In today's digital world, computers are an integral part of our daily lives, and any technical hiccup can cause significant disruptions. Safe Mode provides a simplified environment where you can troubleshoot and fix issues without interference from third-party applications or unnecessary drivers. It's an invaluable tool for IT professionals and everyday users alike, offering a straightforward way to diagnose and repair problems. With the right knowledge, booting into Safe Mode becomes a powerful strategy for maintaining your computer's health.
Whether you're dealing with software conflicts, malware infections, or hardware malfunctions, Safe Mode can be your first line of defense. It offers a clean slate to work with, stripping down your system to the essentials, and allowing you to pinpoint the cause of the issues. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore everything you need to know about booting into Safe Mode, including step-by-step instructions, troubleshooting tips, and answers to common questions. Get ready to empower yourself with the skills needed to tackle computer problems head-on!
What is Safe Mode?
Safe Mode is a diagnostic startup mode in operating systems like Windows and macOS. It's designed to help users troubleshoot and fix problems that may be affecting the normal operation of their computers. When you boot into Safe Mode, your system loads only the essential drivers and software components necessary for basic functionality. This stripped-down environment makes it easier to identify and resolve issues by eliminating potential conflicts caused by third-party applications or additional drivers.
Unlike normal mode, where all drivers and startup programs are loaded, Safe Mode focuses on the core components required for your computer to operate. This includes basic video drivers, system services, and essential hardware drivers. By minimizing the number of variables, Safe Mode provides a controlled environment for diagnosing problems. It's particularly useful when dealing with malware infections, software conflicts, or hardware malfunctions.
Safe Mode comes in different variations, such as Safe Mode with Networking and Safe Mode with Command Prompt, each offering additional capabilities for troubleshooting. Safe Mode with Networking, for example, includes the network drivers and services needed to access the internet or other network resources, while Safe Mode with Command Prompt provides a command-line interface for advanced troubleshooting tasks.
Why Boot into Safe Mode?
Booting into Safe Mode is a critical step when encountering issues with your computer. It allows you to:
- Diagnose and fix software-related problems without interference from third-party applications.
- Identify and remove malware infections that may be hindering your system's performance.
- Resolve hardware conflicts by isolating the core components needed for basic operation.
- Perform system maintenance tasks, such as disk cleanup and defragmentation, in a controlled environment.
Safe Mode is particularly useful when your computer is experiencing stability issues, crashes, or error messages. By booting into this mode, you can determine whether the problems are caused by software conflicts, hardware malfunctions, or other factors. Once the root cause is identified, you can take appropriate action to resolve the issues and restore normal functionality to your system.
Additionally, Safe Mode can be a valuable tool for IT professionals who need to troubleshoot and repair computers remotely. The simplified environment allows them to identify and fix problems without the need for physical access to the device. This can be especially beneficial in enterprise settings, where maintaining system stability and uptime is crucial.
Read also: Angela Bofill Daughter An Inspiring Legacy Explored
How to Boot into Safe Mode on Windows?
Booting into Safe Mode on a Windows computer is a straightforward process. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
- Restart your computer: Begin by restarting your computer. You can do this by clicking on the Start menu, selecting the Power button, and choosing Restart.
- Access Advanced Startup Options: As your computer restarts, press the F8 key repeatedly before the Windows logo appears. This will take you to the Advanced Startup Options menu.
- Select Safe Mode: Use the arrow keys to navigate through the options and select Safe Mode. Press Enter to boot into Safe Mode.
- Choose Safe Mode with Networking or Command Prompt: If you need internet access or command-line tools, select Safe Mode with Networking or Safe Mode with Command Prompt, respectively.
- Log in to your account: After booting into Safe Mode, log in with your user account credentials to access the desktop and begin troubleshooting.
If you're using Windows 10 or Windows 11, the process is slightly different:
- Open the Start menu: Click on the Start menu and select Settings.
- Navigate to Recovery: Go to Update & Security, then select Recovery from the left-hand menu.
- Access Advanced Startup: Under Advanced Startup, click Restart now. Your computer will restart and display the Choose an option screen.
- Select Troubleshoot: Click on Troubleshoot, then select Advanced options.
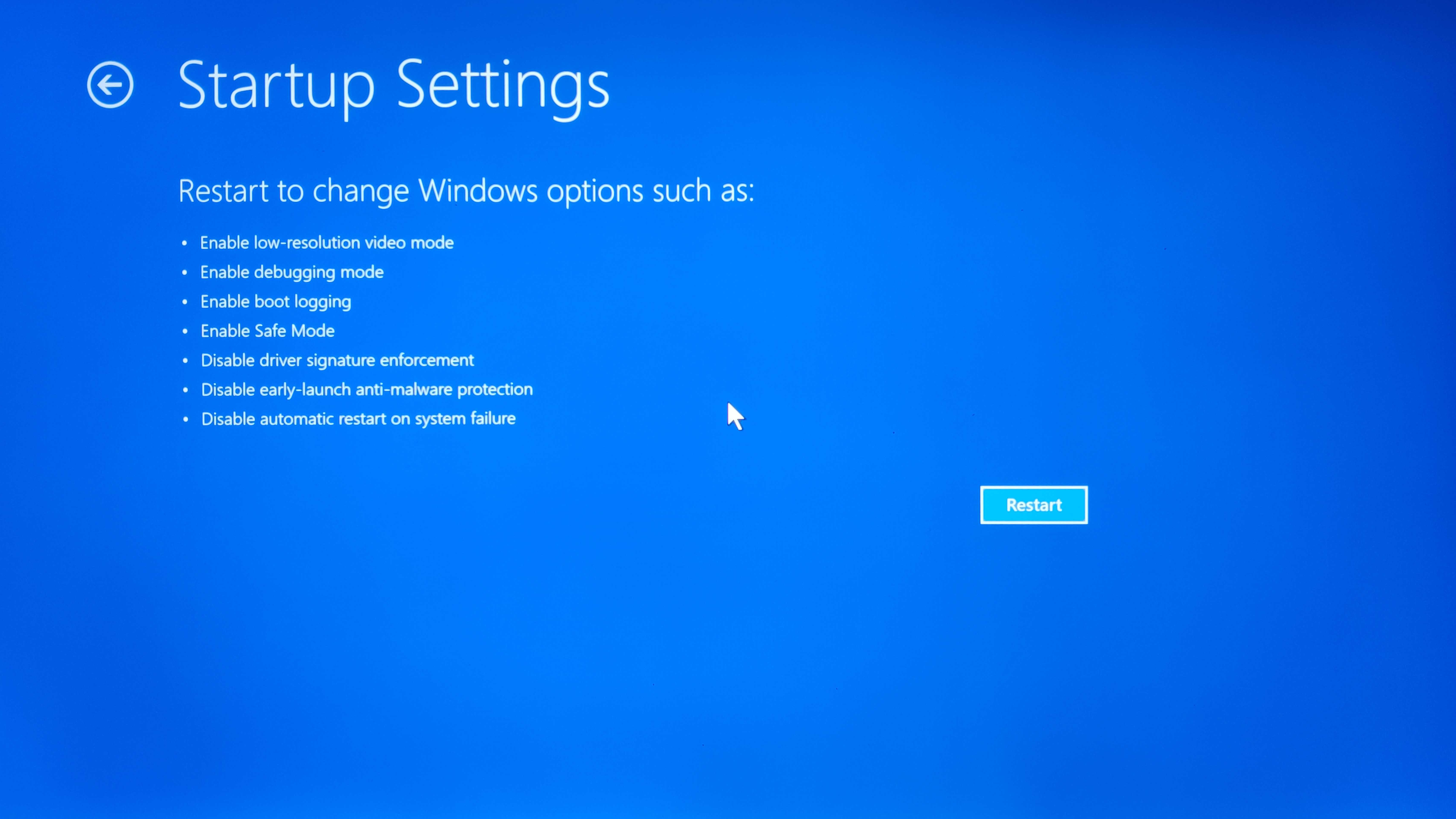
- Choose Startup Settings: Click on Startup Settings, then select Restart.
- Select Safe Mode: After your computer restarts, press F4 to boot into Safe Mode, F5 for Safe Mode with Networking, or F6 for Safe Mode with Command Prompt.
By following these steps, you can easily boot into Safe Mode on your Windows computer and begin diagnosing and resolving any issues you may be experiencing.
How to Boot into Safe Mode on a Mac?
Booting into Safe Mode on a Mac is a bit different from Windows, but it's equally simple. Follow these steps to start your Mac in Safe Mode:
- Shut down your Mac: Begin by shutting down your Mac completely. You can do this by clicking on the Apple menu and selecting Shut Down.
- Wait a few seconds: Once your Mac is off, wait a few seconds before proceeding to the next step.
- Press and hold the Shift key: Turn on your Mac by pressing the power button, and immediately press and hold the Shift key.
- Release the Shift key: Release the Shift key when you see the login window. Your Mac will now be in Safe Mode.
- Log in to your account: Enter your user account credentials to log in and access the desktop in Safe Mode.
While in Safe Mode, your Mac will perform a basic check of your startup disk, disable third-party extensions, and load only essential system components. This provides a clean environment for troubleshooting and resolving issues. It's important to note that some features, like Wi-Fi and certain hardware devices, may not work while in Safe Mode.
To exit Safe Mode and return to normal operation, simply restart your Mac without holding any keys. Your system will boot back into its regular mode, allowing you to verify whether the issues have been resolved.
Benefits of Booting into Safe Mode
Booting into Safe Mode offers several benefits for diagnosing and resolving computer issues. Some of the key advantages include:
- Isolation of Potential Conflicts: Safe Mode disables non-essential drivers and third-party applications, allowing you to isolate and identify the root cause of problems without interference.
- Enhanced Security: By booting into Safe Mode, you can perform security scans and remove malware without it being active or interfering with the scanning process.
- System Maintenance: Safe Mode provides a controlled environment for performing system maintenance tasks, such as disk cleanup, defragmentation, and error checking.
- Resource Management: With minimal drivers and services running, Safe Mode conserves system resources, making it easier to troubleshoot performance-related issues.
- Repair and Recovery: Safe Mode allows you to access recovery tools and system restore points, enabling you to repair system files and recover from major system failures.
These benefits make Safe Mode an invaluable tool for both novice and experienced users. It provides a straightforward way to address a wide range of issues, from software conflicts to hardware malfunctions, ensuring your computer remains in optimal condition.
Troubleshooting with Safe Mode
Troubleshooting with Safe Mode involves a systematic approach to identifying and resolving computer problems. Here are some common troubleshooting steps you can take while in Safe Mode:
- Uninstall Problematic Software: If you've recently installed a program that's causing issues, boot into Safe Mode and uninstall it. This can help resolve software conflicts and restore system stability.
- Update Drivers: Outdated or incompatible drivers can cause hardware malfunctions. In Safe Mode, you can update or roll back drivers to resolve these issues.
- Run Antivirus Scans: Safe Mode allows you to run antivirus scans without interference from active malware, making it easier to detect and remove infections.
- Perform System Restore: Use the System Restore feature to revert your computer to a previous state when it was functioning correctly, undoing recent changes that may have caused problems.
- Check Disk for Errors: Run disk error-checking tools to identify and repair file system errors that may be affecting your computer's performance or stability.
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can effectively diagnose and resolve a wide range of computer issues, ensuring your device operates smoothly and efficiently.
Common Issues Resolved by Safe Mode
Safe Mode is a powerful tool for addressing a variety of computer issues. Some of the common problems that can be resolved by booting into Safe Mode include:
- Software Conflicts: Safe Mode helps identify and resolve conflicts between software applications, ensuring compatibility and stability.
- Driver Issues: Incompatible or outdated drivers can cause hardware malfunctions. Safe Mode allows you to update or roll back drivers to fix these problems.
- Malware Infections: Safe Mode disables active malware, making it easier to run antivirus scans and remove infections.
- System Crashes: By isolating the core system components, Safe Mode helps diagnose and fix issues that cause system crashes or freezes.
- Performance Problems: Safe Mode conserves system resources, allowing you to identify and address performance-related issues more effectively.
These are just a few examples of the issues that can be resolved by booting into Safe Mode. By understanding how to use this diagnostic tool, you can tackle a wide range of problems and keep your computer running smoothly.
Safe Mode vs. Normal Mode
The primary difference between Safe Mode and Normal Mode lies in the components loaded during startup. In Normal Mode, your computer loads all drivers, services, and startup programs, providing full functionality and support for all hardware and software components. This mode is ideal for everyday use, offering a complete user experience with access to all features and applications.
In contrast, Safe Mode loads only the essential drivers and services needed for basic operation. This includes minimal video drivers, core system services, and essential hardware drivers. By reducing the number of variables, Safe Mode provides a controlled environment for diagnosing and resolving issues. While in Safe Mode, certain features and applications may be unavailable, as the focus is on troubleshooting and repair.
Understanding the differences between Safe Mode and Normal Mode is crucial for effective troubleshooting. Safe Mode is a valuable tool for diagnosing and fixing problems, while Normal Mode offers a complete and fully functional user experience for everyday tasks.
Advanced Safe Mode Options
For users seeking additional troubleshooting capabilities, advanced Safe Mode options provide enhanced functionality. These options include:
- Safe Mode with Networking: This option loads the network drivers and services needed to access the internet or other network resources, allowing you to perform online troubleshooting tasks.
- Safe Mode with Command Prompt: This option provides access to a command-line interface for advanced troubleshooting tasks, such as running diagnostic commands or script-based repairs.
- Enable Boot Logging: This option creates a log file of all drivers and services loaded during startup, helping you identify any components causing issues.
- Enable Low-Resolution Video: This option loads basic video drivers, allowing you to troubleshoot display-related issues without interference from higher-resolution settings.
These advanced Safe Mode options offer additional tools for diagnosing and resolving complex computer issues. By understanding how to utilize these features, you can enhance your troubleshooting capabilities and address a wider range of problems.
How to Exit Safe Mode?
Exiting Safe Mode is a simple process that allows your computer to return to its normal operating state. Here's how to exit Safe Mode on both Windows and macOS:
Exiting Safe Mode on Windows:
- Restart your computer: Click on the Start menu, select the Power button, and choose Restart. Your computer will boot back into Normal Mode.
- Use System Configuration: Press Windows + R to open the Run dialog, type "msconfig" and press Enter. In the System Configuration window, go to the Boot tab and uncheck the "Safe boot" option. Click Apply, then OK, and restart your computer.
Exiting Safe Mode on macOS:
- Restart your Mac: Click on the Apple menu and select Restart. Your Mac will boot back into Normal Mode.
Exiting Safe Mode allows your computer to resume full functionality, enabling you to verify whether the issues have been resolved and continue using your device for everyday tasks.
Safe Mode and Security
Safe Mode plays an important role in enhancing computer security by providing a controlled environment for detecting and removing malware. By disabling unnecessary drivers and services, Safe Mode minimizes the risk of interference from active malware, making it easier to run antivirus scans and other security tools.
In addition to malware removal, Safe Mode allows you to perform security-related tasks, such as updating antivirus software, configuring firewall settings, and removing unauthorized applications. These measures help protect your computer from potential threats and ensure your system remains secure.
While Safe Mode is a valuable tool for enhancing security, it's important to remember that it should be used in conjunction with other security practices, such as regular software updates, strong passwords, and safe browsing habits. By combining Safe Mode with these practices, you can create a comprehensive security strategy that protects your computer from a wide range of threats.
Safe Mode on Different Devices
Safe Mode is not limited to traditional computers; it's also available on other devices, such as smartphones and tablets. While the process for booting into Safe Mode varies depending on the device, the purpose remains the same: to provide a simplified environment for troubleshooting and repair.
On Android devices, for example, Safe Mode can be accessed by pressing and holding the power button, then tapping and holding the "Power off" option until the Safe Mode prompt appears. On iOS devices, troubleshooting options are available through recovery mode and DFU mode, which allow you to perform system repairs and updates.
Understanding how to access Safe Mode on different devices expands your troubleshooting capabilities, allowing you to address issues on a wide range of platforms. By familiarizing yourself with the process for each device, you can ensure your devices remain in optimal condition and continue to operate smoothly.
What to Do if Safe Mode Doesn't Work?
If booting into Safe Mode doesn't resolve the issues you're experiencing, there are several additional troubleshooting steps you can take:
- Perform a System Restore: Use the System Restore feature to revert your computer to a previous state when it was functioning correctly.
- Run a Startup Repair: Use the Startup Repair tool to automatically fix problems that may be preventing your computer from starting properly.
- Check for Hardware Issues: Run hardware diagnostics to identify and resolve any hardware-related problems that may be affecting your computer's performance.
- Seek Professional Help: If you're unable to resolve the issues on your own, consider seeking assistance from a professional technician or IT support service.
By taking these additional steps, you can effectively address more complex issues and restore your computer to full functionality.
FAQs
1. Can I access the internet in Safe Mode?
Yes, you can access the internet in Safe Mode by selecting the "Safe Mode with Networking" option. This mode loads the necessary network drivers and services to enable internet connectivity.
2. Will Safe Mode delete my files?
No, booting into Safe Mode does not delete any files. It simply loads a minimal set of drivers and services for troubleshooting purposes. Your files and data remain intact.
3. How do I know if I'm in Safe Mode?
When you're in Safe Mode, you'll notice a "Safe Mode" label in the corners of the screen. Additionally, the resolution may be lower, and certain features or applications may be unavailable.
4. Can I use Safe Mode to remove viruses?
Yes, Safe Mode can be used to remove viruses by running antivirus scans without interference from active malware. It's an effective way to detect and remove infections.
5. Why does my computer keep booting into Safe Mode?
If your computer keeps booting into Safe Mode, it may be due to a configuration setting or a persistent issue. Check the System Configuration settings and ensure "Safe boot" is unchecked.
6. Is Safe Mode the same on all devices?
While the purpose of Safe Mode remains the same across devices, the process for accessing it may vary. Familiarize yourself with the specific steps for each device to effectively troubleshoot issues.
Conclusion
Booting into Safe Mode is an essential skill for diagnosing and resolving computer issues. Whether you're dealing with software conflicts, malware infections, or hardware malfunctions, Safe Mode provides a simplified environment for troubleshooting and repair. By understanding how to access and utilize Safe Mode, you can effectively address a wide range of problems and ensure your computer remains in optimal condition.
Incorporating Safe Mode into your troubleshooting toolkit empowers you to take control of your device's health and performance. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can confidently tackle computer issues and maintain a smooth, efficient computing experience. Remember, Safe Mode is just one part of a comprehensive approach to computer maintenance and security, so be sure to combine it with other best practices for optimal results.