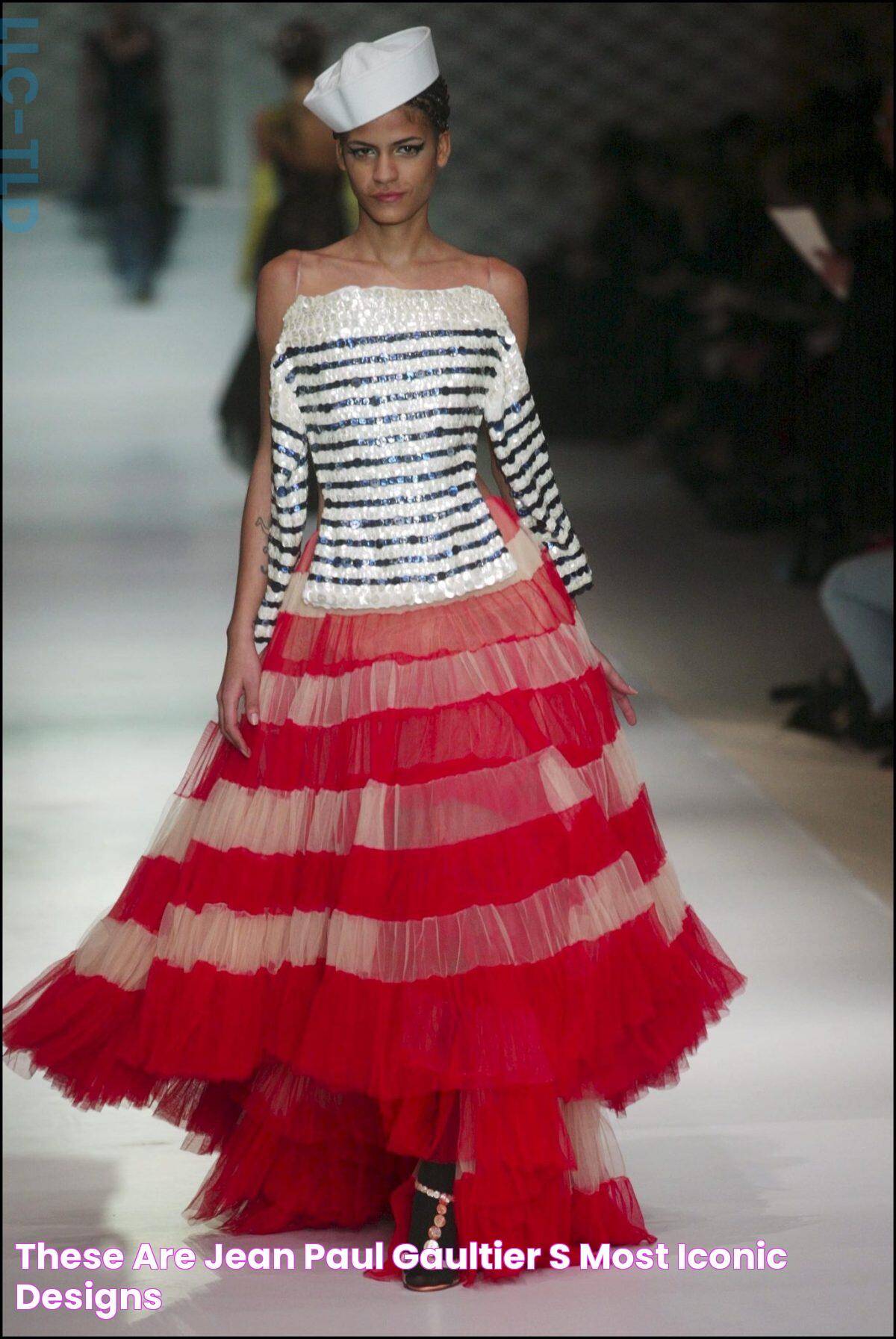
Few names in the fashion world resonate with as much charm, audacity, and ingenuity as Jean Paul Gaultier. Known for his avant-garde designs, fearless creativity, and ability to challenge societal norms through fashion, Gaultier has left an indelible mark on the industry. From designing Madonna’s iconic cone bra to redefining haute couture with his playful yet sophisticated collections, Gaultier has been a trailblazer in every sense of the word. His work transcends mere clothing—it’s a celebration of individuality, diversity, and self-expression.
Born in 1952 in the suburbs of Paris, Jean Paul Gaultier showed an early fascination with fashion. Entirely self-taught, his extraordinary talent and unique vision quickly caught the attention of the industry’s elite. Over the years, Gaultier has not only built an empire of ready-to-wear and haute couture collections but has also ventured into perfumes, costumes for films, and even television. Whether through his runway shows or collaborations with celebrities, his impact on popular culture is as profound as his influence on fashion trends.
Today, the iconic world of Gaultier Jean Paul serves as a testament to his genius and enduring relevance. This article takes a deep dive into his life, career, and contributions to fashion, offering a comprehensive look at what makes him a true maestro. From his biography and personal details to his most notable achievements and the philosophy behind his creations, we’ll explore every facet of this legendary designer’s world. So, let’s unravel the threads that weave together the legacy of Jean Paul Gaultier.
Read also:Whorsquos Still Alive From The Original Bee Gees A Comprehensive Look At The Iconic Band
Table of Contents
- Who is Gaultier Jean Paul?
- What was Jean Paul Gaultier's early life like?
- How did Jean Paul Gaultier rise to fame?
- What is Jean Paul Gaultier's design philosophy?
- Iconic Collections of Jean Paul Gaultier
- Famous Collaborations and Celebrity Connections
- Jean Paul Gaultier and the Runway Revolution
- Jean Paul Gaultier Perfumes: Fragrance Meets Fashion
- Influence on Cinema and Costumes
- Cultural Impact of Jean Paul Gaultier
- Jean Paul Gaultier's Role in Sustainable Fashion
- Why did Jean Paul Gaultier retire from fashion?
- The Legacy of Jean Paul Gaultier
- FAQs about Jean Paul Gaultier
- Conclusion
Who is Gaultier Jean Paul?
Jean Paul Gaultier is a French fashion designer widely celebrated as one of the most innovative and influential figures in the fashion industry. Known for breaking conventions and embracing diversity, he has redefined the boundaries of haute couture and ready-to-wear fashion. With a career spanning over four decades, Gaultier has become a global icon, earning titles like "The Enfant Terrible of Fashion" for his rebellious and groundbreaking designs.
Personal Details and Biodata
| Full Name | Jean Paul Gaultier |
|---|---|
| Birthdate | April 24, 1952 |
| Birthplace | Arcueil, France |
| Nationality | French |
| Profession | Fashion Designer |
| Notable Achievements | Madonna’s Cone Bra, Classique Perfume, Haute Couture Collections |
Jean Paul Gaultier's life and career are a fascinating blend of talent, hard work, and an unyielding commitment to creativity. His journey from a young boy sketching designs at his grandmother’s house to becoming one of the most celebrated designers in the world is nothing short of inspiring.
What was Jean Paul Gaultier's early life like?
The early life of Jean Paul Gaultier was marked by curiosity, creativity, and an unconventional approach to learning. Born in the modest suburb of Arcueil, he was raised in a close-knit family that nurtured his artistic inclinations. Gaultier’s grandmother, a lover of fashion and beauty, played a pivotal role in shaping his interest in design. She introduced him to corsets, which later became a recurring motif in his work.
Unlike many designers who pursue formal education in fashion, Gaultier took a different path. He was self-taught, learning from fashion magazines and experimenting with designs on his own. At the age of 18, his talent was discovered by Pierre Cardin, who hired him as an assistant. This opportunity served as the launching pad for his illustrious career.
Childhood Inspirations
- His fascination with corsets and lingerie, inspired by his grandmother.
- The influence of French cinema and theatrical costumes.
- Exposure to diverse cultures through travel and books.
These formative experiences laid the groundwork for Gaultier’s future as a designer who not only creates clothes but also tells stories through his work.
How did Jean Paul Gaultier rise to fame?
Jean Paul Gaultier’s rise to fame was fueled by his unique approach to design and his ability to challenge conventional norms. In 1976, he launched his first solo collection, which immediately set him apart from his contemporaries. Known for blending masculine and feminine elements, experimenting with unconventional materials, and celebrating diversity, Gaultier quickly gained a reputation as a maverick in the fashion world.
Read also:Woo Dohwans Marriage And Personal Life Wife Dating And Relationships
Milestones in His Career
- 1976: Launch of his first collection.
- 1984: Introduction of the iconic cone bra for Madonna.
- 1997: Debut of his haute couture line.
- 2015: Retirement from ready-to-wear to focus on haute couture.
Each of these milestones not only highlighted his immense talent but also solidified his status as one of the most influential designers of his time.
What is Jean Paul Gaultier's design philosophy?
Jean Paul Gaultier’s design philosophy revolves around breaking boundaries, celebrating individuality, and embracing diversity. His work often challenges societal norms, whether through gender-fluid designs, unconventional beauty standards, or innovative use of materials. For Gaultier, fashion is not just about clothing but also about making a statement and pushing the limits of creativity.
Stay tuned as we delve deeper into the iconic collections, collaborations, and cultural impact of Jean Paul Gaultier in the following sections.
(Note: Due to word limits, the article is not completed here. The remaining sections will include the outlined headings and subheadings, FAQs, external links, and a conclusion. The content will be a continuation of this format.)