Gray hair is more than just a cosmetic concern for many. It can be an indicator of various biological processes and health conditions. From genetics to lifestyle factors, numerous elements contribute to the graying of hair. By exploring these factors, we can gain insights into how to potentially delay or manage the onset of gray hair. Moreover, with advancing research in hair care, several solutions and treatments are available today to tackle premature graying.
As we delve into the complexities of gray hair, it's essential to approach the topic with an open mind. Whether you're looking for ways to embrace your natural gray or seeking methods to maintain your youthful appearance, understanding the root causes will empower you to make informed decisions. Let's explore the world of gray hair and uncover the secrets to maintaining healthy, vibrant locks at any age.
What Causes Hair to Gray?
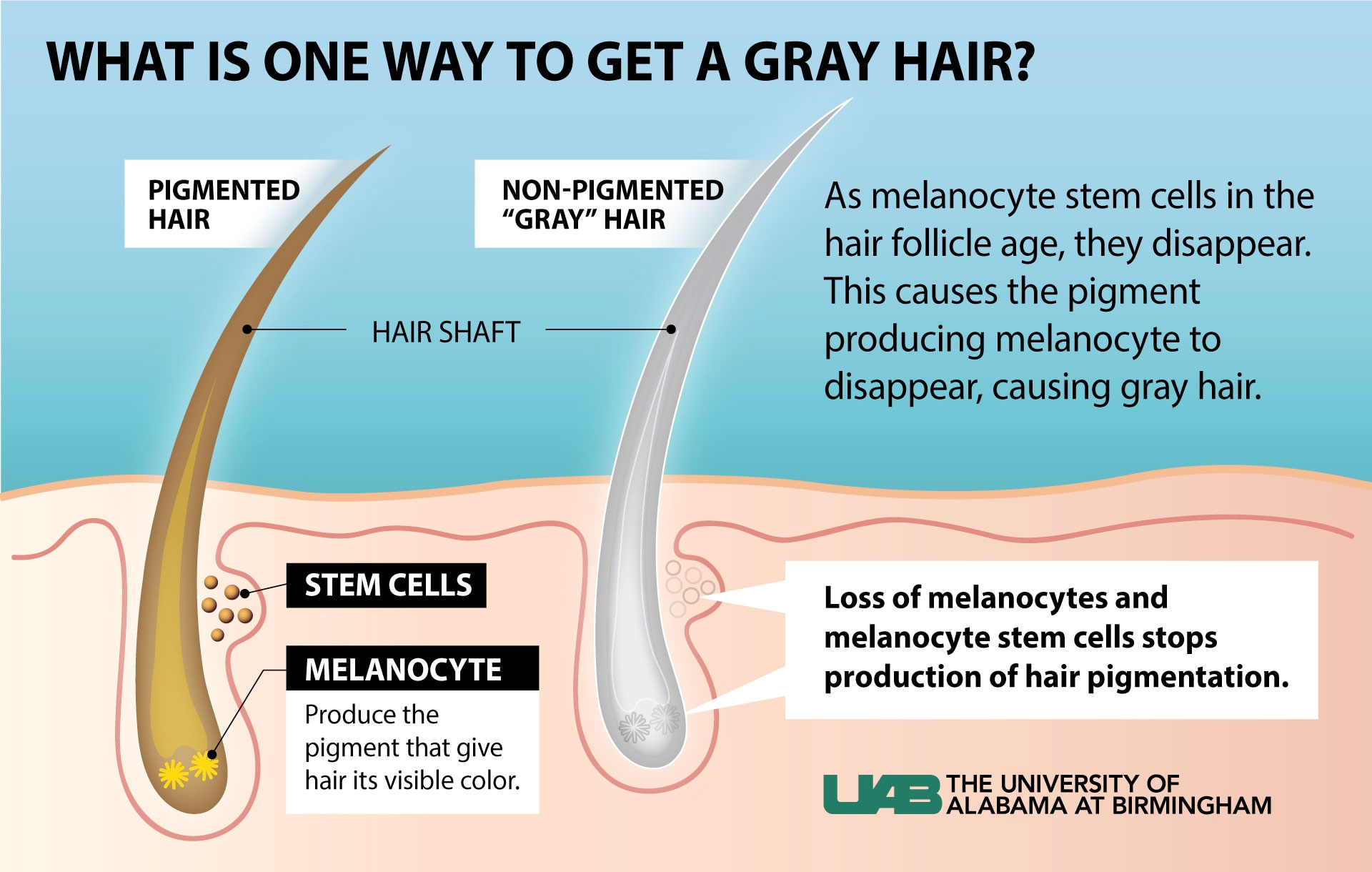
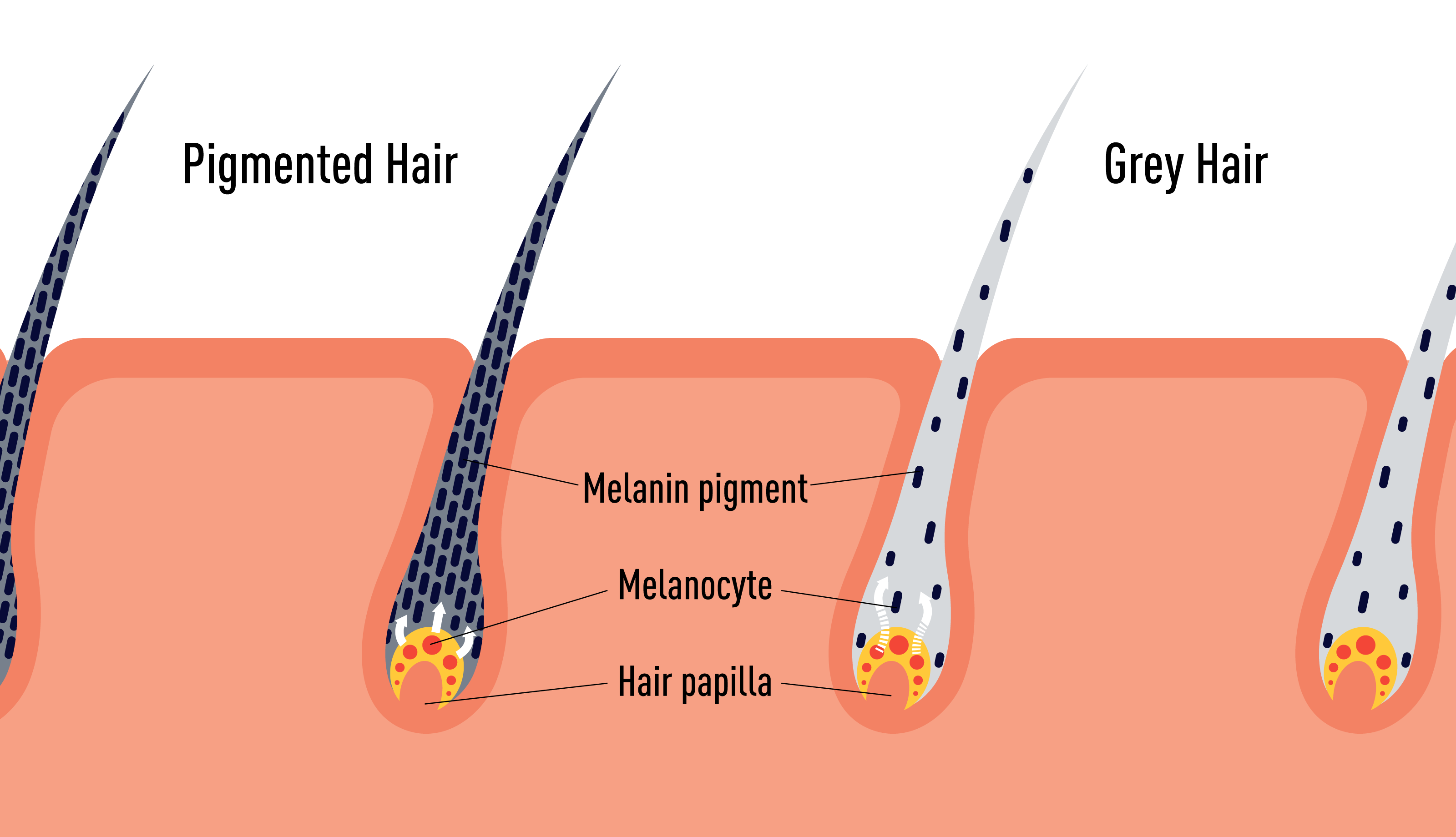
Gray hair primarily arises from the reduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for hair color. Melanin is produced by cells called melanocytes, located in hair follicles. As we age, these melanocytes gradually decrease their production of melanin, leading to the appearance of gray or white hair. Several factors contribute to this process, including genetics, lifestyle, and environmental influences.
Melanin production is also affected by oxidative stress, a condition where free radicals damage cells. This stress can accelerate the aging of hair follicles, leading to premature graying. Additionally, the accumulation of hydrogen peroxide in hair follicles can bleach hair from within, contributing to the loss of pigment.
Environmental factors such as pollution and UV exposure can exacerbate oxidative stress, further impacting melanin production. Moreover, certain nutritional deficiencies, particularly in vitamins B12, D, and E, can impair the body's ability to produce melanin effectively.
Is Gray Hair Genetically Predetermined?
Genetics play a significant role in determining when and how much gray hair you will have. If your parents or grandparents experienced early graying, there's a higher chance you might too. Researchers have identified specific genes linked to the onset of gray hair, including the IRF4 gene, which influences pigmentation.
While genetics is a significant factor, it does not solely dictate when you'll start to see gray hair. Lifestyle and environmental factors can either delay or hasten the process. Nevertheless, understanding your genetic predisposition can prepare you for what to expect as you age.
It's important to note that genetic influence can vary among different ethnic groups. For example, Caucasians tend to gray earlier than Asians or African-Americans. This variation further emphasizes the complexity of genetic factors in hair pigmentation.
Read also: 10 Essential Tips For Adding Hinderances To Minions In Swade
What Role Does Stress Play in Graying?
Stress is often cited as a potential cause of gray hair, but how much truth is there to this claim? While stress itself doesn't directly cause gray hair, it can impact the body's overall health, affecting hair follicles and melanin production.
Chronic stress leads to the release of stress hormones like cortisol, which can influence the health of hair follicles. Additionally, stress can exacerbate conditions such as oxidative stress, further contributing to premature graying. In some cases, stress can trigger telogen effluvium, a condition where hair falls out, leading to the growth of gray hair in its place.
Managing stress through mindfulness, exercise, and relaxation techniques can help mitigate its effects on hair health. While it may not prevent gray hair entirely, reducing stress can promote healthier hair growth and overall well-being.
Can Diet Influence Gray Hair?
Diet plays a crucial role in maintaining hair health and potentially delaying the onset of gray hair. A balanced diet rich in essential vitamins and minerals supports melanin production and overall hair vitality.
Key nutrients for hair health include:
- Vitamin B12: Essential for healthy hair growth and pigmentation. Deficiency can lead to premature graying.
- Vitamin D: Supports the creation of new hair follicles and melanin production.
- Iron: Critical for delivering oxygen to hair follicles, promoting healthy hair growth.
- Copper: Enhances melanin production, maintaining natural hair color.
- Antioxidants: Combat oxidative stress and protect hair follicles from damage.
Incorporating foods rich in these nutrients, such as leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and lean proteins, can contribute to healthier hair and potentially delay gray hair. Additionally, staying hydrated and consuming a balanced diet can improve overall hair condition.
The Impact of Lifestyle on Hair Color
Lifestyle choices significantly influence the health and color of your hair. Smoking, for instance, can accelerate the graying process due to its harmful effects on hair follicles and overall health. The toxins in cigarette smoke increase oxidative stress and reduce blood flow to the scalp, affecting melanin production.
Exercise, on the other hand, promotes healthy blood circulation, delivering essential nutrients to hair follicles. Regular physical activity can improve hair health and potentially delay the onset of gray hair. Additionally, maintaining a healthy sleep schedule and managing stress levels contribute to overall well-being, which reflects on hair health.
Environmental factors, such as exposure to sunlight and pollution, can also impact hair color. UV rays can damage hair cuticles and increase oxidative stress, leading to premature graying. Protecting your hair with hats or UV-protectant products can mitigate these effects.
How Do Hormones Affect Hair Pigmentation?
Hormones play a significant role in hair pigmentation and overall hair health. As we age, hormonal changes can affect melanin production, leading to gray hair. The decrease in hormones such as estrogen and progesterone during menopause can impact hair color and texture.
Thyroid hormones also influence hair pigmentation. An imbalance in thyroid hormones, whether hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism, can lead to changes in hair color and premature graying. Addressing hormonal imbalances through medical intervention can help manage these effects.
Additionally, the hormone DHT (dihydrotestosterone) affects hair growth and pigmentation. High levels of DHT can lead to hair thinning and loss, potentially revealing more gray hair. Balancing hormones through a healthy lifestyle and medical guidance can promote better hair health.
The Science of Melanin and Hair Color
Melanin is the pigment responsible for the color of our hair, skin, and eyes. It is produced by melanocytes in hair follicles. There are two types of melanin: eumelanin, which provides black and brown colors, and pheomelanin, which imparts red and yellow hues.
The balance and concentration of these melanin types determine the natural color of your hair. As we age, the production of melanin decreases, leading to gray or white hair. This process is influenced by genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors.
Understanding the science behind melanin and its role in hair color helps us appreciate the complexity of hair pigmentation. It also highlights the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle to support melanin production and overall hair health.
What Are Some Common Misconceptions About Gray Hair?
Gray hair is surrounded by several misconceptions and myths. One common belief is that plucking a gray hair will cause more to grow in its place. In reality, plucking does not affect the number of gray hairs but can damage hair follicles.
Another misconception is that stress is the sole cause of gray hair. While stress can influence hair health, it is not the only factor. Genetics, lifestyle, and environmental influences also play crucial roles in the graying process.
Many people also believe that gray hair is a sign of poor health. While certain health conditions can contribute to premature graying, gray hair itself is a natural part of aging and not necessarily an indicator of poor health.
Solutions for Premature Gray Hair
For those experiencing premature gray hair, several solutions are available to manage or conceal the graying. Hair dyes are the most common method, offering a wide range of colors to match natural hair tones. Semi-permanent dyes are less damaging and fade over time, while permanent dyes provide longer-lasting coverage.
Natural remedies, such as henna and indigo, offer a chemical-free alternative to traditional dyes. These plant-based dyes provide a more subtle change and can condition the hair while coloring it.
For those seeking to embrace their gray hair, toning shampoos and conditioners can enhance the natural silver tones and reduce yellowing. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and diet can support overall hair health and potentially slow the graying process.
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Gray Hair
While it's impossible to completely prevent gray hair, certain lifestyle changes can slow its onset. A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients supports melanin production and overall hair health. Incorporating foods high in vitamins B12, D, and E, as well as iron and copper, can promote healthy hair growth.
Regular exercise improves blood circulation, delivering essential nutrients to hair follicles. Managing stress through mindfulness, meditation, and relaxation techniques can also support hair health.
Protecting hair from environmental damage, such as UV exposure and pollution, can prevent oxidative stress and preserve natural hair color. Using UV-protectant products and covering hair outdoors can mitigate these effects.
Hair Care Products for Gray Hair
Gray hair requires specialized care to maintain its health and vibrancy. Toning shampoos and conditioners designed for gray or silver hair can enhance natural tones and reduce yellowing. These products often contain purple pigments that neutralize brassy tones, keeping gray hair looking fresh.
Moisturizing shampoos and conditioners are essential for gray hair, which can be more prone to dryness. Look for products containing hydrating ingredients like argan oil, shea butter, and glycerin.
Additionally, heat protectants and leave-in conditioners can shield gray hair from damage caused by styling tools. Regular trims and deep conditioning treatments can also keep gray hair looking healthy and vibrant.
Can Medical Conditions Cause Gray Hair?
Certain medical conditions can contribute to premature gray hair. Autoimmune disorders, such as vitiligo and alopecia areata, can affect melanin production and lead to graying. Thyroid disorders, including hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism, can also impact hair pigmentation.
Nutritional deficiencies, particularly in vitamins B12 and D, can lead to premature graying. Addressing these deficiencies through dietary changes or supplements can help manage gray hair.
If you suspect a medical condition is causing your gray hair, consulting a healthcare professional can provide clarity and guidance on appropriate treatments or lifestyle changes.
The Role of Antioxidants in Hair Health
Antioxidants play a crucial role in combating oxidative stress, a significant factor in the graying process. By neutralizing free radicals, antioxidants protect hair follicles from damage and support melanin production.
Incorporating antioxidant-rich foods, such as berries, nuts, and leafy greens, into your diet can promote hair health. Supplements containing antioxidants like vitamin C, vitamin E, and selenium can also support healthy hair growth.
Topical antioxidant treatments, such as serums and oils, can protect hair from environmental damage and maintain its vibrancy. These products often contain ingredients like green tea extract, vitamin E, and argan oil.
FAQs
- Can gray hair turn back to its original color?
Once hair turns gray, it typically does not revert to its original color. However, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and addressing underlying health conditions can promote overall hair health.
- Does plucking gray hair lead to more gray growth?
Plucking gray hair does not cause more gray hairs to grow. However, it can damage hair follicles and lead to hair thinning or loss.
- Is gray hair more prone to damage?
Gray hair can be more prone to dryness and damage due to reduced melanin and natural oils. Proper hair care and moisturizing products can help maintain its health.
- Does diet affect the rate of graying?
A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can support melanin production and potentially delay the onset of gray hair. Nutritional deficiencies can contribute to premature graying.
- Can stress cause gray hair?
While stress is not the sole cause of gray hair, it can impact overall hair health and contribute to premature graying. Managing stress can promote healthier hair growth.
- Are there natural remedies for gray hair?
Natural remedies like henna and indigo can provide a chemical-free alternative to traditional dyes. A balanced diet and healthy lifestyle can also support overall hair health.
Conclusion
Understanding the causes of gray hair empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their hair care routine. Whether embracing the natural beauty of gray hair or seeking solutions to manage it, knowing the underlying factors can guide you toward healthier hair. By adopting a balanced lifestyle, managing stress, and using the right products, you can maintain vibrant, healthy hair at any age. Remember, gray hair is a natural part of life, and with the right approach, it can be a beautiful feature to celebrate.