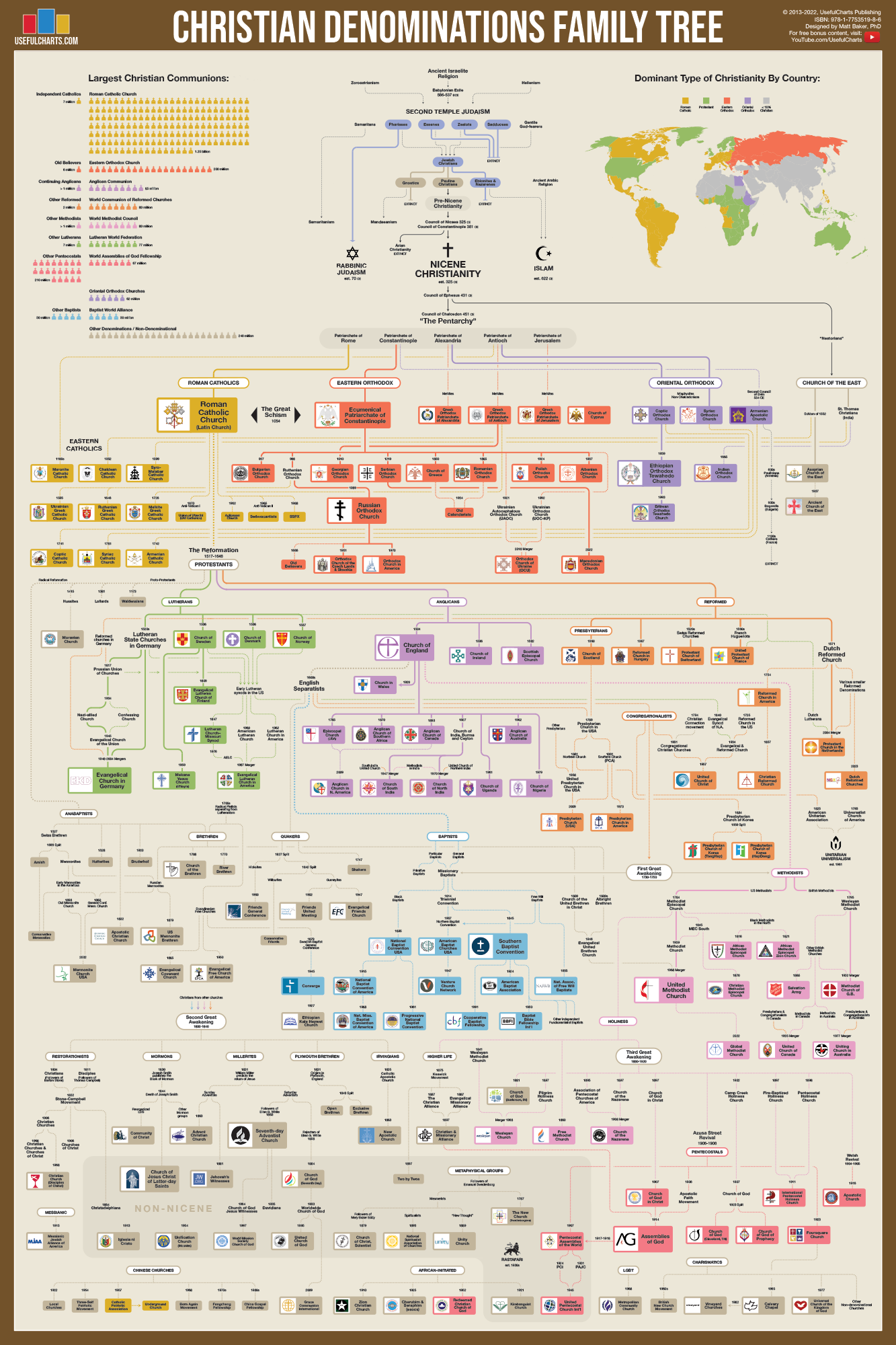
Europe, a continent rich in history and culture, is home to a vast array of Christian denominations, each contributing to the religious tapestry that has shaped the region's identity for centuries. From the grand cathedrals of the Roman Catholic Church to the humble chapels of Protestant congregations, the diversity of Christian beliefs and practices in Europe is indeed remarkable. With the rise of new religious movements and the enduring presence of ancient traditions, understanding the different Christian denominations in Europe offers insights into the continent's complex spiritual landscape.
The history of Christianity in Europe is a tale of transformation and evolution. Over the centuries, various events such as the Great Schism, the Reformation, and the Enlightenment have left indelible marks on the continent's religious fabric. These events led to the formation of distinct Christian denominations, each with unique beliefs, practices, and cultural influences. Today, Europe remains a pivotal region for Christianity, hosting a myriad of denominations that continue to shape the spiritual and social life of its inhabitants.
In this article, we will delve deep into the Christian denominations in Europe, exploring their origins, beliefs, and impact on society. We will examine the major branches of Christianity present in Europe, including Roman Catholicism, Eastern Orthodoxy, and Protestantism, among others. Additionally, we will discuss the role of Christianity in contemporary European society and its influence on culture, politics, and social issues. Through this comprehensive exploration, readers will gain a clearer understanding of the religious diversity that characterizes Europe and the significant role that Christianity plays in the region's past, present, and future.
Read also:Escape To Tranquil Wardle Fields Regional Park A Haven For Nature Lovers
Table of Contents
- The Historical Evolution of Christianity in Europe
- The Roman Catholic Church: A Dominant Force
- Understanding Eastern Orthodoxy in Europe
- Protestant Denominations and Their Impact
- What is Anglicanism?
- Exploring Lutheranism's Influence
- Calvinism: A Theological Perspective
- The Rise of Methodism in Europe
- Who are the Baptists?
- Pentecostalism: A Modern Movement
- Smaller Christian Denominations in Europe
- Christianity's Role in Contemporary European Society
- The Cultural Impact of Christianity in Europe
- Christianity's Political Influence in Europe
- What Does the Future Hold for Christianity in Europe?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
The Historical Evolution of Christianity in Europe
The story of Christianity in Europe is one of profound change, marked by significant historical events that have shaped its development. The spread of Christianity began in the Roman Empire, with early communities forming in major cities such as Rome and Constantinople. Over time, the religion expanded across the continent, influenced by various cultural and political contexts. Several key events played pivotal roles in the evolution of Christianity in Europe:
- The Edict of Milan (313 AD): This decree by Emperor Constantine legalized Christianity, allowing it to spread more freely across the Roman Empire.
- The Great Schism (1054 AD): Marked the division between the Roman Catholic Church and the Eastern Orthodox Church, leading to distinct developments in Christian theology and practice.
- The Protestant Reformation (16th century): Initiated by figures like Martin Luther and John Calvin, this movement challenged the authority of the Catholic Church and resulted in the formation of various Protestant denominations.
Through these and other events, Christianity in Europe diversified into a multitude of denominations, each with its own beliefs and traditions. This rich tapestry of faith continues to influence European culture and society.
The Roman Catholic Church: A Dominant Force
The Roman Catholic Church has been a central pillar of Christianity in Europe for centuries. As the largest Christian denomination, it boasts a significant following and plays a vital role in European religious life. The Church's influence extends beyond religious matters, impacting various aspects of culture and politics. Key characteristics of the Roman Catholic Church include:
- Papal Authority: The Pope, as the spiritual leader, holds significant authority over the Church's doctrine and governance.
- Sacraments: The Church emphasizes the importance of sacraments, such as baptism, Eucharist, and confirmation, as essential elements of faith practice.
- Tradition and Scripture: Catholic theology is built on a combination of sacred tradition and scripture, providing a comprehensive framework for understanding the faith.
The Roman Catholic Church's presence in Europe is marked by majestic cathedrals, monastic communities, and a rich liturgical tradition that continues to inspire millions of believers.
Understanding Eastern Orthodoxy in Europe
Eastern Orthodoxy represents one of the major branches of Christianity in Europe, with a substantial following in countries like Greece, Russia, and Serbia. This denomination is known for its rich liturgical heritage and emphasis on maintaining the traditions of the early Church. Key aspects of Eastern Orthodoxy include:
- Theology and Worship: Eastern Orthodoxy places a strong emphasis on the mystical aspects of faith, with worship centered around the Divine Liturgy and the sacraments.
- Icons and Symbolism: Icons play a significant role in Orthodox worship, serving as windows to the divine and aids for contemplation and prayer.
- Ecumenical Councils: The teachings of the Ecumenical Councils are fundamental to Orthodox theology, providing a framework for understanding doctrine and practice.
Eastern Orthodoxy's influence in Europe is evident in its architectural masterpieces, vibrant festivals, and the deep spiritual life of its adherents.
Read also:Unbeknownst Kim Hoyt And Leavenworth A Captivating Tale
Protestant Denominations and Their Impact
Protestantism emerged as a significant Christian movement during the Reformation, challenging the authority of the Roman Catholic Church and promoting a return to scriptural foundations. This movement gave rise to numerous denominations, each with distinct theological perspectives. Some of the notable Protestant denominations in Europe include:
- Lutheranism: Founded by Martin Luther, this denomination emphasizes justification by faith and the authority of scripture.
- Calvinism: Known for its focus on predestination and the sovereignty of God, Calvinism has had a profound impact on European theology.
- Anglicanism: A bridge between Catholic and Protestant traditions, Anglicanism maintains a unique identity with a focus on liturgy and tradition.
Protestant denominations have played a crucial role in shaping European society, influencing education, social reform, and political thought.
What is Anglicanism?
Anglicanism, often described as a middle way between Roman Catholicism and Protestantism, has a unique place in the Christian landscape of Europe. Originating in England during the 16th century, Anglicanism is characterized by its emphasis on tradition, scripture, and reason. Notable features of Anglicanism include:
- The Book of Common Prayer: A foundational text for Anglican worship, it provides a structured approach to liturgy and prayer.
- The Thirty-Nine Articles: These articles define the core beliefs of the Anglican faith, balancing Catholic and Reformed theology.
- Episcopal Governance: The Anglican Church is governed by bishops, maintaining a hierarchical structure similar to that of the Catholic Church.
Anglicanism's influence extends beyond Europe, with the Anglican Communion representing a global fellowship of churches united by shared beliefs and traditions.
Exploring Lutheranism's Influence
Lutheranism, one of the earliest Protestant movements, has had a significant impact on European Christianity since its inception in the early 16th century. Founded by Martin Luther, this denomination emphasizes the primacy of scripture and justification by faith. Key elements of Lutheranism include:
- Sola Scriptura: Lutheranism upholds scripture as the sole authority for faith and practice, rejecting the authority of church traditions that contradict biblical teachings.
- Justification by Faith: The belief that individuals are justified before God through faith in Jesus Christ, rather than through works or rituals, is central to Lutheran theology.
- The Book of Concord: This collection of confessional documents outlines the core beliefs and practices of Lutheranism, serving as a guide for adherents.
Lutheranism's influence in Europe is evident in its vibrant worship communities, theological contributions, and commitment to education and social justice.
Calvinism: A Theological Perspective
Calvinism, another major branch of Protestantism, is known for its distinctive theological perspectives, particularly concerning the sovereignty of God and predestination. Founded by John Calvin, this denomination has left an indelible mark on European Christianity. Key features of Calvinism include:
- Predestination: Calvinism teaches that God has predetermined who will be saved and who will be damned, emphasizing divine sovereignty over human free will.
- The Five Points of Calvinism: Often summarized by the acronym TULIP, these doctrines outline Calvinist beliefs, including total depravity, unconditional election, and irresistible grace.
- Reformed Church Governance: Calvinism advocates for a Presbyterian form of church governance, with authority vested in a body of elders.
Calvinism's theological insights have influenced a wide range of Christian thought and practice, contributing to the development of Reformed traditions across Europe.
The Rise of Methodism in Europe
Methodism, a movement that emerged from within the Anglican Church in the 18th century, has become a prominent Christian denomination in Europe. Founded by John Wesley, Methodism is characterized by its emphasis on personal holiness and social justice. Key aspects of Methodism include:
- Wesleyan Theology: Methodism emphasizes the role of grace in salvation, with a focus on sanctification and the pursuit of a holy life.
- Methodist Circuit System: The use of itinerant ministers and circuit preaching has allowed Methodism to expand rapidly and reach diverse communities.
- Social Reform: Methodism has a strong tradition of social activism, advocating for issues such as abolition, education, and healthcare.
Methodism's influence in Europe is evident in its vibrant congregations, commitment to social justice, and contributions to education and healthcare.
Who are the Baptists?
Baptists, a diverse group of Protestant Christians, are known for their emphasis on believer's baptism and congregational governance. This denomination has a significant presence in Europe, contributing to the continent's religious diversity. Key features of Baptist beliefs include:
- Believer's Baptism: Baptists practice baptism by immersion for individuals who profess faith, rejecting infant baptism as unscriptural.
- Congregational Governance: Baptist churches operate independently, with each congregation responsible for its own governance and decision-making.
- Religious Liberty: Baptists have historically championed the cause of religious freedom and separation of church and state.
The Baptist tradition in Europe is marked by its commitment to evangelism, social justice, and theological diversity.
Pentecostalism: A Modern Movement
Pentecostalism, a movement that emerged in the early 20th century, has become one of the fastest-growing Christian denominations in Europe. Known for its emphasis on the gifts of the Holy Spirit, Pentecostalism offers a dynamic and experiential approach to faith. Key characteristics of Pentecostalism include:
- Charismatic Worship: Pentecostal services are often marked by expressive worship, including speaking in tongues, prophecy, and healing.
- The Baptism in the Holy Spirit: Pentecostals emphasize the importance of a post-conversion experience of empowerment and spiritual gifts.
- Evangelism and Mission: Pentecostalism is characterized by a strong focus on evangelism and global mission efforts.
Pentecostalism's growth in Europe reflects its appeal to those seeking a vibrant and transformative faith experience, as well as its commitment to social engagement and community development.
Smaller Christian Denominations in Europe
In addition to the major Christian traditions, Europe is home to a variety of smaller denominations and independent churches, each contributing to the continent's religious diversity. These groups often represent unique theological perspectives and cultural expressions of faith. Some of these smaller denominations include:
- Anabaptists: Known for their commitment to nonviolence and simple living, Anabaptists include groups such as the Mennonites and Amish.
- Unitarians: Emphasizing reason and individual conscience, Unitarians promote a liberal approach to Christian theology.
- Quakers: The Religious Society of Friends, or Quakers, is known for its emphasis on inner spirituality and social justice.
These smaller denominations add to the rich tapestry of Christian faith in Europe, offering diverse perspectives and practices that enrich the religious landscape.
Christianity's Role in Contemporary European Society
Christianity continues to play a significant role in contemporary European society, influencing various aspects of culture, politics, and social issues. Despite the rise of secularism and religious pluralism, Christianity remains a vital force in shaping the values and norms of European communities. Key areas where Christianity impacts society include:
- Education: Christian institutions, from primary schools to universities, contribute to the educational landscape, promoting values of integrity and service.
- Social Services: Christian organizations are active in providing social services, such as healthcare, poverty relief, and support for marginalized groups.
- Cultural Heritage: Christianity's influence is evident in Europe's art, music, literature, and architecture, reflecting the rich cultural heritage of the continent.
As Europe continues to navigate the challenges of globalization and multiculturalism, Christianity remains a key contributor to the ongoing dialogue about identity and values.
The Cultural Impact of Christianity in Europe
The cultural impact of Christianity in Europe is profound, with the religion shaping various aspects of art, literature, music, and architecture. Throughout history, Christian themes and motifs have been central to European cultural expression, leaving a lasting legacy. Key areas of cultural impact include:
- Art and Architecture: From the Gothic cathedrals to Renaissance paintings, Christian themes have inspired countless masterpieces that continue to captivate audiences.
- Literature and Philosophy: Christian thought has influenced European literature and philosophy, with writers and thinkers exploring themes of faith, morality, and the human condition.
- Music: Christian music, from Gregorian chants to contemporary hymns, has enriched Europe's musical heritage, offering a diverse range of spiritual expression.
Christianity's cultural contributions continue to resonate in modern Europe, providing a source of inspiration and reflection for individuals across the continent.
Christianity's Political Influence in Europe
Christianity has historically played a significant role in European politics, influencing governance, law, and public policy. While the relationship between church and state has evolved over time, Christianity remains a key player in shaping political discourse and values. Areas of political influence include:
- Human Rights and Social Justice: Christian principles have contributed to the development of human rights frameworks and social justice initiatives, advocating for the dignity and worth of all individuals.
- Ethical Debates: Christianity provides a moral framework for addressing complex ethical issues, such as bioethics, environmental stewardship, and economic inequality.
- Interfaith Dialogue: Christian leaders and organizations are actively engaged in promoting interfaith dialogue and cooperation, fostering understanding and peace among diverse religious communities.
As Europe continues to address pressing social and political challenges, Christianity remains a vital voice in the conversation, offering insights and solutions grounded in faith and compassion.
What Does the Future Hold for Christianity in Europe?
The future of Christianity in Europe is a topic of much discussion, with various trends and developments shaping the religious landscape. While the continent has seen a decline in religious affiliation and church attendance, Christianity remains a dynamic and evolving presence. Potential future developments include:
- Renewal and Revitalization: Many Christian communities are exploring new models of ministry and outreach, seeking to engage with younger generations and address contemporary issues.
- Ecumenical and Interfaith Collaboration: Increased collaboration between Christian denominations and other faith traditions may lead to greater unity and shared action on global challenges.
- Digital Engagement: The rise of digital technologies offers new opportunities for evangelism, community building, and theological education, expanding the reach of Christianity in innovative ways.
As Europe continues to navigate the complexities of the modern world, Christianity will likely adapt and evolve, remaining a significant force in shaping the continent's spiritual and cultural identity.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the major Christian denominations in Europe? The major denominations include Roman Catholicism, Eastern Orthodoxy, and Protestantism, with further sub-divisions within Protestantism such as Lutheranism, Calvinism, and Anglicanism.
- How has the Reformation impacted Christianity in Europe? The Reformation led to the emergence of various Protestant denominations, challenging the authority of the Roman Catholic Church and promoting scriptural foundations.
- What role does Christianity play in European culture? Christianity has significantly influenced European art, literature, music, and philosophy, shaping the continent's cultural identity.
- Is Christianity declining in Europe? While there has been a decline in religious affiliation and church attendance, Christianity remains a dynamic presence with ongoing renewal efforts.
- How do Christian denominations in Europe engage in social services? Many denominations run hospitals, schools, and charities, providing essential services and advocating for social justice.
- What is the future of Christianity in Europe? The future may involve renewal efforts, increased ecumenical collaboration, and digital engagement, adapting to contemporary challenges and opportunities.
Conclusion
Christian denominations in Europe represent a diverse and evolving tapestry of faith, each contributing unique perspectives and practices to the continent's religious landscape. From the historic roots of Roman Catholicism and Eastern Orthodoxy to the dynamic movements of Protestantism and Pentecostalism, Christianity continues to shape European society and culture. Despite the challenges of secularization and religious pluralism, Christianity remains a vital force, offering a rich heritage of spirituality, ethics, and community. As Europe looks to the future, the ongoing dialogue between tradition and innovation will likely define Christianity's role in addressing both timeless and contemporary issues, ensuring its continued relevance and influence in the lives of millions.