In the realm of education, understanding reading levels is crucial for both parents and educators to support a child's literacy development effectively. The Lexile Framework for Reading provides a scientific approach to measuring reading ability and text complexity, making it easier to match students with appropriate reading materials. One of the common questions that arise is: what age is a 1080 Lexile level suitable for? This question is essential as it helps in selecting suitable texts that align with a child's reading capabilities, ensuring both comprehension and engagement.
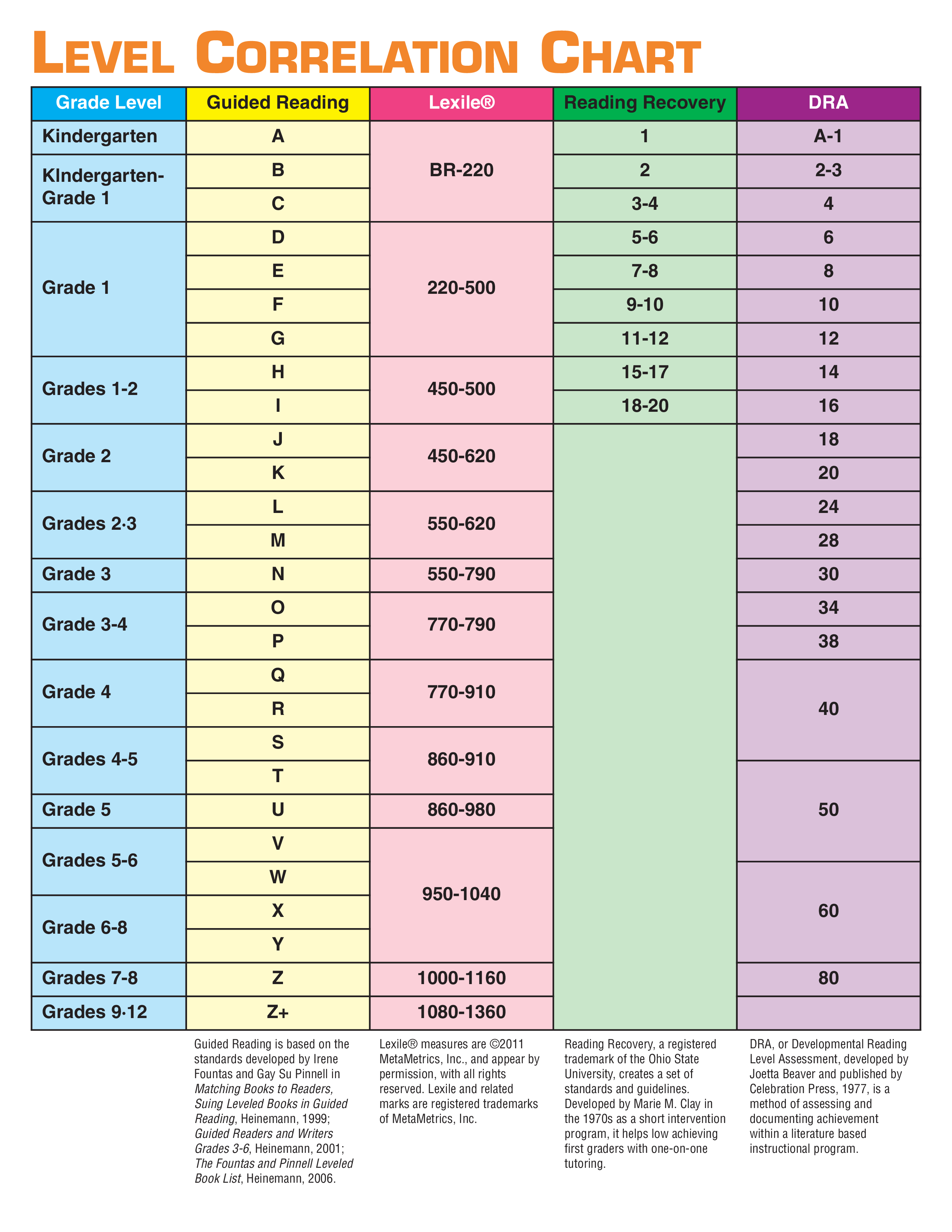
Determining the appropriate age or grade level for a specific Lexile measure, such as 1080, involves understanding the correlation between Lexile levels and academic curriculum standards. A Lexile measure of 1080 typically corresponds to the reading ability of students in the middle school range, specifically around grades 6 to 8. However, it's important to note that reading ability varies among individuals, and some students may reach or exceed this level earlier or later than their peers. The goal is to provide reading materials that challenge students without causing frustration, thereby fostering a love for reading and continuous learning.
In this article, we'll delve into the intricacies of Lexile levels and explore the factors that contribute to a child's reading development. We'll examine the relationship between age, grade, and Lexile measures, and offer guidance to parents and educators on how to use this information to support young readers. Additionally, we'll address frequently asked questions about Lexile levels to provide a comprehensive understanding of this important educational tool.
Read also:Erie Timesnews Your Local News Source
Table of Contents
- What is a Lexile Level?
- The Importance of Lexile Levels in Education
- How are Lexile Levels Determined?
- What Age is a 1080 Lexile Level Suitable For?
- Factors Affecting Reading Development
- How Can Parents Support Reading Development?
- Selecting Appropriate Reading Materials
- Role of Educators in Enhancing Reading Skills
- Balancing Challenge and Enjoyment in Reading
- Using Lexile Levels to Track Progress
- Common Misconceptions About Lexile Levels
- FAQs
- Conclusion
What is a Lexile Level?
A Lexile level is a standard score that matches a student's reading ability with the difficulty of text material. The Lexile Framework for Reading is a scientifically backed methodology used to assess both reading ability and text complexity. The framework assigns a Lexile measure to a text, indicating its difficulty level, while a student's reading ability is also expressed in terms of a Lexile measure.
The Lexile scale ranges from below 200L for beginning readers and text to above 1600L for advanced readers and text. This scale helps in making informed decisions about which texts are appropriate for students based on their reading abilities. The Lexile measure is a valuable tool in creating personalized reading experiences, allowing educators and parents to select books that are challenging yet achievable for the reader.
Components of Lexile Measures
Lexile measures consist of two main components:
- Lexile Reader Measure: This indicates the reading ability of an individual. It is determined through assessments and is used to gauge a student's current reading level.
- Lexile Text Measure: This indicates the complexity of a text. It is calculated based on various factors, including word frequency and sentence length.
Uses of Lexile Levels
Lexile levels are used in various educational settings to:
- Match students with appropriate reading materials.
- Set goals for reading improvement.
- Monitor student progress over time.
- Facilitate differentiated instruction in the classroom.
The Importance of Lexile Levels in Education
Lexile levels play a significant role in education by providing a clear, objective measure of a student's reading ability. This information is crucial for educators and parents as they strive to support the literacy development of young learners.
Enhancing Instructional Strategies
Understanding a student's Lexile level allows educators to tailor their instructional strategies to meet the individual needs of each learner. By selecting texts that are within a student's Lexile range, teachers can ensure that students are challenged appropriately, promoting growth in reading skills.
Read also:Discover Marketplace Sarasota Your Goto Hub For Local Finds
Supporting Reading Comprehension
Lexile levels help in identifying texts that are suitable for a student's reading ability, thus enhancing their comprehension. When students read texts that align with their Lexile measures, they are more likely to understand and retain the information, leading to a more meaningful learning experience.
Facilitating Parental Involvement
For parents, Lexile levels provide a valuable insight into their child's reading progress. By understanding the level at which their child is reading, parents can better support their learning at home by selecting appropriate books and engaging in reading activities that complement their child's abilities.
How are Lexile Levels Determined?
Determining Lexile levels involves a systematic process that takes into account various factors related to both the reader and the text. The Lexile Framework utilizes a combination of psychometrics and linguistic analyses to assign Lexile measures.
Assessment of Reading Ability
To determine a student's Lexile reader measure, assessments are conducted that evaluate their reading comprehension skills. These assessments may include standardized tests, state assessments, or reading-specific evaluations designed to gauge a student's ability to understand and process text.
Analysis of Text Complexity
The Lexile text measure is calculated by analyzing the text's complexity based on:
- Word Frequency: The occurrence of words within the English language. Texts with more common words typically have lower Lexile measures, whereas those with rare words have higher measures.
- Sentence Length: Longer sentences often contribute to higher Lexile measures due to the increased complexity in structure and thought.
These analyses are combined to produce a Lexile measure, providing a reliable indicator of both reading ability and text difficulty.
What Age is a 1080 Lexile Level Suitable For?
The question "what age is a 1080 Lexile level suitable for?" is best answered by considering the typical reading development of students in middle school. A Lexile measure of 1080 is generally aligned with the reading ability expected of students in grades 6 to 8, which corresponds to ages 11 to 14. However, it's important to recognize that reading abilities can vary widely among students, and some may reach this level earlier or later than their peers.
Understanding Grade-Level Expectations
At a 1080 Lexile level, students should be able to comprehend complex narratives and informational texts, engaging with content that requires critical thinking and analysis. This level often includes texts with advanced vocabulary, intricate sentence structures, and sophisticated themes.
Individual Variability in Reading Development
While grade-level expectations provide a general guideline, individual students may progress at different rates due to a variety of factors, including:
- Exposure to Reading: Students with greater exposure to diverse reading materials may develop their skills more rapidly.
- Cognitive Abilities: Natural variations in cognitive development can influence reading comprehension and fluency.
- Instructional Support: The quality of instruction and support from educators and parents plays a key role in reading development.
Therefore, while a 1080 Lexile level is typical for middle school students, the primary focus should be on providing texts that match the individual learner's capacity to comprehend and engage.
Factors Affecting Reading Development
Reading development is influenced by a multitude of factors that shape a child's ability to understand and process written language. Recognizing these factors is essential for creating effective strategies to support literacy growth.
Environmental Influences
The environment in which a child is raised significantly impacts their reading development. Factors such as access to books, parental involvement, and encouragement to read play a crucial role in fostering a positive reading culture.
Cognitive and Linguistic Skills
Cognitive abilities, including memory, attention, and processing speed, are foundational to reading development. Additionally, linguistic skills such as vocabulary knowledge and phonemic awareness are critical components of reading proficiency.
Role of Socioeconomic Status
Socioeconomic status (SES) can affect access to reading materials and educational resources, potentially influencing reading development. Children from higher SES backgrounds often have greater exposure to books and educational opportunities, which can contribute to more advanced reading skills.
Instructional Quality and Support
The quality of instruction and the level of support provided by teachers and parents are vital in shaping a child's reading abilities. Effective instructional strategies, personalized learning experiences, and encouragement from adults foster a supportive learning environment.
How Can Parents Support Reading Development?
Parents play a pivotal role in nurturing their child's reading development. By creating a supportive and enriching reading environment, parents can significantly enhance their child's literacy skills.
Creating a Reading-Friendly Environment
To support reading development, parents can create a home environment that encourages reading:
- Provide a variety of age-appropriate books and reading materials.
- Designate a quiet and comfortable reading space.
- Establish regular reading routines, such as reading before bedtime.
Engaging in Reading Activities
Interactive reading activities foster a love for reading and improve comprehension skills. Parents can:
- Read aloud to their child to model fluent reading.
- Discuss the content of books to enhance understanding and critical thinking.
- Encourage their child to express opinions and make connections between texts and real-life experiences.
Selecting Appropriate Reading Materials
Choosing the right reading materials is crucial for promoting literacy development. The selection should be based on the child's interests, reading level, and educational goals.
Matching Texts with Interests
Children are more likely to engage with texts that align with their interests. Parents and educators can:
- Identify topics that captivate the child's curiosity.
- Select books with themes that resonate with the child's experiences.
- Encourage exploration of various genres to broaden reading exposure.
Considering Lexile Levels
Utilizing Lexile measures helps in selecting texts that are both challenging and accessible. It's important to:
- Choose texts within the child's Lexile range to ensure comprehension.
- Incorporate a mix of texts slightly below and above the child's level to build confidence and encourage growth.
Role of Educators in Enhancing Reading Skills
Educators are instrumental in shaping a student's reading abilities. Through effective teaching strategies and a supportive classroom environment, they can significantly impact literacy development.
Implementing Differentiated Instruction
Differentiated instruction involves tailoring teaching methods to meet the diverse needs of students. Educators can:
- Group students based on reading levels and provide targeted instruction.
- Utilize a variety of instructional materials to cater to different learning styles.
- Provide individualized feedback and support to foster improvement.
Promoting a Culture of Reading
Creating a classroom culture that values reading encourages students to engage with texts:
- Incorporate regular reading activities and discussions into the curriculum.
- Celebrate reading achievements to motivate students.
- Encourage peer collaboration and book sharing.
Balancing Challenge and Enjoyment in Reading
Striking a balance between challenging and enjoyable reading experiences is key to fostering a lifelong love for reading. It's important to ensure that reading is both stimulating and pleasurable.
Setting Realistic Reading Goals
Setting achievable reading goals helps students stay motivated and track their progress. Educators and parents can:
- Encourage goal-setting based on the child's interests and abilities.
- Regularly review and adjust goals to reflect progress and new challenges.
Incorporating Variety in Reading Materials
A diverse selection of reading materials keeps students engaged and prevents monotony. Consider offering:
- A mix of fiction and non-fiction texts.
- Different formats, such as graphic novels, eBooks, and audiobooks.
- Texts that relate to current events or cultural topics of interest.
Using Lexile Levels to Track Progress
Monitoring a student's reading progress through Lexile levels provides valuable insights into their literacy development. This information can guide instructional decisions and support the setting of realistic goals.
Assessing Growth Over Time
Regular assessments of Lexile levels allow educators and parents to track a student's reading growth. By comparing Lexile measures over time, they can identify trends in development and areas that may require additional support.
Adjusting Instructional Strategies
Based on Lexile data, educators can adjust their instructional strategies to better meet the needs of their students. This may involve providing more challenging texts or offering additional support for students who need it.
Common Misconceptions About Lexile Levels
While Lexile levels are a valuable tool in education, there are several misconceptions that may lead to their misuse.
Lexile Levels as the Sole Measure of Reading Ability
It's important to recognize that Lexile levels are just one measure of reading ability. They should be used in conjunction with other assessments and observations to provide a comprehensive understanding of a student's literacy skills.
Equating Lexile Levels with Grade Levels
While there is often a correlation between Lexile levels and grade levels, they are not synonymous. Individual reading abilities can vary widely, and Lexile measures should be used to guide, not dictate, educational decisions.
FAQs
What is a 1080 Lexile level?
A 1080 Lexile level indicates a reading ability typical of students in grades 6 to 8, corresponding to ages 11 to 14. It reflects the complexity of texts that these students are expected to comprehend.
How can I determine my child's Lexile level?
Your child's Lexile level can be determined through standardized reading assessments conducted at school. These assessments evaluate reading comprehension and provide a Lexile measure.
Can a Lexile level change over time?
Yes, a Lexile level can change over time as a student's reading abilities develop. Regular assessments can track progress and reflect improvements in reading skills.
Should I only choose books within my child's Lexile range?
While it's beneficial to select books within your child's Lexile range, it's also important to offer a variety of texts, including those slightly below and above their level, to promote growth and maintain interest.
Are Lexile levels applicable to all types of texts?
Lexile levels are primarily used for prose texts. Other factors may need to be considered for texts such as poetry, plays, or texts with significant visual elements.
How can educators use Lexile levels effectively?
Educators can use Lexile levels to match students with appropriate reading materials, set individualized reading goals, and track progress over time.
Conclusion
Understanding "what age is a 1080 Lexile level" is essential for selecting reading materials that align with a student's reading ability and promote literacy development. By leveraging Lexile measures, parents and educators can tailor reading experiences to foster both comprehension and enjoyment, ultimately nurturing a lifelong love of reading. It's important to recognize the variability in individual reading development and provide support that addresses the unique needs of each learner. Through thoughtful selection of texts and instructional strategies, we can empower young readers to reach their full potential.