Food safety is a critical concern in both domestic kitchens and the food industry at large. One of the most significant aspects of ensuring food safety is understanding the "temperature danger zone for food." This concept is crucial because improper temperature control can lead to the growth of harmful bacteria, which may cause foodborne illnesses. Thus, knowing and maintaining the correct temperatures for storing and preparing food is vital for preventing potential health risks and ensuring the well-being of consumers.
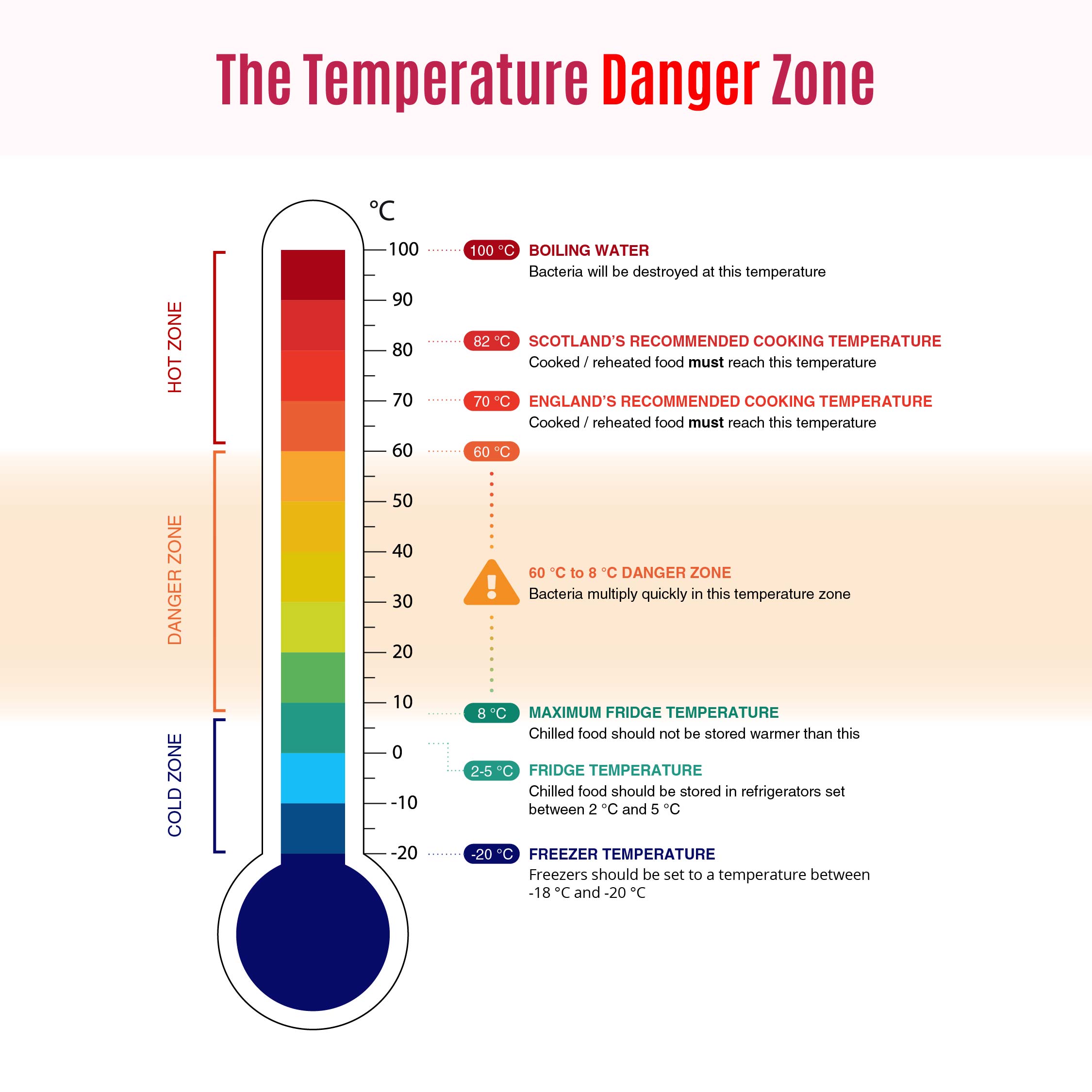
The "temperature danger zone for food" refers to the temperature range where bacteria grow most rapidly in food, typically between 40°F and 140°F (4°C and 60°C). In this zone, bacteria can double in number in as little as 20 minutes, making it essential to minimize the time food spends in this range to reduce the risk of contamination. By understanding this concept, individuals and businesses involved in food handling can implement effective strategies to keep food safe.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of the "temperature danger zone for food," exploring its implications for food safety, providing practical tips for maintaining safe temperatures, and discussing the impact of temperature control on different types of food. This article aims to equip readers with the knowledge and tools needed to ensure safe food handling, thereby enhancing public health and safety.
Read also:Hilarious Tank Jokes The Ultimate Military Laughfest
Table of Contents
- What is the Temperature Danger Zone for Food?
- Why is the Temperature Danger Zone Important?
- How Does Temperature Affect Bacterial Growth?
- What Foods are Most at Risk?
- How to Avoid the Temperature Danger Zone?
- Safe Cooling and Reheating Practices
- Impact of Temperature on Food Quality
- The Role of Technology in Temperature Control
- Common Myths About Food Safety and Temperature
- What Are the Temperature Guidelines for Different Foods?
- How Does the Temperature Danger Zone Affect Food Storage?
- What Are the Best Practices for Monitoring Food Temperature?
- FAQs About Temperature Danger Zone for Food
- Conclusion: Ensuring Food Safety
What is the Temperature Danger Zone for Food?
The "temperature danger zone for food" is a critical concept in food safety, referring to the temperature range between 40°F and 140°F (4°C and 60°C). Within this range, bacteria can multiply rapidly, potentially leading to foodborne illnesses. Understanding and controlling this temperature range is essential for anyone involved in food preparation and storage.
When food is left in the danger zone, bacteria such as Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria can thrive, posing significant health risks to consumers. These bacteria can cause symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, and in severe cases, even death. Therefore, it's crucial to keep food out of the danger zone to ensure safety.
To avoid the temperature danger zone, it's important to store perishable foods in a refrigerator set below 40°F (4°C) and to cook foods to safe internal temperatures above 140°F (60°C). By doing so, you can significantly reduce the risk of bacterial growth and the likelihood of foodborne illnesses.
Why is the Temperature Danger Zone Important?
The importance of the "temperature danger zone for food" cannot be overstated, as it plays a crucial role in ensuring food safety and preventing foodborne illnesses. When food is held within this temperature range, bacteria can multiply rapidly, increasing the risk of contamination and illness.
Understanding the danger zone allows individuals and businesses to implement effective measures for controlling food temperatures. This includes proper refrigeration, cooking, cooling, and reheating practices. By keeping food out of the danger zone, you can protect consumers from harmful bacteria and enhance overall food safety.
Moreover, adhering to temperature guidelines can help prevent food spoilage, reducing waste and saving money. Proper temperature control is a key component of any food safety management system, making it essential for anyone involved in food handling to understand and respect the temperature danger zone.
Read also:Ultimate Guide To Sean Strickland Vs Israel Adesanya Fight
How Does Temperature Affect Bacterial Growth?
Temperature plays a crucial role in bacterial growth, with the "temperature danger zone for food" being the range where bacteria multiply most rapidly. Within this range, temperatures provide an ideal environment for bacteria to thrive, leading to a higher risk of foodborne illnesses.
Bacteria typically grow in a temperature range between 40°F and 140°F (4°C and 60°C). In this zone, certain types of bacteria can double every 20 minutes, which can quickly lead to significant contamination if food is not properly handled. This rapid growth highlights the importance of minimizing the time food spends in the danger zone.
To control bacterial growth, it's essential to store food at temperatures below 40°F (4°C) or above 140°F (60°C). This prevents bacteria from multiplying, reducing the risk of contamination and ensuring safe food consumption. Understanding and managing temperature is a key aspect of effective food safety practices.
What Foods are Most at Risk?
Certain foods are more susceptible to bacterial growth within the "temperature danger zone for food" and require careful handling to ensure safety. These include perishable items such as meat, poultry, seafood, dairy products, and cooked grains or vegetables. These foods provide an ideal environment for bacteria to thrive, making them particularly vulnerable to contamination.
High-risk foods should always be stored and cooked at safe temperatures to minimize the risk of bacterial growth. This includes keeping perishable items refrigerated below 40°F (4°C) and cooking proteins to recommended internal temperatures. Additionally, leftovers should be promptly cooled and reheated to ensure safety.
By understanding which foods are most at risk, individuals and businesses can implement targeted food safety measures to prevent contamination and protect consumers from foodborne illnesses. Proper temperature control is a key component of these efforts, helping to ensure safe food handling and consumption.
How to Avoid the Temperature Danger Zone?
Avoiding the "temperature danger zone for food" is essential for preventing bacterial growth and ensuring food safety. Several strategies can be implemented to minimize the time food spends in this temperature range, thereby reducing the risk of contamination.
- Store perishable foods in a refrigerator set below 40°F (4°C).
- Cook foods to safe internal temperatures, typically above 140°F (60°C).
- Use a food thermometer to accurately measure food temperatures.
- Promptly refrigerate leftovers to prevent bacterial growth.
- Avoid leaving perishable foods out at room temperature for extended periods.
By following these guidelines, individuals and businesses can effectively manage food temperatures and minimize the risk of foodborne illnesses. Proper temperature control is a key aspect of any food safety management system, helping to ensure safe food handling and consumption.
Safe Cooling and Reheating Practices
Proper cooling and reheating practices are essential for maintaining food safety and avoiding the "temperature danger zone for food." These practices help prevent bacterial growth and ensure that food remains safe for consumption.
When cooling food, it's important to do so quickly and efficiently to minimize the time spent in the danger zone. This can be achieved by dividing large portions into smaller containers, using shallow pans, and placing them in the refrigerator promptly. Avoid leaving food out at room temperature for more than two hours, as this can increase the risk of bacterial growth.
Reheating food to the correct temperature is equally important for ensuring safety. Use a food thermometer to ensure that leftovers reach an internal temperature of at least 165°F (74°C) to eliminate any bacteria that may have developed during storage.
By following these safe cooling and reheating practices, individuals and businesses can effectively manage food temperatures and protect consumers from foodborne illnesses. Proper temperature control is a key component of any food safety management system.
Impact of Temperature on Food Quality
Temperature not only affects food safety but also plays a significant role in determining food quality. Proper temperature control is essential for maintaining the taste, texture, and nutritional value of food, ensuring that it remains fresh and appealing to consumers.
When food is stored or cooked at incorrect temperatures, it can lead to spoilage, loss of flavor, and degradation of nutrients. For example, overcooking can lead to tough, dry proteins, while improper refrigeration can cause produce to wilt or become mushy.
By understanding the impact of temperature on food quality, individuals and businesses can implement effective measures to maintain the desired characteristics of their products. This includes proper storage, cooking, and handling practices that prioritize temperature control, ensuring that food remains safe and of high quality.
The Role of Technology in Temperature Control
Technology plays a crucial role in helping individuals and businesses maintain proper temperature control and avoid the "temperature danger zone for food." Various tools and devices can be used to monitor and regulate food temperatures, ensuring safety and quality.
- Refrigerators and freezers with built-in temperature controls and alarms.
- Food thermometers for accurately measuring cooking and storage temperatures.
- Temperature monitoring systems for commercial kitchens and storage facilities.
- Smart appliances with remote monitoring capabilities.
- Data logging devices for tracking temperature over time.
By utilizing these technologies, individuals and businesses can more effectively manage food temperatures, reducing the risk of bacterial growth and ensuring that food remains safe and of high quality. Proper temperature control is a key component of any food safety management system, and technology is an invaluable tool in achieving this goal.
Common Myths About Food Safety and Temperature
There are several misconceptions about food safety and temperature that can lead to improper handling and increased risk of contamination. Addressing these myths is essential for promoting safe food practices and avoiding the "temperature danger zone for food."
One common myth is that food that smells or looks fine is safe to eat. However, many harmful bacteria do not affect the smell or appearance of food, making it essential to rely on temperature control rather than sensory cues to determine safety.
Another misconception is that reheating food kills all bacteria, making it safe to eat. While reheating can reduce bacterial levels, it is not a substitute for proper storage and handling practices. Ensuring that food is stored and cooked to safe temperatures is essential for minimizing the risk of contamination.
By debunking these myths and promoting accurate information, individuals and businesses can implement effective food safety measures and protect consumers from foodborne illnesses.
What Are the Temperature Guidelines for Different Foods?
Different types of food have specific temperature guidelines to ensure safety and prevent bacterial growth. Understanding these guidelines is essential for avoiding the "temperature danger zone for food" and maintaining safe food handling practices.
- Refrigerate perishable foods below 40°F (4°C).
- Cook poultry to an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C).
- Cook ground meats to an internal temperature of 160°F (71°C).
- Cook steaks, roasts, and chops to an internal temperature of 145°F (63°C).
- Reheat leftovers to an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C).
By adhering to these temperature guidelines, individuals and businesses can effectively manage food temperatures and reduce the risk of bacterial growth, ensuring that food remains safe and of high quality.
How Does the Temperature Danger Zone Affect Food Storage?
The "temperature danger zone for food" plays a significant role in determining food storage practices, as it affects the growth of bacteria and the risk of contamination. Proper storage is essential for maintaining food safety and quality.
To avoid the danger zone, perishable foods should be stored in a refrigerator set below 40°F (4°C) and consumed within a reasonable timeframe. This prevents bacterial growth and ensures that food remains safe to eat.
Freezing is another effective method for extending the shelf life of perishable foods, as it halts bacterial growth by keeping temperatures well below the danger zone. However, it's important to thaw frozen foods safely, using methods that prevent them from entering the danger zone.
By understanding the impact of temperature on food storage, individuals and businesses can implement effective practices that prioritize safety and quality, protecting consumers from foodborne illnesses.
What Are the Best Practices for Monitoring Food Temperature?
Monitoring food temperature is a critical aspect of ensuring food safety and avoiding the "temperature danger zone for food." By implementing best practices for temperature monitoring, individuals and businesses can effectively manage food handling and storage.
- Use food thermometers to accurately measure internal cooking and storage temperatures.
- Regularly check and calibrate thermometers to ensure accuracy.
- Implement temperature monitoring systems for commercial kitchens and storage facilities.
- Keep records of temperature checks to identify potential issues and trends.
- Educate staff on the importance of temperature control and proper monitoring techniques.
By following these best practices, individuals and businesses can reduce the risk of bacterial growth and ensure that food remains safe and of high quality. Effective temperature monitoring is a key component of any food safety management system.
FAQs About Temperature Danger Zone for Food
1. What is the "temperature danger zone for food"?
The "temperature danger zone for food" is the temperature range between 40°F and 140°F (4°C and 60°C) where bacteria can multiply rapidly, increasing the risk of foodborne illnesses.
2. Why is it important to avoid the temperature danger zone?
Avoiding the temperature danger zone is crucial for preventing bacterial growth and ensuring food safety. By keeping food out of this range, you can reduce the risk of contamination and protect consumers from foodborne illnesses.
3. How can I keep food out of the danger zone?
Store perishable foods in a refrigerator set below 40°F (4°C), cook foods to safe internal temperatures above 140°F (60°C), and promptly refrigerate leftovers to minimize the time spent in the danger zone.
4. What foods are most vulnerable to the danger zone?
Perishable foods such as meat, poultry, seafood, dairy products, and cooked grains or vegetables are most vulnerable to bacterial growth within the danger zone and require careful handling.
5. How does the danger zone affect food storage?
The danger zone affects food storage by determining the temperatures at which perishable foods should be stored to prevent bacterial growth and ensure safety. Proper refrigeration and freezing practices are essential.
6. What are the best practices for monitoring food temperature?
Use food thermometers, implement temperature monitoring systems, regularly check and calibrate thermometers, keep records of temperature checks, and educate staff on proper monitoring techniques to ensure effective temperature control.
Conclusion: Ensuring Food Safety
Understanding the "temperature danger zone for food" is essential for maintaining food safety and preventing foodborne illnesses. By implementing effective temperature control measures, individuals and businesses can protect consumers from harmful bacteria and ensure that food remains safe for consumption.
Proper storage, cooking, cooling, and reheating practices are key components of any food safety management system. By adhering to temperature guidelines and utilizing technology to monitor and regulate food temperatures, you can significantly reduce the risk of contamination and enhance overall food safety.
As we continue to prioritize food safety, it's important to remain vigilant and informed about best practices for temperature control. By doing so, we can ensure that food is handled safely and responsibly, protecting the health and well-being of consumers everywhere.