The symbiotic relationship between the sun and the moon has been a subject of fascination and wonder for centuries. These celestial bodies, while vastly different in size, energy, and composition, work together in a delicate balance that impacts life on Earth in profound ways. By understanding this relationship, we gain insight into the natural rhythms that govern our planet and the universe beyond. From the tides that ebb and flow with the moon's pull to the life-giving energy of the sun, their interaction is a testament to the interconnectedness of all things in the cosmos.
Throughout history, cultures around the world have looked to the sun and the moon for guidance, inspiration, and understanding. These luminaries have been revered as gods, symbols of power, and markers of time. Modern science has uncovered even more about their relationship, revealing the complex gravitational dance that keeps our planet in a stable orbit. This celestial partnership affects everything from our climate to the biological rhythms of plants and animals, illustrating the profound impact these entities have on life as we know it.
In this comprehensive exploration, we will delve into the many facets of the symbiotic relationship between the sun and the moon. We'll examine the physics behind their interactions, how they influence Earth's environment, and the cultural significance they've held throughout human history. By the end of this article, you'll have a deeper appreciation for these celestial giants and the harmonious balance they maintain, which is crucial for sustaining life on our planet.
Read also:The Ultimate Guide To Babysitting Jobs For Teens Everything You Need To Know
Table of Contents
- Celestial Dynamics: How do the Sun and Moon Interact?
- Gravitational Influences on Earth
- How do the Sun and Moon Affect Tides and Ocean Currents?
- Solar Energy and Its Impact on Earth
- What Causes the Phases of the Moon?
- Eclipses: The Dance of Shadows
- Cultural Significance of the Sun and Moon
- Astronomical Observation and Discoveries
- Biological Rhythms: The Sun, the Moon, and Life Cycles
- How Do the Sun and Moon Influence Climate?
- Mythology and Mysticism Surrounding the Sun and Moon
- Future Exploration: What Lies Ahead in Celestial Studies?
- Symbiosis in Nature: Lessons from the Sun and Moon
- FAQs
- Conclusion: The Eternal Cosmic Ballet
Celestial Dynamics: How do the Sun and Moon Interact?
The sun and the moon, though vastly different in nature, engage in a fascinating cosmic interaction that defines much of Earth's natural phenomena. The sun, a massive ball of gas, is the primary source of energy for our planet. It provides the heat and light necessary for life, driving the processes of photosynthesis and influencing weather patterns. The moon, on the other hand, is Earth's natural satellite, significantly smaller and lacking its own light. It reflects the sun's light, illuminating our night sky and exerting a gravitational pull that affects our planet in myriad ways.
Their interaction is primarily governed by gravitational forces. The sun's gravity keeps the Earth in orbit, while the moon's gravity causes the ocean tides and stabilizes the Earth's axial tilt. This stability is crucial for maintaining a consistent climate, which in turn supports diverse ecosystems. The sun and moon's gravitational relationship is a prime example of celestial mechanics, illustrating the delicate balance of forces in our solar system.
In addition to gravity, the electromagnetic radiation from the sun plays a significant role in this symbiotic relationship. Solar radiation influences the Earth's atmosphere and can impact the moon's surface by causing temperature fluctuations and even slight shifts in its orbit. The moon, in response, reflects this radiation back to Earth, enhancing nighttime visibility and, in some cases, affecting nocturnal wildlife behavior.
Gravitational Influences on Earth
The gravitational pull between the sun, the moon, and the Earth is a powerful force that orchestrates a variety of natural phenomena. The most observable effect of this gravitational interaction is the ocean tides. The moon's gravity pulls on the Earth's water, creating high and low tides as it orbits our planet. The sun's gravity also contributes to tidal forces, albeit to a lesser extent. When the sun, moon, and Earth align during full and new moons, we experience spring tides, which are higher than usual. Conversely, when the sun and moon are at right angles relative to the Earth, we experience neap tides, which are lower.
Beyond tides, the gravitational influence of the sun and moon helps stabilize the Earth's axial tilt. This tilt is responsible for the changing seasons, as different parts of the Earth receive varying amounts of sunlight throughout the year. The moon's gravitational pull prevents the Earth's tilt from fluctuating wildly, which would otherwise lead to severe climate changes and potentially disrupt life.
The gravitational relationship between these celestial bodies also affects Earth's rotation. The moon exerts a torque on the Earth, gradually slowing its rotation over long periods. This process, known as tidal friction, is gradually lengthening the day by approximately 1.7 milliseconds per century. While this change is imperceptible on a human timescale, it demonstrates the profound influence of celestial mechanics on our planet.
Read also:Discover Hilton Suites Ocean City Your Oceanfront Paradise
How do the Sun and Moon Affect Tides and Ocean Currents?
The interplay between the sun and the moon is most prominently observed in the movement of Earth's oceans. Tides, the regular rising and falling of sea levels, are primarily driven by the gravitational pull of the moon, with the sun playing a secondary role. The moon's gravitational force causes the water on Earth to bulge out in the direction of the moon, creating what we perceive as high tide. As the Earth rotates, different areas experience these tidal effects, leading to the rhythmic ebb and flow of the oceans.
When the sun, moon, and Earth are aligned, the gravitational forces combine to produce spring tides, which are higher and lower than average tides. In contrast, neap tides occur when the sun and moon are at right angles relative to the Earth, resulting in weaker tidal forces. These tidal patterns play a crucial role in marine ecosystems, influencing the distribution of nutrients, the behavior of marine organisms, and the overall health of coastal environments.
Ocean currents, though primarily driven by wind patterns and the Earth's rotation, are also affected by the gravitational forces of the sun and moon. These currents are essential for regulating the Earth's climate by redistributing heat across the planet. The interplay between tides and currents shapes coastal landscapes, affects weather patterns, and influences global climate systems. Understanding this dynamic interaction is key to comprehending the full impact of the symbiotic relationship between the sun and the moon.
Solar Energy and Its Impact on Earth
Solar energy, the radiant light and heat emitted by the sun, is the primary source of energy for life on Earth. This energy drives the processes of photosynthesis, enabling plants to convert sunlight into chemical energy, which forms the base of the food chain. Without the sun's energy, life as we know it would not exist. The sun's influence extends beyond biological processes, affecting weather patterns, climate, and even the Earth's magnetic field.
The sun's energy is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, oceans, and land, driving weather systems and influencing climate. Solar radiation causes air to warm, rise, and circulate, creating wind patterns and contributing to the formation of clouds and precipitation. This process is essential for maintaining the Earth's climate balance and supporting diverse ecosystems. The distribution of solar energy across the planet also affects temperature gradients, leading to the development of ocean currents that regulate global climate.
In recent years, solar energy has gained prominence as a renewable energy source, offering a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. Advances in technology have enabled us to harness this energy through solar panels, converting sunlight into electricity to power homes, businesses, and industries. This shift towards solar energy has the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, mitigate climate change, and create a more sustainable future. Understanding the sun's role in this context highlights the importance of the symbiotic relationship between the sun and the moon in shaping our planet's environment.
What Causes the Phases of the Moon?
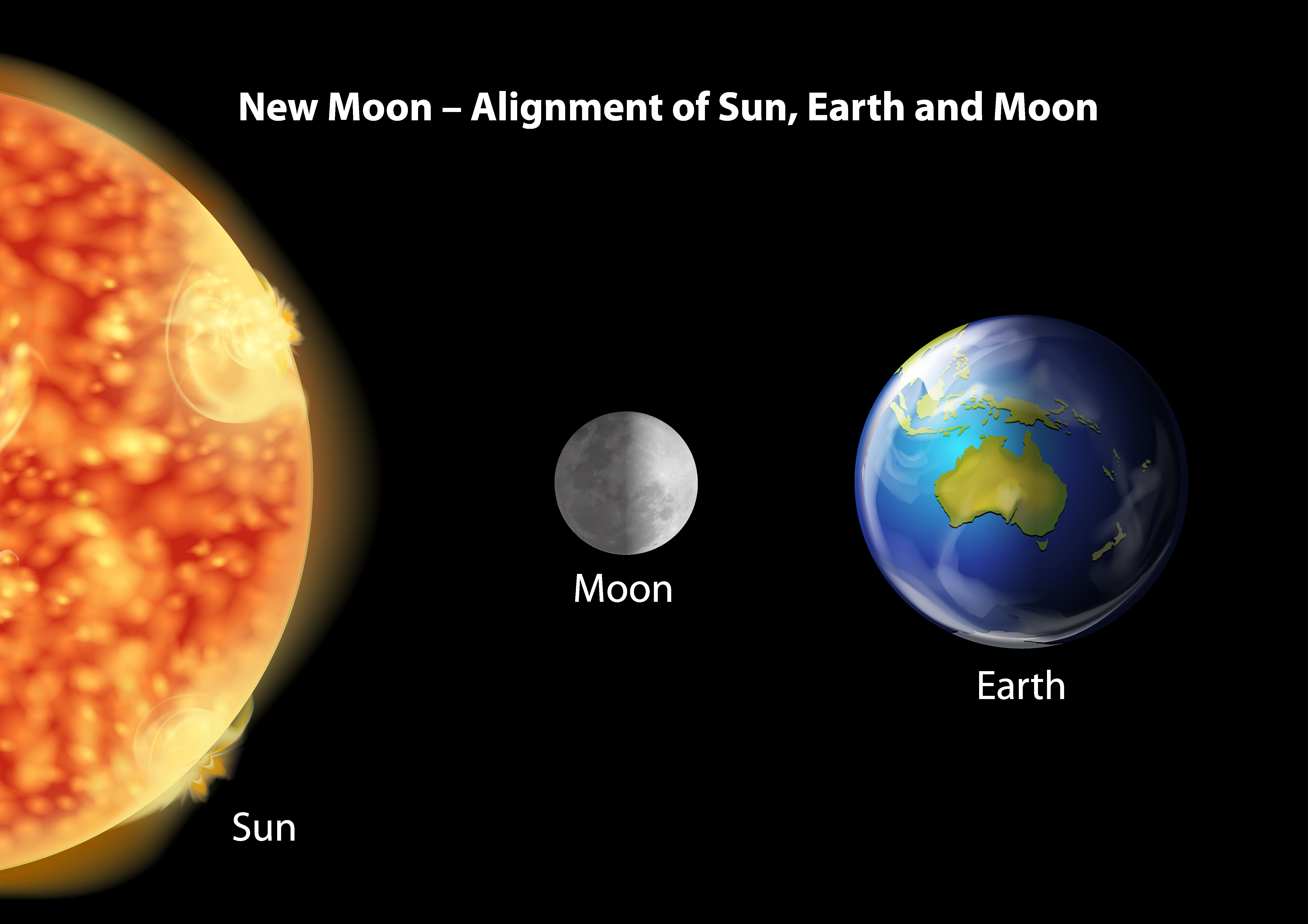
The phases of the moon, a mesmerizing celestial phenomenon, are a direct result of its position relative to the Earth and the sun. As the moon orbits the Earth, different portions of its surface are illuminated by the sun, creating the phases we observe from our planet. These phases, which cycle approximately every 29.5 days, include the new moon, waxing crescent, first quarter, waxing gibbous, full moon, waning gibbous, last quarter, and waning crescent.
The new moon occurs when the moon is positioned between the Earth and the sun, with its illuminated side facing away from us. As the moon progresses in its orbit, more of its illuminated side becomes visible, leading to the waxing crescent phase. The first quarter phase occurs when half of the moon's illuminated side is visible from Earth. This pattern continues with the waxing gibbous phase until the full moon, when the entire illuminated side is visible.
After the full moon, the cycle reverses with the waning gibbous phase, followed by the last quarter, waning crescent, and finally, the new moon again. These phases have been used throughout history to mark time, influence cultural practices, and guide agricultural activities. The moon's phases also impact natural phenomena, such as animal behavior and plant growth, illustrating the profound influence of the symbiotic relationship between the sun and the moon on life on Earth.
Eclipses: The Dance of Shadows
Eclipses, captivating celestial events, occur when the sun, moon, and Earth align in a way that causes one body to cast a shadow on another. There are two main types of eclipses: solar eclipses and lunar eclipses. Solar eclipses happen when the moon passes between the Earth and the sun, casting a shadow on the Earth's surface and blocking the sun's light. Depending on the alignment, solar eclipses can be total, partial, or annular. During a total solar eclipse, the moon completely covers the sun, revealing the sun's outer atmosphere, known as the corona, in a breathtaking display.
Lunar eclipses, on the other hand, occur when the Earth is positioned between the sun and the moon, causing the Earth's shadow to fall on the moon. These eclipses can be total, partial, or penumbral, depending on the degree of alignment. During a total lunar eclipse, the moon takes on a reddish hue, often referred to as a "blood moon," due to the Earth's atmosphere scattering sunlight and allowing only red wavelengths to reach the moon's surface.
Eclipses have long been sources of wonder and awe, inspiring myths and legends across cultures. They serve as reminders of the intricate dance of celestial bodies and the symbiotic relationship between the sun and the moon. Understanding eclipses provides valuable insights into the mechanics of our solar system and the forces that govern the universe.
Cultural Significance of the Sun and Moon
The sun and the moon have held significant cultural importance throughout human history. They have been revered, worshipped, and celebrated in countless ways, forming the basis of myths, legends, and religious practices across different cultures. The sun, with its life-giving energy and light, has often been associated with deities of power, vitality, and creation. Many ancient civilizations, such as the Egyptians, Aztecs, and Greeks, worshipped sun gods, believing them to be essential for the sustenance of life and the continuity of time.
The moon, with its mysterious phases and nightly presence, has been linked to deities of femininity, fertility, and change. It has been a symbol of time, guiding agricultural practices and marking the passage of months. In many cultures, lunar calendars were developed based on the moon's cycles, influencing religious observances and societal events. The moon's role in shaping tides and its connection to the natural world further emphasized its cultural significance.
The symbiotic relationship between the sun and the moon is often depicted in folklore and mythology as a cosmic dance, symbolizing balance and harmony. This relationship has inspired art, music, literature, and rituals, reflecting humanity's deep connection to these celestial bodies. By understanding their cultural significance, we gain insight into the diverse ways in which the sun and moon have shaped human history and continue to influence our lives today.
Astronomical Observation and Discoveries
Throughout history, the sun and the moon have been subjects of astronomical observation and study, leading to significant discoveries about our solar system and the universe. Ancient astronomers meticulously tracked the movements of these celestial bodies, developing early calendars and understanding the cycles of the heavens. The study of the sun and moon laid the foundation for the field of astronomy, leading to advancements in mathematics, physics, and navigation.
One of the most significant contributions to our understanding of the sun and moon came with the development of the heliocentric model by Nicolaus Copernicus in the 16th century. This model proposed that the Earth and other planets orbit the sun, challenging the previously accepted geocentric model. Copernicus's work, along with observations by astronomers like Galileo Galilei and Johannes Kepler, revolutionized our understanding of the solar system and the symbiotic relationship between the sun and the moon.
Modern astronomy continues to explore the sun and moon through advanced telescopes, space missions, and satellite technology. The study of solar and lunar phenomena has provided insights into the nature of celestial bodies, the dynamics of our solar system, and the potential for life beyond Earth. Astronomical observation remains a vital tool for unraveling the mysteries of the universe and deepening our understanding of the symbiotic relationship between the sun and the moon.
Biological Rhythms: The Sun, the Moon, and Life Cycles
The sun and the moon play crucial roles in regulating biological rhythms and life cycles on Earth. These celestial bodies influence the behavior, physiology, and ecology of organisms through their respective cycles of light and gravity. The sun's daily cycle of light and darkness governs the circadian rhythms of most living organisms, dictating patterns of activity, sleep, and metabolism. These rhythms are essential for maintaining homeostasis and ensuring the survival of species.
The moon, with its phases and gravitational pull, also affects biological rhythms. Many marine organisms, such as fish and corals, synchronize their reproductive cycles with the lunar phases, taking advantage of the increased tidal activity to enhance their chances of successful reproduction. The moon's influence extends to terrestrial animals as well, with some species exhibiting heightened activity during full moons or adapting their behaviors to the changing light conditions.
Plants, too, are impacted by the sun and moon. Solar energy drives photosynthesis, enabling plants to grow and produce food, while the moon's gravitational pull can affect the movement of water within plant tissues. Understanding these biological rhythms and their connection to the sun and moon highlights the profound impact of the symbiotic relationship between these celestial bodies and life on Earth.
How Do the Sun and Moon Influence Climate?
The sun and the moon are key players in shaping Earth's climate, influencing weather patterns, temperature, and precipitation. The sun's energy drives the Earth's climate system, providing the heat necessary for atmospheric circulation and the formation of weather patterns. Solar radiation varies with the Earth's tilt and orbit, causing the changing seasons and affecting temperature gradients across the planet. These variations play a crucial role in determining regional climates and supporting diverse ecosystems.
The moon, though not a direct source of energy, influences climate through its gravitational pull, which affects ocean tides and currents. Tidal forces contribute to the mixing of ocean waters, distributing heat and nutrients and impacting global climate systems. The moon's presence also stabilizes the Earth's axial tilt, preventing dramatic shifts in climate that could result from a more erratic orbit.
While the sun and moon are natural drivers of climate, human activities have increasingly disrupted these systems through the release of greenhouse gases and other pollutants. Understanding the natural influences of the sun and moon on climate is essential for developing strategies to mitigate the impacts of climate change and preserve the delicate balance of Earth's environment.
Mythology and Mysticism Surrounding the Sun and Moon
The sun and the moon have been central figures in mythology and mysticism for millennia, embodying the mysteries of the cosmos and the duality of existence. Myths and legends from cultures around the world have sought to explain the origins, movements, and interactions of these celestial bodies, weaving stories that reflect human understanding of the universe and our place within it.
In many mythologies, the sun is depicted as a powerful deity, a symbol of life, strength, and creation. The ancient Egyptians revered Ra, the sun god, as the king of the gods and the creator of all things. Similarly, in Hindu mythology, the sun god Surya is worshipped as the source of light and life. The moon, in contrast, is often associated with mystery, change, and the feminine. In Greek mythology, the goddess Selene personifies the moon, riding her chariot across the night sky.
These myths and legends highlight the enduring fascination with the symbiotic relationship between the sun and the moon and their influence on human life. Mystical beliefs and practices, such as astrology, have also drawn on the movements and positions of these celestial bodies to interpret human destinies and events. While modern science has provided explanations for the phenomena once attributed to myth, the cultural and symbolic significance of the sun and moon remains deeply ingrained in our collective consciousness.
Future Exploration: What Lies Ahead in Celestial Studies?
The study of the sun and moon continues to evolve, driven by advances in technology and a deepening understanding of the universe. Future exploration efforts aim to uncover new insights into the symbiotic relationship between these celestial bodies and their impact on Earth and beyond. One area of focus is the continued observation of solar and lunar phenomena, such as solar flares, sunspots, and lunar surface changes, using sophisticated telescopes and satellites.
Space missions, such as NASA's Artemis program, plan to return humans to the moon and establish a sustainable presence, paving the way for future exploration of Mars and other celestial bodies. These missions will provide valuable opportunities to study the moon's geology, atmosphere, and potential resources, enhancing our understanding of its role in the solar system and its relationship with the sun.
Additionally, the study of exoplanets and their potential for hosting life is a growing field of interest. By examining the sun and moon's interactions, scientists can draw parallels with other star-planet-moon systems, offering clues about the conditions necessary for life elsewhere in the universe. As our exploration of the cosmos continues, the symbiotic relationship between the sun and the moon will remain a central theme, guiding our quest for knowledge and discovery.
Symbiosis in Nature: Lessons from the Sun and Moon
The symbiotic relationship between the sun and the moon serves as a powerful metaphor for the interconnectedness of all things in nature. Just as these celestial bodies rely on each other to maintain the balance of forces in our solar system, living organisms on Earth engage in symbiotic relationships that sustain ecosystems and promote biodiversity. These interactions, whether mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasitic, illustrate the complex web of life and the interdependence of species.
Mutualistic symbiosis, where both parties benefit, is exemplified by the relationship between bees and flowering plants. Bees pollinate flowers while collecting nectar, aiding plant reproduction and receiving nourishment in return. Commensalism occurs when one organism benefits without affecting the other, as seen in barnacles attaching to whales to gain mobility and access to food. Parasitic relationships, such as those between ticks and mammals, involve one organism benefiting at the expense of the other.
These symbiotic relationships in nature mirror the balance and harmony exemplified by the sun and moon. By studying these interactions, we gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of life and the importance of preserving biodiversity. The lessons of symbiosis remind us of our responsibility to protect the delicate equilibrium of our planet and the symbiotic relationship between the sun and the moon.
FAQs
- How do the sun and moon affect Earth's tides?
- What is the significance of the moon's phases?
- How do solar and lunar eclipses occur?
- Why are the sun and moon important in various cultures?
- How do the sun and moon influence Earth's climate?
- What future explorations are planned for studying the moon?
Conclusion: The Eternal Cosmic Ballet
The symbiotic relationship between the sun and the moon is a testament to the intricate balance of forces that govern our universe. This celestial partnership influences life on Earth in profound ways, from regulating tides and biological rhythms to shaping climate and cultural practices. By understanding this relationship, we gain insight into the natural rhythms that sustain our planet and the interconnectedness of all things in the cosmos.
The sun and moon's interactions serve as a reminder of the delicate equilibrium that exists in nature and the importance of preserving this balance for future generations. As we continue to explore and study these celestial bodies, we deepen our understanding of the universe and our place within it. The eternal cosmic ballet of the sun and the moon will remain a source of inspiration and wonder, guiding our quest for knowledge and discovery in the vast expanse of space.
In this exploration, we have uncovered the many facets of the symbiotic relationship between the sun and the moon, highlighting their significance in science, culture, and nature. By appreciating the harmony between these celestial giants, we foster a greater connection to the universe and our shared journey through the cosmos.