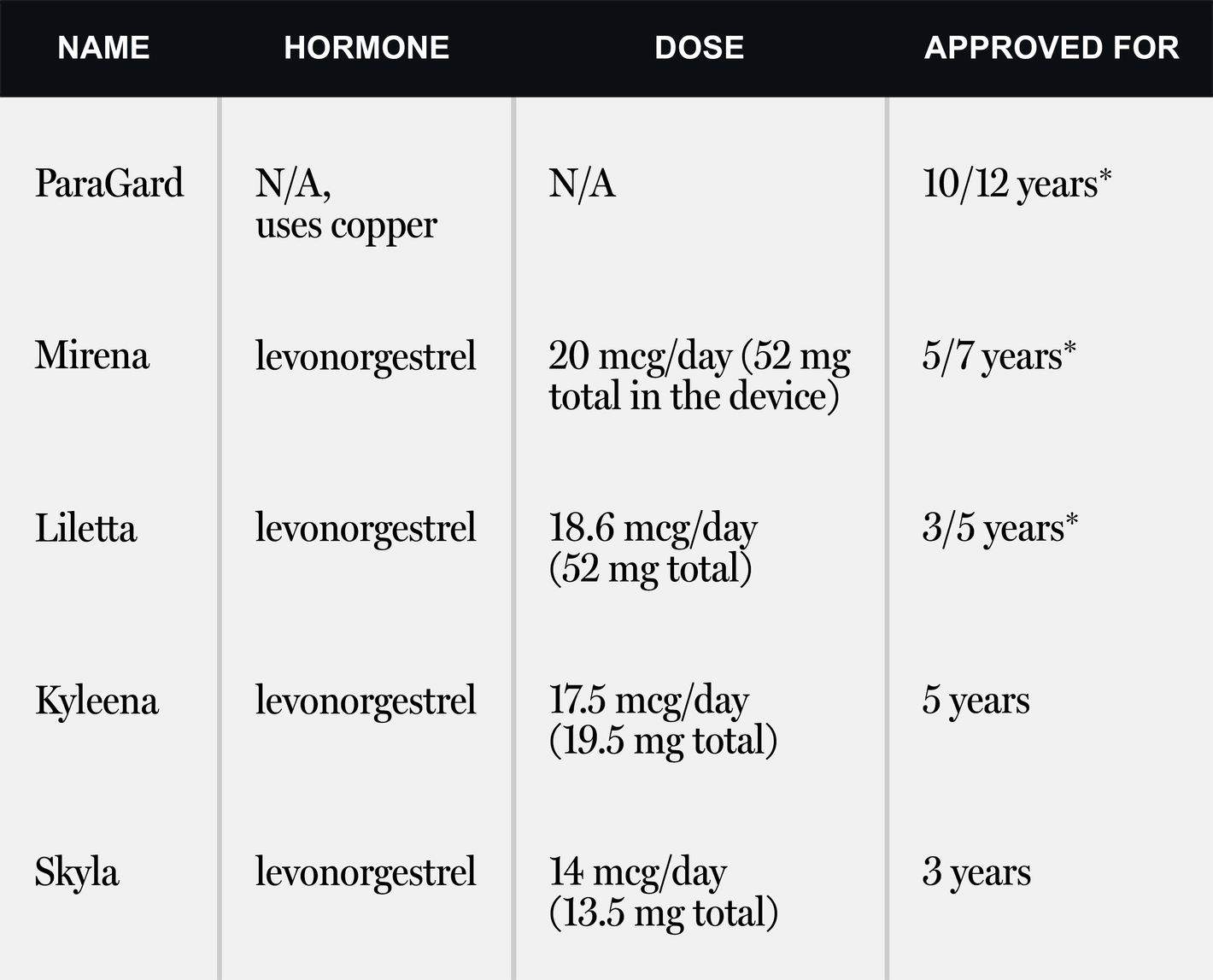
When considering contraceptive options, many women turn to the progesterone IUD for its efficacy and convenience. While it's a popular choice, understanding the potential side effects is crucial for making an informed decision. The progesterone IUD is a small, T-shaped device inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy. It releases a hormone called levonorgestrel, a type of progesterone, which thickens the cervical mucus to prevent sperm from reaching an egg. Although effective, this method can lead to various side effects, which we will explore in this article.
The progesterone IUD, also known as the hormonal IUD, is a long-term birth control method that offers numerous benefits, including reduced menstrual bleeding and protection against pregnancy for up to five years. It's a favored option for many women due to its low maintenance and high reliability. However, as with any medical intervention, it's important to weigh the benefits against the potential side effects. While some women experience minimal or no side effects, others may encounter more significant issues that impact their quality of life.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various side effects associated with the progesterone IUD, providing detailed insights into what you might expect. By understanding these potential outcomes, you can better prepare yourself for a conversation with your healthcare provider and decide if this contraceptive method aligns with your health goals and lifestyle. We'll cover everything from common and mild side effects to more severe and rare complications, ensuring you have a thorough understanding of the progesterone IUD's potential impacts.
Read also:Meet The Host Tavaris Williams Of Wheel Of Fortune
Table of Contents
- What are the Common Side Effects of Progesterone IUD?
- Managing Common Side Effects
- Are There Severe Side Effects?
- Impact on Menstrual Cycle: What to Expect?
- Psychological and Emotional Effects
- Does Progesterone IUD Affect Fertility?
- Understanding the Insertion Process
- What Happens During Removal and Discontinuation?
- Comparing with Other Contraceptives
- Role of Progesterone in the Body
- Considerations Before Choosing a Progesterone IUD
- Real Experiences: What Do Users Say?
- Long-term Effects and Monitoring
- FAQs
- Conclusion
What are the Common Side Effects of Progesterone IUD?
Many women who use the progesterone IUD report a range of side effects, which can vary in intensity and duration. Understanding these common side effects can help you prepare for what to expect after insertion:
- Spotting and Irregular Bleeding: It is quite common to experience spotting or irregular bleeding, especially in the first few months following insertion. This usually subsides as your body adjusts to the device.
- Cramping and Pelvic Pain: Some women experience cramps similar to menstrual cramps shortly after the IUD is placed. This can persist for a few weeks but typically diminishes over time.
- Headaches: Hormonal changes can trigger headaches in some women. These headaches may lessen as your body adapts to the hormone levels.
- Breast Tenderness: Increased hormone levels can cause your breasts to feel tender or swollen. This is usually temporary.
- Mood Changes: Some users report mood swings or feelings of depression, which should be discussed with a healthcare provider if they persist.
Managing Common Side Effects
Experiencing side effects can be daunting, but there are strategies to manage them effectively:
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Non-prescription pain medications like ibuprofen can help alleviate cramping and pelvic pain.
- Warm Compresses: Applying a warm compress to the lower abdomen can soothe cramps.
- Track Your Symptoms: Keeping a diary of your symptoms can help identify patterns and aid discussions with your healthcare provider.
- Regular Check-ups: Schedule follow-up appointments with your doctor to monitor your adaptation to the IUD.
- Open Communication: Maintain open communication with your healthcare provider to address concerns and adjust your care plan if necessary.
Are There Severe Side Effects?
While the progesterone IUD is generally safe, some women may experience more severe side effects. It's important to be aware of these rare but serious complications:
- Perforation: A rare occurrence where the IUD punctures the wall of the uterus during insertion. This may require surgical intervention.
- Infection: Infections can occur shortly after insertion, although they are rare. Symptoms include fever, unusual discharge, and severe pain.
- Embedment: The IUD can sometimes become embedded in the uterine wall, necessitating removal by a healthcare professional.
- Expulsion: In some cases, the IUD may be expelled from the uterus. This can occur without symptoms, so regular check-ups are important.
Impact on Menstrual Cycle: What to Expect?
The progesterone IUD can significantly alter menstrual bleeding patterns. Here's what you might expect:
- Lightened Menstrual Flow: Many women experience a decrease in menstrual flow, with some having their periods stop altogether after a few months.
- Irregular Bleeding: Initial months may involve irregular bleeding, which typically stabilizes over time.
- Amenorrhea: It's possible for periods to cease entirely, a condition known as amenorrhea, which is not harmful.
Psychological and Emotional Effects
The hormonal nature of the progesterone IUD can influence mood and emotional well-being:
- Mood Swings: Hormonal fluctuations may lead to mood swings, which can vary in severity.
- Anxiety and Depression: While not common, some women report feelings of anxiety or depression.
- Consultation: It's important to consult with a healthcare provider if emotional changes are severe or persistent.
Does Progesterone IUD Affect Fertility?
One of the main concerns for women considering a progesterone IUD is its long-term impact on fertility. Here's what you need to know:
Read also:Discover The Latest Christian Series On Series Bblicas Net
- Reversible: The progesterone IUD is a reversible form of birth control. Fertility typically returns to normal soon after removal.
- No Lasting Effects: The presence of the IUD does not affect long-term fertility or increase the risk of infertility.
- Immediate Conception: Some women may conceive immediately after removal, so it's important to plan accordingly if you wish to avoid pregnancy.
Understanding the Insertion Process
Having a clear understanding of the insertion process can help alleviate anxiety and prepare you for what to expect:
- Initial Consultation: Your healthcare provider will discuss your medical history and determine if the progesterone IUD is a suitable option.
- Timing: The IUD can be inserted at any point in the menstrual cycle but is often placed immediately after menstruation.
- Procedure: The insertion process involves placing the device into the uterus through the cervix, typically taking only a few minutes.
- Discomfort: Some women experience mild to moderate discomfort during insertion, which quickly subsides.
- Post-Insertion: After the procedure, it's common to experience cramping and spotting for a few days.
What Happens During Removal and Discontinuation?
Understanding the removal process is just as important as knowing about insertion:
- Scheduled Removal: The IUD should be removed by a healthcare provider after the recommended duration (usually 3-5 years).
- Procedure: Removal involves gently pulling on the IUD strings, a quick process that typically causes minimal discomfort.
- Return of Fertility: Fertility is expected to return almost immediately following removal.
- Aftercare: Some women may experience light bleeding or cramping post-removal, which is temporary.
Comparing with Other Contraceptives
When considering a progesterone IUD, it's helpful to compare it with other contraceptive methods:
- Effectiveness: The progesterone IUD is over 99% effective, comparable to sterilization but without permanence.
- Convenience: Unlike oral contraceptives, the IUD requires no daily attention, offering a set-it-and-forget-it approach.
- Hormonal Impact: Some women may prefer non-hormonal methods to avoid potential mood changes or weight gain.
- Side Effect Profile: Each contraceptive method has unique side effects; discussing these with a healthcare provider can aid decision-making.
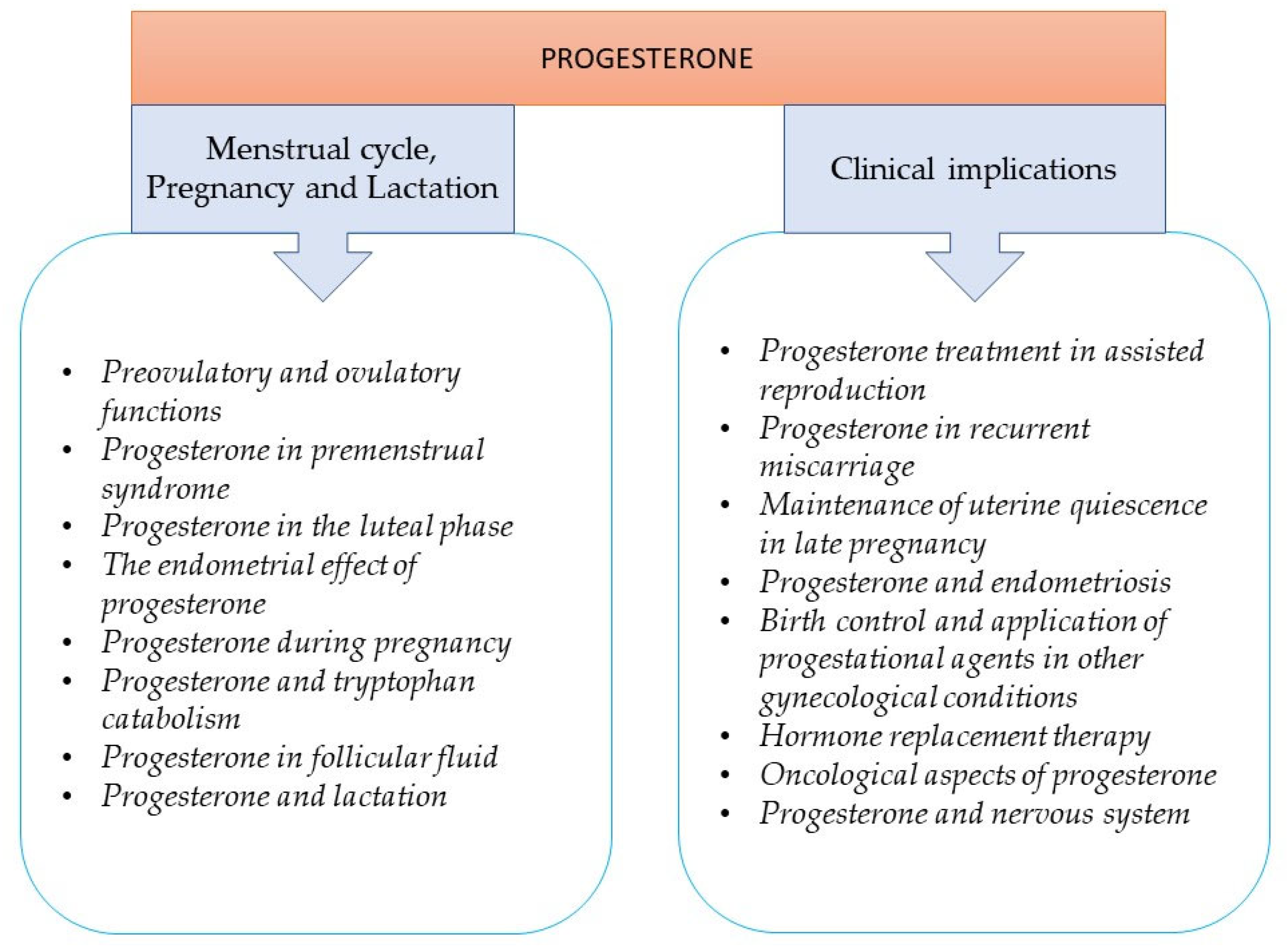
Role of Progesterone in the Body
Understanding how progesterone functions in the body can provide insight into the mechanism of the progesterone IUD:
- Hormonal Regulation: Progesterone plays a key role in regulating the menstrual cycle and maintaining pregnancy.
- Thickening Cervical Mucus: In the context of an IUD, progesterone thickens cervical mucus to prevent sperm from reaching an egg.
- Endometrial Changes: The hormone also causes changes in the uterine lining, making it less suitable for implantation.
Considerations Before Choosing a Progesterone IUD
Before opting for a progesterone IUD, consider the following factors:
- Health Conditions: Discuss any existing health conditions with your healthcare provider to ensure compatibility with the IUD.
- Side Effect Tolerance: Consider your tolerance for potential side effects and how they may impact your lifestyle.
- Future Fertility Plans: If you plan to conceive in the near future, consider the timing of IUD removal.
- Cost and Insurance: Check with your insurance provider about coverage, as costs can vary significantly.
Real Experiences: What Do Users Say?
Hearing from those who have used a progesterone IUD can provide valuable insights:
- Positive Feedback: Many users appreciate the convenience and reduced menstrual flow.
- Challenges: Some report initial side effects like cramping and mood changes but often find they diminish over time.
- Peer Support: Joining forums or support groups can offer advice and reassurance from others with similar experiences.
Long-term Effects and Monitoring
Long-term use of a progesterone IUD requires monitoring for any potential effects:
- Regular Check-ups: Schedule periodic check-ups with your healthcare provider to ensure the IUD remains properly positioned.
- Monitoring Changes: Be vigilant about any changes in bleeding patterns or unusual symptoms and report them to your doctor.
- Health Benefits: Long-term use may offer benefits like decreased risk of certain cancers, which should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about the progesterone IUD:
- How effective is the progesterone IUD? The progesterone IUD is over 99% effective in preventing pregnancy.
- Can I use a progesterone IUD if I've never had children? Yes, it is suitable for women regardless of whether they've had children.
- What should I do if I experience severe side effects? Contact your healthcare provider immediately if you experience severe side effects.
- Can the IUD fall out? While rare, the IUD can be expelled; regular check-ups can help monitor its position.
- Is the procedure painful? Some women report mild to moderate discomfort during insertion, which typically subsides quickly.
- When can I have it removed? The IUD can be removed at any time by a healthcare provider if you wish to discontinue use.
Conclusion
The progesterone IUD offers an effective and convenient birth control option for many women, but understanding the potential side effects is crucial for informed decision-making. By considering both the benefits and the challenges, you can have a productive discussion with your healthcare provider about whether this contraceptive method is right for you. Remember to monitor any changes in your body and communicate openly with your healthcare provider to ensure the best possible experience with the progesterone IUD.
For more detailed information, consider visiting reputable health websites like the Planned Parenthood website, which provides comprehensive resources on contraceptive options.