shapes the political landscape of many Muslim-majority countries, impacting their governance, policies, and diplomatic relations.
The relationship between Islam and politics is complex and multifaceted, with various interpretations of Islamic teachings influencing political ideologies and movements. From the rise of political Islam to the role of Islamic organizations in global affairs, Islam's impact on politics is both profound and enduring.
- Key Aspects of Islam and Global Politics:
- Political Islam: The emergence of Islamist political movements advocating for the implementation of Islamic principles in governance.
- International Relations: The influence of Islamic values and norms on the foreign policies of Muslim-majority countries.
- Conflict and Cooperation: The role of Islam in both fueling and resolving conflicts, as well as fostering cooperation and dialogue between nations.
- Challenges and Opportunities:
- Addressing Extremism: Efforts to combat radicalism and promote moderate interpretations of Islam.
- Promoting Peace and Stability: The potential for Islam to serve as a force for peace and reconciliation in global politics.
Islam's role in global politics is a reflection of its significance as a cultural and religious force, shaping the course of history and contributing to the ongoing dialogue between civilizations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of the Hijra in Islamic history?
The Hijra, or migration of Muhammad and his followers from Mecca to Medina in 622 CE, is a pivotal event in Islamic history. It marks the beginning of the Islamic calendar and the establishment of the first Islamic community, where Muhammad laid the foundation for a society governed by Islamic principles.
How did the Quran influence Islamic culture and society?
The Quran is the central religious text of Islam, providing spiritual guidance and a comprehensive framework for personal conduct, social justice, and legal principles. Its teachings have shaped Islamic culture and society, influencing art, literature, and governance across the Islamic world.
What role did the caliphate play in the spread of Islam?
The caliphate was the political and religious leadership of the Islamic community, responsible for governing and expanding the Islamic empire. The early caliphs played a crucial role in spreading Islam through military conquests, trade, and missionary work, uniting diverse peoples under a common faith.
How did Islamic civilization contribute to global knowledge and innovation?
During the Islamic Golden Age, scholars made significant advancements in various fields, including mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and philosophy. These contributions laid the groundwork for the European Renaissance and continue to influence modern science and technology.
How do modern-day Muslims engage with their faith?
Modern-day Muslims engage with their faith through a variety of practices, including daily prayers, charitable acts, and participation in religious and cultural events. They also navigate contemporary challenges, such as globalization and technological advancements, by finding ways to integrate Islamic values with modern life.
What challenges do Islamic societies face in the modern world?
Islamic societies face challenges such as addressing misconceptions about Islam, balancing tradition with modernity, and promoting social and political engagement. Efforts to counter extremism and foster interfaith dialogue are also important aspects of navigating the complexities of the modern world.
Conclusion
The story of Islam, from its origins in the 7th century to its impact on modern-day society, is a testament to the enduring power and influence of this major world religion. From the initial revelations received by the Prophet Muhammad to the rise of the caliphate and the Islamic Golden Age, Islam has shaped the course of history and enriched global civilization.
Today, Islam continues to be a source of spiritual guidance, cultural identity, and social cohesion for millions of people around the world. As Islamic societies navigate the challenges and opportunities of the modern world, the teachings of Islam offer a framework for promoting justice, peace, and understanding in an increasingly interconnected global community.
By exploring the rich history and cultural contributions of Islam, we can gain a deeper appreciation for its role in shaping the world we live in today and the potential it holds for fostering a more inclusive and harmonious future.